(Press-News.org) Live tracking and analyzing of the dynamics of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells targeting cancer cells can open new avenues for the development of cancer immunotherapy. However, imaging via conventional microscopy approaches can result in cellular damage, and assessments of cell-to-cell interactions are extremely difficult and labor-intensive. When researchers applied deep learning and 3D holographic microscopy to the task, however, they not only avoided these difficultues but found that AI was better at it than humans were.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is helping researchers decipher images from a new holographic microscopy technique needed to investigate a key process in cancer immunotherapy "live" as it takes place. The AI transformed work that, if performed manually by scientists, would otherwise be incredibly labor-intensive and time-consuming into one that is not only effortless but done better than they could have done it themselves. The research, conducted by scientists at KAIST, appeared in the journal eLife last December.
A critical stage in the development of the human immune system's ability to respond not just generally to any invader (such as pathogens or cancer cells) but specifically to that particular type of invader and remember it should it attempt to invade again is the formation of a junction between an immune cell called a T-cell and a cell that presents the antigen, or part of the invader that is causing the problem, to it. This process is like when a picture of a suspect is sent to a police car so that the officers can recognize the criminal they are trying to track down. The junction between the two cells, called the immunological synapse, or IS, is the key process in teaching the immune system how to recognize a specific type of invader.
Since the formation of the IS junction is such a critical step for the initiation of an antigen-specific immune response, various techniques allowing researchers to observe the process as it happens have been used to study its dynamics. Most of these live imaging techniques rely on fluorescence microscopy, where genetic tweaking causes part of a protein from a cell to fluoresce, in turn allowing the subject to be tracked via fluorescence rather than via the reflected light used in many conventional microscopy techniques.
However, fluorescence-based imaging can suffer from effects such as photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, preventing the assessment of dynamic changes in the IS junction process over the long term. Fluorescence-based imaging still involves illumination, whereupon the fluorophores (chemical compounds that cause the fluorescence) emit light of a different color. Photo-bleaching or photo-toxicity occur when the subject is exposed to too much illumination, resulting in chemical alteration or cellular damage.
One recent option that does away with fluorescent labelling and thereby avoids such problems is 3D holographic microscopy or holotomography (HT). In this technique, the refractive index (the way that light changes direction when encountering a substance with a different density--why a straw looks like it bends in a glass of water) is recorded in 3D as a hologram.
Until now, HT has been used to study single cells, but never cell-cell interactions involved in immune responses. One of the main reasons is the difficulty of "segmentation," or distinguishing the different parts of a cell and thus distinguishing between the interacting cells; in other words, deciphering which part belongs to which cell.
Manual segmentation, or marking out the different parts manually, is one option, but it is difficult and time-consuming, especially in three dimensions. To overcome this problem, automatic segmentation has been developed in which simple computer algorithms perform the identification.
"But these basic algorithms often make mistakes," explained Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, "particularly with respect to adjoining segmentation, which of course is exactly what is occurring here in the immune response we're most interested in."
So, the researchers applied a deep learning framework to the HT segmentation problem. Deep learning is a type of machine learning in which artificial neural networks based on the human brain recognize patterns in a way that is similar to how humans do this. Regular machine learning requires data as an input that has already been labelled. The AI "learns" by understanding the labeled data and then recognizes the concept that has been labelled when it is fed novel data. For example, AI trained on a thousand images of cats labelled "cat" should be able to recognize a cat the next time it encounters an image with a cat in it. Deep learning involves multiple layers of artificial neural networks attacking much larger, but unlabeled datasets, in which the AI develops its own 'labels' for concepts it encounters.
In essence, the deep learning framework that KAIST researchers developed, called DeepIS, came up with its own concepts by which it distinguishes the different parts of the IS junction process. To validate this method, the research team applied it to the dynamics of a particular IS junction formed between chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells and target cancer cells. They then compared the results to what they would normally have done: the laborious process of performing the segmentation manually. They found not only that DeepIS was able to define areas within the IS with high accuracy, but that the technique was even able to capture information about the total distribution of proteins within the IS that may not have been easily measured using conventional techniques.
"In addition to allowing us to avoid the drudgery of manual segmentation and the problems of photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, we found that the AI actually did a better job," Park added.
The next step will be to combine the technique with methods of measuring how much physical force is applied by different parts of the IS junction, such as holographic optical tweezers or traction force microscopy.
INFORMATION:
-About KAIST
KAIST is the first and top science and technology university in Korea. KAIST was established in 1971 by the Korean government to educate scientists and engineers committed to Korea's industrialization and economic growth.
Since then, KAIST and its 67,000 graduates have been the gateway to advanced science and technology, innovation, and entrepreneurship. KAIST has emerged as one of the most innovative universities with nearly 12,000 students enrolled in five colleges and seven schools including 1,039 international students from 90 countries.
Marking its semi-centennial anniversary in 2021, KAIST continues to strive to make the world better through its pursuits in education, research, entrepreneurship, and globalization.
