Scientists describe earliest primate fossils
2021-02-24
(Press-News.org) A new study published Feb. 24 in the journal Royal Society Open Science documents the earliest-known fossil evidence of primates.
A team of 10 researchers from across the U.S. analyzed several fossils of Purgatorius, the oldest genus in a group of the earliest-known primates called plesiadapiforms. These ancient mammals were small-bodied and ate specialized diets of insects and fruits that varied by species. These newly described specimens are central to understanding primate ancestry and paint a picture of how life on land recovered after the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago that wiped out all dinosaurs -- except for birds -- and led to the rise of mammals.
Gregory Wilson Mantilla, a University of Washington professor of biology and curator of vertebrate paleontology at the UW's Burke Museum of Natural History & Culture, co-led the study with Stephen Chester of Brooklyn College and the City University of New York. The team analyzed fossilized teeth found in the Hell Creek area of northeastern Montana. The fossils, which are now part of the collections at the University of California Museum of Paleontology, are estimated to be 65.9 million years old, about 105,000 to 139,000 years after the mass extinction event. Based on the age of the fossils, the team estimates that the ancestor of all primates --including plesiadapiforms and today's primates such as lemurs, monkeys and apes -- likely emerged by the Late Cretaceous and lived alongside large dinosaurs.
"It's mind blowing to think of our earliest archaic primate ancestors," said Wilson Mantilla. "They were some of the first mammals to diversify in this new post-mass extinction world, taking advantage of the fruits and insects up in the forest canopy."
The fossils include two species of Purgatorius: Purgatorius janisae and a new species described by the team named Purgatorius mckeeveri. Three of the teeth found have distinct features compared to any previously known Purgatorius species and led to the description of the new species.
Purgatorius mckeeveri is named after Frank McKeever, who was among the first residents of the area where the fossils were discovered, and also the family of John and Cathy McKeever, who have since supported the field work where the oldest specimen of this new species was discovered.
"This was a really cool study to be a part of, particularly because it provides further evidence that the earliest primates originated before the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs," said co-author Brody Hovatter, a UW graduate student in Earth and space sciences. "They became highly abundant within a million years after that extinction."
"This discovery is exciting because it represents the oldest dated occurrence of archaic primates in the fossil record," said Chester. "It adds to our understanding of how the earliest primates separated themselves from their competitors following the demise of the dinosaurs."
INFORMATION:
Co-author on the study was the late William Clemens who was a professor emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley and former director of the UC Museum of Paleontology. Additional co-authors are Jason Moore and Wade Mans of the University of New Mexico; Courtney Sprain of the University of Florida; William Mitchell of Minnesota IT Services; Roland Mundil of the Berkeley Geochronology Center; and Paul Renne of UC Berkeley and the Berkeley Geochronology Center. The research was funded by the National Science Foundation, the UC Museum of Paleontology, the Myhrvold and Havranek Charitable Family Fund, the UW, the CUNY and the Leakey Foundation.
For high resolution images and interviews, contact burkepr@uw.edu.
Link to full release with images:
https://www.washington.edu/news/2021/02/24/earliest-primate-fossils/
Contact: Andrea Godinez
University of Washington, Burke Museum of Natural History & Culture
206-616-7538
burkepr@uw.edu
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-24
A research team from Skoltech and FBK (Italy) presented a methodology to derive 4D building models using historical maps and machine learning. The implemented method relies on the geometric, neighbourhood, and categorical attributes to predict building heights. The method is useful for understanding urban phenomena and changes contributing to defining our cities' actual shapes. The results were published in the MDPI Applied Sciences journal.
Historical maps are the most powerful source used to analyze changes in urban development. Nevertheless, maps represent the 3D world ...
2021-02-24
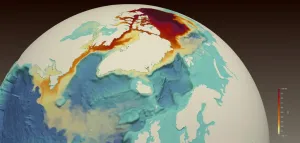
Freshwater is accumulating in the Arctic Ocean. The Beaufort Sea, which is the largest Arctic Ocean freshwater reservoir, has increased its freshwater content by 40% over the past two decades. How and where this water will flow into the Atlantic Ocean is important for local and global ocean conditions.
A study from the University of Washington, Los Alamos National Laboratory and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration shows that this freshwater travels through the Canadian Archipelago to reach the Labrador Sea, rather than through the wider marine passageways that connect to seas in Northern Europe. The open-access study was published Feb. 23 ...
