(Press-News.org) Washington, DC - February 24, 2021 - In the absence of effective treatments for COVID-19, many countries have approved the therapeutic use of blood plasma from recovering patients because it contains antibodies against the coronavirus. But not every type of antibody can neutralize the virus and render it noninfectious. New research published this week in mSphere, an open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, explores variation in virus neutralization capabilities, which can vary widely by type of antibody.
"What we need for plasma therapy is not only high levels of antibodies but also high neutralization capability," said virologist Michael Schindler, Ph.D, at University Hospital Tübingen, in Germany.
The researchers analyzed COVID-19 antibodies in the blood of 49 people with asymptomatic or mild cases, then tested those antibodies on human cell lines infected with the virus for neutralization capabilities. In agreement with other studies, they found that in the vast majority of cases (88%) infected individuals mounted a robust SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody response that neutralizes the virus. Furthermore, neutralization correlated strongly with the abundance of antibodies against the receptor-binding domain of coronavirus's S protein.
But that wasn't the entire story, Schindler said. Only 6 patients produced antibodies in sufficient amounts to neutralize virus at high serum dilutions. Four patients in the study who showed symptoms and tested positive for infection didn't develop antibodies specific to SARS-CoV-2 at all. Another 4 patients developed fairly high antibody levels, Schindler said, but poorly neutralized the virus in the experiments on human cell lines.
"It shows that we cannot generalize assumptions about the antibodies," said virologist Natalia Ruetalo, Ph.D, also at University Hospital Tübingen. Ruetalo, first author of the study, added that not everyone has the same immune response.
The findings suggest that some proportion of patients mount an immune response that doesn't lead to a neutralizing effect, Ruetalo said. "Those people may remain below some threshold of protective immunity and eventually get re-infected," she said.
In subsequent experiments, the researchers used an assay to quantify levels of antibodies from other coronaviruses in the serum of patients. They correlated those results to the ability of the sera to neutralize the COVID-19 coronavirus. They found, surprisingly, an association with antibodies against coronavirus 229E, which can cause the common cold. Antibodies produced during an infection with the cold likely aren't sufficient to protect a person against COVID-19, Schindler said, but they may help the body neutralize the virus.
The new work highlights the complexity of trying to use antibodies as evidence of immune protection, but without measuring neutralization, Schindler said. His group is now conducting similar experiments to identify which antibodies may neutralize variants of SARS-CoV-2 that have emerged in South Africa and elsewhere.?
INFORMATION:
The American Society for Microbiology is one of the largest professional societies dedicated to the life sciences and is composed of 30,000 scientists and health practitioners. ASM's mission is to promote and advance the microbial sciences.
ASM advances the microbial sciences through conferences, publications, certifications, educational opportunities and advocacy efforts. It enhances laboratory capacity around the globe through training and resources. It provides a network for scientists in academia, industry and clinical settings. Additionally, ASM promotes a deeper understanding of the microbial sciences to diverse audiences.
X-rays are used to study the atomic and microstructure properties of matter. Such studies are conducted with special accelerator complexes called synchrotrons. A synchrotron source generates powerful electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength equal to fractions of a nanometer. Some X-rays are reflected from the atomic planes of a crystal and some go through the crystal plane that plays the role of a beam-splitter (or the so-called semitransparent mirror). If the radiation passes through monochromators-optical devices that consist of two or more ideal crystals - its optimal exit wavelength can be regulated. ...
Researchers have developed a data transfer system that can transmit information 10 times faster than a USB. The new link pairs high-frequency silicon chips with a polymer cable as thin a strand of hair. The system may one day boost energy efficiency in data centers and lighten the loads of electronics-rich spacecraft.
The research was presented at this month's IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. The lead author is Jack Holloway '03, MNG '04, who completed his PhD in MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) last fall and currently works for Raytheon. Co-authors include Ruonan Han, associate professor and Holloway's PhD adviser in EECS, and Georgios Dogiamis, ...
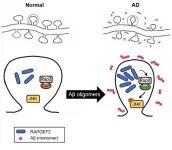
Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI, Pann-Ghill Suh (President)) announced that Dr. Kea Joo Lee and Dr. You-Na Jang of the Neural Circuits Research Group have identified the mechanism causing synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease as the aberrant expression of RAPGEF2, a synaptic protein.
- The results were published on January 2021, in the online Early View of Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology.
* (Title) RAPGEF2 mediates oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic loss and cognitive dysfunction in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) accounts for about 75% of dementia cases and is the most common type of degenerative brain disease. AD is a devastating because disease progression can cause ...
Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society (ACS), is celebrating Black chemists and chemical engineers with a special issue highlighting Black chemists who work across the fields of biotechnology, solar energy, pharmaceuticals and more. Guest edited by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) drug delivery pioneer Paula Hammond, Ph.D., this special issue showcases Black scientists, spotlighting their scientific passions and career accomplishments.
"In bringing into focus the unique lives of this set of accomplished Black scientists in chemistry and chemical engineering, ...
The steadily increasing prevalence and high costs of treating chronic joint pain worldwide poses a challenge for healthcare systems and healthcare payers. New research published today in END ...
The family of ENDOU enzymes is found in most organisms, yet its functions are only poorly understood. In humans, it has been connected with cancer. RNA viruses, such as SARS-CoV2, contain a gene corresponding to ENDOU, and this is important for virus replication and the suppression of the immune response. However, so far only few details of the role of these enzymes are known. The research group led by the molecular geneticist Dr. Wenjing Qi from the University of Freiburg now contributes some more details to its function in a study published by the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications. They suggest that the gene ENDU-2 could ...
Responding to artificial intelligence's exploding demands on computer networks, Princeton University researchers in recent years have radically increased the speed and slashed the energy use of specialized AI systems. Now, the researchers have moved their innovation closer to widespread use by creating co-designed hardware and software that will allow designers to blend these new types of systems into their applications.
"Software is a critical part of enabling new hardware," said Naveen Verma, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Princeton and a leader of the research team. "The ...
More U.S. adults reported receiving or planning to receive an influenza vaccination during the 2020-2021 flu season than ever before, according to findings from a national survey.
The survey of 1,027 adults, conducted by the University of Georgia, found that 43.5% of respondents reported having already received a flu vaccination with an additional 13.5% stating they "definitely will get one" and 9.3% stating they "probably will get one." Combined, 66.3% have received or intend to receive an influenza vaccination.
By comparison, 48.4% of adults 18 and older received the vaccine during the 2019-2020 flu season, according to the Centers for Disease ...
A new analysis of education debates on both social media and in traditional media outlets suggests that the education sector is being increasingly influenced by populism and the wider social media 'culture wars'.
The study also suggests that the type of populism in question is not quite the same as that used to explain large-scale political events, such as the UK's 'Brexit' from the European Union, or Donald Trump's recent presidency in the United States.
Instead, the researchers - from the University of Cambridge, UK, and Queensland University of Technology, Australia - identify a phenomenon called 'micropopulism': a localised populism which spotlights an aspect of public ...
CHICAGO, February 24, 2021 -- Despite having been designated as high risk for COVID-19 by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, a new study finds 3.1 percent of dental hygienists have had COVID-19 based on data collected in October 2020. This is in alignment with the cumulative infection prevalence rate among dentists and far below that of other health professionals in the U.S, although slightly higher than that of the general population.
The research, published by The Journal of Dental Hygiene, is the first large-scale collection and publication of U.S. dental hygienists' infection rates and infection control practices related to COVID-19. In partnership, the American Dental Hygienists' Association (ADHA) and the American Dental Association (ADA) ...