For more information about KAIST, please visit http://www.kaist.ac.kr/en
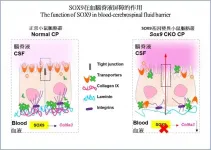
The finding, recently published in the prestigious scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), has provided the scientific community a novel understanding to the molecular regulatory mechanisms behind the function of the blood-CSF barrier and lays the groundwork for developing novel therapeutic strategies for preventing and treating neurodevelopmental disorders.
Dysfunction of blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier is common in various neurological diseases
CSF is a clear, colourless body fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, providing them a cushion against injuries. It also ...
In Japan, the suppression of Christianity increased from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 17th century, and many missionaries and Japanese believers were martyred during this period. New research has uncovered a letter indicating that Hosokawa Tadaoki, lord of the Kokura domain from 1600 to 1620, ordered the execution of Diego Hayato Kagayama, a chief vassal of the Hosokawa family, and the banishment of Genya Ogasawara, both Christians. The punishment and martyrdom of both men was previously known only from reports by Jesuit missionaries to Rome. The discovery of primary historical documents created within the Hosokawa ...
Integrated photonics was rejuvenated as Si starting challenging the dominant position of conventional III-V compound semiconductors at onset of the new millennium. Heterogeneous Si photonics utilizes wafer bonding to transfer functioning non-Si thin film onto Si substrate to make up missing or weak optoelectronic functionalities of Si material. In the past 15 years, it has evolved into a broad technology with many branches as shown in Fig. 1. As the most mature one among them, heterogeneous III-V-on-silicon integration provides an ideal platform to marry their respective material and production advantages. Two veteran researchers in this field, Dr. Di Liang from Hewlett Packard Labs and Prof. ...
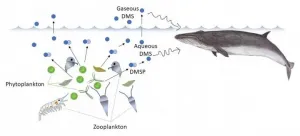
A joint research project between organizations in Japan and the US has demonstrated that zooplankton, a major food source for marine predators, can be located by following the concentration gradient of the chemical dimethyl sulfide (DMS) in ocean water and air. Currently, little is known about how marine predators search for and find enough food to maintain their body size. This study is expected to expand research into the chemical triggers of marine organisms while foraging.
Zooplankton, such as krill and copepods are the main energy source for many large marine animals. The big predators must consume a large amount of these tiny creatures to provide ...
LOS ANGELES (Feb. 11, 2021) -- A new strain of the coronavirus in Southern California, first reported last month by Cedars-Sinai, is rapidly spreading across the country and around the world as travelers apparently carry the virus with them to a growing list of global destinations, according to new research published today in the peer-reviewed Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA).
The strain, known as CAL.20C, was first observed in July 2020 in a single Los Angeles County case, as Cedars-Sinai earlier reported. It reemerged in October in Southern California and then quickly END ...
Many materials in the modern world--from the plastics that dominate it to the electronic chips that drive it--are constructed of polymers. Given their ubiquity and the evolving requirements of our world, finding better and more efficient methods of making them is an ongoing research concern. In addition, current environmental issues necessitate the use of methods and input materials that are environment friendly.
Recent research by scientists from Nagoya Institute of Technology, Japan, has been in this vein, adding a new twist to a polymerization technique that has been around and successful since the 1980s: living cationic polymerization, where the polymer chain growth does not have the ability to terminate until the monomer is consumed. The scientists have, for the first ...
New York, February 24, 2021 - Graduate Center, CUNY/Brooklyn College professor was part of a discovery of the first fossil evidence of any primate, illustrating the earliest steps of primates 66 million years ago following the mass extinction that wiped out all dinosaurs and led to the rise of mammals.
Stephen Chester, an assistant professor of anthropology and paleontologist at the Graduate Center, CUNY and Brooklyn College, was part of a team of 10 researchers from across the United States who analyzed several fossils of Purgatorius, the oldest genus in a group of the earliest-known primates called plesiadapiforms. ...
According to a new study published in The American Journal of Human Genetics, more than one third of genetic variants that increase the risk of coronary artery disease regulate the expression of genes in the liver. These variants have an impact on the expression of genes regulating cholesterol metabolism, among other things. The findings provide valuable new insight into the genetics of coronary artery disease. The study was conducted in collaboration between the University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio University Hospital, the University of California Los Angeles, and the University of Arizona.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) and its most important complication ...
Australian researchers have called for additional services for survivors of intimate partner violence - warning those who have these experiences are more vulnerable to elder abuse.
Women who survive domestic violence continue to experience negative effects well into their older years but they are also more vulnerable to elder abuse, says Flinders University researcher Dr Monica Cations, lead author of the study published in the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
"This is the first time this relationship has been demonstrated and tells us that older survivors need close monitoring and prevention efforts to keep them safe from further abuse."
The study looked at the psychological and physical impacts and risk for elder abuse associated ...
Before the corona pandemic, tens of millions international travellers annually headed to the tropics, getting exposed to local intestinal bacteria. A total of 20-70% of those returning from the tropics carry - for the most unknowingly - ESBL-producing bacteria resistant to multiple antibiotics. The likelihood of acquiring such superbacteria depends on destination and health behaviour abroad. The risk is greatest in South and Southeast Asia, and a substantial increase is associated with contracting travellers' diarrhoea and taking antibiotics while abroad.
An investigation led by professor ...