Yale scientists capture the choreography of a developing brain
2021-02-24
(Press-News.org) The formation of a brain is one of nature's most staggeringly complex accomplishments. The intricate intermingling of neurons and a labyrinth of connections also make it a particularly difficult feat for scientists to study.
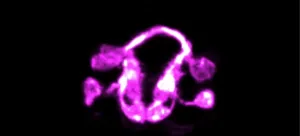
Now, Yale researchers and collaborators have devised a strategy that allows them to see this previously impenetrable process unfold in a living animal -- the worm Caenorhabditis elegans, they report February 24 in the journal Nature.
"Before, we were able to study single cells, or small groups of cells, in the context of the living C. elegans, and for relatively short periods of time," said Mark Moyle, an associate research scientist in neuroscience at Yale School of Medicine and first author of the study. "It has been a breathtaking experience to now be able to watch development unfold for hours, across the entire brain of the organism, and visualize this highly orchestrated dance."
The researchers describe the choreography of a developing brain in this video.
Moyle works in the lab headed by corresponding author Daniel Colón-Ramos, the Dorys McConnell Duberg Professor of Neuroscience and Cell Biology and senior author of the study.
The lab collaborated with computational and microscopy scientists to develop novel network algorithms and imaging technologies that allowed them to study complex webs of interconnected neurons in living C. elegans, a common type of roundworm often used in research. Despite its simplicity, it shares key molecular and genetic characteristics with human biology.
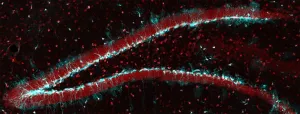
The researchers found that interconnected neurons, densely packed into units called neuropils, are organized to sort signals which dictate many functions and behaviors in the organisms. The study details architectural principles in the neuropil structure that determines how functional brain circuits are developed and assembled.
The authors found that neuronal processes and connections in the worm's brain are organized into layers, each containing modular components of functional circuits that are linked to distinct behaviors.
Then, using high-resolution light sheet microscopy, the researchers were able to track single cells over the course of the organism's development, providing insights into how these cells help choreograph the assembly of the brain.
"When you see the architecture, you realize that all this knowledge that was out there about the animal's behaviors has a home in the structure of the brain," Colón-Ramos said.
For instance, researchers can trace reflex behavior in animals to circuits leading to muscles and how these same circuits integrate with still others to regulate the animal's movement.
He said the brain is organized like a city such as New York, with areas like Wall Street or Broadway organized to carry out the specific functions of finance and entertainment, respectively.
"Suddenly you see how the city fits together and you understand the relationships between the neighborhoods," Colon-Ramos said.
INFORMATION:
The work is the result of a decade long collaboration between the labs of Colón-Ramos and Smita Krishnaswamy of Yale; Hari Shroff of the National Institutes of Health; Zhirong Bao of the Sloan Kettering Institute; and William A. Mohler of the University of Connecticut Health Center. The Colón-Ramos, Shroff, Bao, and Mohler labs are part of the consortium WormGUIDES.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-02-24
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Understanding how the brain works is a paramount goal of medical science. But with its billions of tightly packed, intermingled neurons, the human brain is dauntingly difficult to visualize and map, which can provide the route to therapies for long-intractable disorders.
In a major advance published next week in Nature, scientists for the first time report the structure of a fundamental type of tissue organization in brains, called neuropil, as well as the developmental pathways that lead to neuropil assembly in the roundworm C. elegans. This multidisciplinary study ...
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: Medicare claims and clinical data were used to estimate health care costs associated with delirium in older adults one year after major elective surgery.
Authors: Tammy T. Hshieh, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2020.7260)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study ...
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: Researchers use a large set of clinical laboratory data linked to other clinical information such as claims to investigate the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 antibody status and subsequent nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) results in an effort to understand how serostatus may predict risk of reinfection.
Authors: Lynne T. Penberthy, M.D., M.P.H., of the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health in Rockville, Maryland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.0366)
Editor's ...
2021-02-24
In the last 60,000 years, humans have emerged as an ecologically dominant species and have successfully colonized every terrestrial habitat. Our evolutionary success has been facilitated by a heavy reliance on an ever-advancing technology. Understanding how human technology evolves is crucial to understanding why humans have enjoyed such unprecedented evolutionary success.
ASU doctoral graduate Jacob Harris, working with ASU researcher Robert Boyd and Brian Wood from the University of California Las Angeles and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, are interested in the role of causal ...
2021-02-24
What The Study Did: This study combined the results of 12 studies with 1.8 million participants to examine the association between attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in childhood and adolescence and the subsequent risk of developing a psychotic disorder.
Authors: Mikaïl Nourredine, M.D., M.Sc., of the Hospices Civils de Lyon in Lyon, France, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2020.4799)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
2021-02-24
BOSTON (February 24, 2021) - Results of a study published today in JAMA Surgery reveal the impact post-operative delirium has on health care costs in the U.S. Data from the study shows that if delirium were prevented or made less severe for patients, it could reduce health care costs by $33 billion per year, that is, $44,300 per patient per year. Severe delirium resulted in an additional $56,500 per patient per year, as compared to routine health care costs for older post-operative patients.
Tammy Hshieh, M.D., M.P.H., Adjunct Scientist, and Ray Yun Gou, M.A., Data Scientist II, both with the Aging Brain Center in the Hinda and Arthur Marcus Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife, are co-first authors. Sharon K. Inouye, M.D., M.P.H., Director ...
2021-02-24
CHAPEL HILL, N.C.--For the last decade, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has required tobacco manufacturers and importers to report the levels of harmful and potentially harmful chemicals found in their tobacco products and tobacco smoke. The idea was to educate the public and ultimately to decrease tobacco use, but little research has demonstrated if such information can impact on people's decisions to quit smoking.
A new study from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has found that smokers who saw messages about tobacco chemicals with associated ...
2021-02-24
The stem cells in our brain generate new neurons throughout life, for example in the hippocampus. This region of the brain plays a key role for a range of memory processes. With increasing age, and in patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease, the hippocampus' ability to create new neurons declines steadily - and with it, its memory functions.
Distribution of age-dependent cell damage
A study conducted by the research group of Sebastian Jessberger, a professor at the Brain Research Institute of the University of Zurich, shows how the formation of new neurons is impaired with advancing age. Protein structures in the nuclei of neural stem cells make sure that harmful proteins accumulating ...
2021-02-24
The most modern light sources for research are based on particle accelerators. These are large facilities in which electrons are accelerated to almost the speed of light, and then emit light pulses of a special character. In storage-ring-based synchrotron radiation sources, the electron bunches travel in the ring for billions of revolutions, then generate a rapid succession of very bright light pulses in the deflecting magnets. In contrast, the electron bunches in free-electron lasers (FELs) are accelerated linearly and then emit a single super-bright flash of ...
2021-02-24
Researchers have mapped the physical organization of the brain of a microscopic soil-living nematode worm called Caenorhabditis elegans, creating a new model for the architecture of the animal's brain and how it processes information.
In a surprise twist, they found a large degree of variation in the structure of some neural circuits or pathways in individual worms which complemented a core set of neural circuits common to different animals.
The scientists say the worms' brains might have a lot more in common with larger animals than previously thought.
Created by neuroscientists at the University of Leeds in collaboration with researchers in New York's Albert Einstein College of Medicine, the brain map reveals that ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Yale scientists capture the choreography of a developing brain