Study finds digital treatment for osteoarthritis is superior to traditional routine care
Joint Academy's online treatment effectively addresses growing and costly chronic disease safely during the global pandemic
2021-02-24
(Press-News.org) The steadily increasing prevalence and high costs of treating chronic joint pain worldwide poses a challenge for healthcare systems and healthcare payers. New research published today in END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A gene provides both protection and destruction
2021-02-24
The family of ENDOU enzymes is found in most organisms, yet its functions are only poorly understood. In humans, it has been connected with cancer. RNA viruses, such as SARS-CoV2, contain a gene corresponding to ENDOU, and this is important for virus replication and the suppression of the immune response. However, so far only few details of the role of these enzymes are known. The research group led by the molecular geneticist Dr. Wenjing Qi from the University of Freiburg now contributes some more details to its function in a study published by the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications. They suggest that the gene ENDU-2 could ...
Pushing computing to the edge by rethinking microchips' design
2021-02-24
Responding to artificial intelligence's exploding demands on computer networks, Princeton University researchers in recent years have radically increased the speed and slashed the energy use of specialized AI systems. Now, the researchers have moved their innovation closer to widespread use by creating co-designed hardware and software that will allow designers to blend these new types of systems into their applications.
"Software is a critical part of enabling new hardware," said Naveen Verma, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Princeton and a leader of the research team. "The ...
Flu vaccination this season likely to be highest ever
2021-02-24
More U.S. adults reported receiving or planning to receive an influenza vaccination during the 2020-2021 flu season than ever before, according to findings from a national survey.
The survey of 1,027 adults, conducted by the University of Georgia, found that 43.5% of respondents reported having already received a flu vaccination with an additional 13.5% stating they "definitely will get one" and 9.3% stating they "probably will get one." Combined, 66.3% have received or intend to receive an influenza vaccination.
By comparison, 48.4% of adults 18 and older received the vaccine during the 2019-2020 flu season, according to the Centers for Disease ...
'Micropopulism' may be turning education into a battlefield in the culture wars
2021-02-24
A new analysis of education debates on both social media and in traditional media outlets suggests that the education sector is being increasingly influenced by populism and the wider social media 'culture wars'.
The study also suggests that the type of populism in question is not quite the same as that used to explain large-scale political events, such as the UK's 'Brexit' from the European Union, or Donald Trump's recent presidency in the United States.
Instead, the researchers - from the University of Cambridge, UK, and Queensland University of Technology, Australia - identify a phenomenon called 'micropopulism': a localised populism which spotlights an aspect of public ...
Study finds low rate of COVID-19 among dental hygienists
2021-02-24
CHICAGO, February 24, 2021 -- Despite having been designated as high risk for COVID-19 by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, a new study finds 3.1 percent of dental hygienists have had COVID-19 based on data collected in October 2020. This is in alignment with the cumulative infection prevalence rate among dentists and far below that of other health professionals in the U.S, although slightly higher than that of the general population.
The research, published by The Journal of Dental Hygiene, is the first large-scale collection and publication of U.S. dental hygienists' infection rates and infection control practices related to COVID-19. In partnership, the American Dental Hygienists' Association (ADHA) and the American Dental Association (ADA) ...
Sulfur: the consequences
2021-02-24
The transition from single-celled organisms to multicellular ones was a major step in the evolution of complex life forms. Multicellular organisms arose hundreds of millions of years ago, but the forces underlying this event remain mysterious. To investigate the origins of multicellularity, Erika Pearce's group at the MPI of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg turned to the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum, which can exist in both a unicellular and a multicellular state, lying on the cusp of this key evolutionary step. These dramatically different states depend on just one thing - food.
A core question of Pearce's lab is to answer how changes in metabolism drive cell function and differentiation. Usually, they study immune cells ...
NCI study finds people with SARS-CoV-2 antibodies may have low risk of future infection
2021-02-24
People who have had evidence of a prior infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, appear to be well protected against being reinfected with the virus, at least for a few months, according to a newly published study from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). This finding may explain why reinfection appears to be relatively rare, and it could have important public health implications, including decisions about returning to physical workplaces, school attendance, the prioritization of vaccine distribution, and other activities.
For the study, researchers at NCI, part of the National Institutes of Health, collaborated with ...
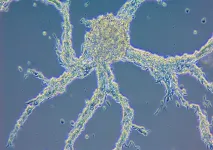
Yale scientists capture the choreography of a developing brain
2021-02-24
The formation of a brain is one of nature's most staggeringly complex accomplishments. The intricate intermingling of neurons and a labyrinth of connections also make it a particularly difficult feat for scientists to study.
Now, Yale researchers and collaborators have devised a strategy that allows them to see this previously impenetrable process unfold in a living animal -- the worm Caenorhabditis elegans, they report February 24 in the journal Nature.
"Before, we were able to study single cells, or small groups of cells, in the context of the living C. elegans, and for relatively short periods of time," said Mark Moyle, an associate research scientist in neuroscience at Yale School of Medicine and first author of the study. "It has been a breathtaking experience to ...
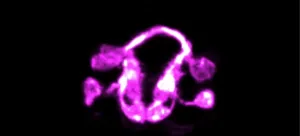
Building a brain: Pioneering study reveals principles of brain tissue structure, assembly
2021-02-24
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Understanding how the brain works is a paramount goal of medical science. But with its billions of tightly packed, intermingled neurons, the human brain is dauntingly difficult to visualize and map, which can provide the route to therapies for long-intractable disorders.
In a major advance published next week in Nature, scientists for the first time report the structure of a fundamental type of tissue organization in brains, called neuropil, as well as the developmental pathways that lead to neuropil assembly in the roundworm C. elegans. This multidisciplinary study ...
Costs associated with delirium in older adults after elective surgery
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: Medicare claims and clinical data were used to estimate health care costs associated with delirium in older adults one year after major elective surgery.
Authors: Tammy T. Hshieh, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2020.7260)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
[Press-News.org] Study finds digital treatment for osteoarthritis is superior to traditional routine careJoint Academy's online treatment effectively addresses growing and costly chronic disease safely during the global pandemic