2021-02-24
Emerging smart mobile health (or mHealth) technologies are changing the way patients track information related to diagnosed conditions. A new study examined the health and economic impacts of mHealth technologies on the outcomes of diabetes patients in Asia. The study concluded that compared to patients who did not use mHealth applications, patients who used the apps had better health outcomes and were able to regulate their health behavior more effectively. They also had fewer hospital visits and lower medical costs.
The study was conducted by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) and New York University ...
2021-02-24
New Orleans, LA -- A new study of how the 2020 major hurricanes and the COVID-19 pandemic affected each other as well as disaster response found that although prior experience enabled community-based organizations to respond to the pandemic, the pandemic is also creating new challenges to preparing for and responding to natural disasters. The research is published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, available here.
"Two major crises hit Louisiana and coastal communities in the Southeastern United States in 2020 - a significant increase in the frequency and severity of hurricanes, and the COVID-19 pandemic," says Benjamin Springgate, MD, MPH, Chief of Community & Population Medicine at ...
2021-02-24
A study aiming to develop a new therapeutic technique could bring a revolution in our approach to treating rare, fatal Sanfilippo syndrome, a disorder that affects children as young as 2 years old and leads to childhood dementia and premature death.
"We are using a combination of gene therapy, stem cells and small molecules to restore metabolic defects in the patient's brain cells" says Dr. Alexey Pshezhetsky, Professor at CHU Ste-Justine and lead GlycoNet Investigator on this project. "First results in the mouse models of the disease are very encouraging."
Sanfilippo syndrome belongs to a group of rare diseases known as lysosomal storage disorders.
The syndrome occurs in ...
2021-02-24
ITHACA, N.Y. - During mating season, male bearded seals make loud calls to attract a mate. How loud? Well, even their "quiet" call can still be as ear-rattling as a chainsaw.
These elaborate vocalizations are essential for bearded seal reproduction, and have to be loud enough to be heard over the cacophony of their equally loud brethren.
But in the rapidly changing Arctic soundscape, where noise from industrial activities is predicted to dramatically increase in the next 15 years, bearded seals may need to adjust their calling behavior if they are ...
2021-02-24
Washington, DC - February 24, 2021 - In the absence of effective treatments for COVID-19, many countries have approved the therapeutic use of blood plasma from recovering patients because it contains antibodies against the coronavirus. But not every type of antibody can neutralize the virus and render it noninfectious. New research published this week in mSphere, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, explores variation in virus neutralization capabilities, which can vary widely by type of antibody.
"What we need for plasma therapy is not only high levels of antibodies but also high neutralization capability," said virologist Michael Schindler, Ph.D, at University Hospital Tübingen, ...
2021-02-24
X-rays are used to study the atomic and microstructure properties of matter. Such studies are conducted with special accelerator complexes called synchrotrons. A synchrotron source generates powerful electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength equal to fractions of a nanometer. Some X-rays are reflected from the atomic planes of a crystal and some go through the crystal plane that plays the role of a beam-splitter (or the so-called semitransparent mirror). If the radiation passes through monochromators-optical devices that consist of two or more ideal crystals - its optimal exit wavelength can be regulated. ...
2021-02-24
Researchers have developed a data transfer system that can transmit information 10 times faster than a USB. The new link pairs high-frequency silicon chips with a polymer cable as thin a strand of hair. The system may one day boost energy efficiency in data centers and lighten the loads of electronics-rich spacecraft.
The research was presented at this month's IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. The lead author is Jack Holloway '03, MNG '04, who completed his PhD in MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) last fall and currently works for Raytheon. Co-authors include Ruonan Han, associate professor and Holloway's PhD adviser in EECS, and Georgios Dogiamis, ...
2021-02-24
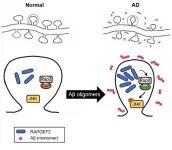
Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI, Pann-Ghill Suh (President)) announced that Dr. Kea Joo Lee and Dr. You-Na Jang of the Neural Circuits Research Group have identified the mechanism causing synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease as the aberrant expression of RAPGEF2, a synaptic protein.
- The results were published on January 2021, in the online Early View of Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology.
* (Title) RAPGEF2 mediates oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic loss and cognitive dysfunction in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) accounts for about 75% of dementia cases and is the most common type of degenerative brain disease. AD is a devastating because disease progression can cause ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists describe earliest primate fossils