(Press-News.org) Researchers have developed a data transfer system that can transmit information 10 times faster than a USB. The new link pairs high-frequency silicon chips with a polymer cable as thin a strand of hair. The system may one day boost energy efficiency in data centers and lighten the loads of electronics-rich spacecraft.
The research was presented at this month's IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference. The lead author is Jack Holloway '03, MNG '04, who completed his PhD in MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) last fall and currently works for Raytheon. Co-authors include Ruonan Han, associate professor and Holloway's PhD adviser in EECS, and Georgios Dogiamis, a senior researcher at Intel.
The need for snappy data exchange is clear, especially in an era of remote work. "There's an explosion in the amount of information being shared between computer chips -- cloud computing, the internet, big data. And a lot of this happens over conventional copper wire," says Holloway. But copper wires, like those found in USB or HDMI cables, are power-hungry -- especially when dealing with heavy data loads. "There's a fundamental tradeoff between the amount of energy burned and the rate of information exchanged." Despite a growing demand for fast data transmission (beyond 100 gigabits per second) through conduits longer than a meter, Holloway says the typical solution has been "increasingly bulky and costly" copper cables.
One alternative to copper wire is fiber-optic cable, though that has its own problems. Whereas copper wires use electrical signaling, fiber-optics use photons. That allows fiber-optics to transmit data quickly and with little energy dissipation. But silicon computer chips generally don't play well with photons, making interconnections between fiber-optic cables and computers a challenge. "There's currently no way to efficiently generate, amplify, or detect photons in silicon," says Holloway. "There are all kinds of expensive and complex integration schemes, but from an economics perspective, it's not a great solution." So, the researchers developed their own.
The team's new link draws on benefits of both copper and fiber optic conduits, while ditching their drawbacks. "It's a great example of a complementary solution," says Dogiamis. Their conduit is made of plastic polymer, so it's lighter and potentially cheaper to manufacture than traditional copper cables. But when the polymer link is operated with sub-terahertz electromagnetic signals, it's far more energy-efficient than copper in transmitting a high data load. The new link's efficiency rivals that of fiber-optic, but has a key advantage: "It's compatible directly with silicon chips, without any special manufacturing," says Holloway.
The team engineered such low-cost chips to pair with the polymer conduit. Typically, silicon chips struggle to operate at sub-terahertz frequencies. Yet the team's new chips generate those high-frequency signals with enough power to transmit data directly into the conduit. That clean connection from the silicon chips to the conduit means the overall system can be manufactured with standard, cost-effective methods, the researchers say.
The new link also beats out copper and fiber optic in terms of size. "The cross-sectional area of our cable is 0.4 millimeters by a quarter millimeter," says Han. "So, it's super tiny, like a strand of hair." Despite its slim size, it can carry a hefty load of data, since it sends signals over three different parallel channels, separated by frequency. The link's total bandwidth is 105 gigabits per second, nearly an order of magnitude faster than a copper-based USB cable. Dogiamis says the cable could "address the bandwidth challenges as we see this megatrend toward more and more data."
In future work, Han hopes to make the polymer conduits even faster by bundling them together. "Then the data rate will be off the charts," he says. "It could be one terabit per second, still at low cost."
The researchers suggest "data-dense" applications, like server farms, could be early adopters of the new links, since they could dramatically cut data centers' high energy demands. The link could also be a key solution for the aerospace and automotive industries, which place a premium on small, light devices. And one day, the link could replace the consumer electronic cables in homes and offices, thanks to the link's simplicity and speed. "It's far less costly than [copper or fiber optic] approaches, with significantly wider bandwidth and lower loss than conventional copper solutions," says Holloway. "So, high fives all round."
INFORMATION:
This research was funded, in part, by Intel, Raytheon, the Naval Research Laboratory, and the Office of Naval Research.
Written by Daniel Ackerman, MIT News Office
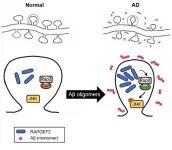
Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI, Pann-Ghill Suh (President)) announced that Dr. Kea Joo Lee and Dr. You-Na Jang of the Neural Circuits Research Group have identified the mechanism causing synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease as the aberrant expression of RAPGEF2, a synaptic protein.
- The results were published on January 2021, in the online Early View of Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology.
* (Title) RAPGEF2 mediates oligomeric Aβ-induced synaptic loss and cognitive dysfunction in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) accounts for about 75% of dementia cases and is the most common type of degenerative brain disease. AD is a devastating because disease progression can cause ...
Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society (ACS), is celebrating Black chemists and chemical engineers with a special issue highlighting Black chemists who work across the fields of biotechnology, solar energy, pharmaceuticals and more. Guest edited by Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) drug delivery pioneer Paula Hammond, Ph.D., this special issue showcases Black scientists, spotlighting their scientific passions and career accomplishments.
"In bringing into focus the unique lives of this set of accomplished Black scientists in chemistry and chemical engineering, ...
The steadily increasing prevalence and high costs of treating chronic joint pain worldwide poses a challenge for healthcare systems and healthcare payers. New research published today in END ...
The family of ENDOU enzymes is found in most organisms, yet its functions are only poorly understood. In humans, it has been connected with cancer. RNA viruses, such as SARS-CoV2, contain a gene corresponding to ENDOU, and this is important for virus replication and the suppression of the immune response. However, so far only few details of the role of these enzymes are known. The research group led by the molecular geneticist Dr. Wenjing Qi from the University of Freiburg now contributes some more details to its function in a study published by the renowned scientific journal Nature Communications. They suggest that the gene ENDU-2 could ...
Responding to artificial intelligence's exploding demands on computer networks, Princeton University researchers in recent years have radically increased the speed and slashed the energy use of specialized AI systems. Now, the researchers have moved their innovation closer to widespread use by creating co-designed hardware and software that will allow designers to blend these new types of systems into their applications.
"Software is a critical part of enabling new hardware," said Naveen Verma, a professor of electrical and computer engineering at Princeton and a leader of the research team. "The ...
More U.S. adults reported receiving or planning to receive an influenza vaccination during the 2020-2021 flu season than ever before, according to findings from a national survey.
The survey of 1,027 adults, conducted by the University of Georgia, found that 43.5% of respondents reported having already received a flu vaccination with an additional 13.5% stating they "definitely will get one" and 9.3% stating they "probably will get one." Combined, 66.3% have received or intend to receive an influenza vaccination.
By comparison, 48.4% of adults 18 and older received the vaccine during the 2019-2020 flu season, according to the Centers for Disease ...
A new analysis of education debates on both social media and in traditional media outlets suggests that the education sector is being increasingly influenced by populism and the wider social media 'culture wars'.
The study also suggests that the type of populism in question is not quite the same as that used to explain large-scale political events, such as the UK's 'Brexit' from the European Union, or Donald Trump's recent presidency in the United States.
Instead, the researchers - from the University of Cambridge, UK, and Queensland University of Technology, Australia - identify a phenomenon called 'micropopulism': a localised populism which spotlights an aspect of public ...
CHICAGO, February 24, 2021 -- Despite having been designated as high risk for COVID-19 by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, a new study finds 3.1 percent of dental hygienists have had COVID-19 based on data collected in October 2020. This is in alignment with the cumulative infection prevalence rate among dentists and far below that of other health professionals in the U.S, although slightly higher than that of the general population.
The research, published by The Journal of Dental Hygiene, is the first large-scale collection and publication of U.S. dental hygienists' infection rates and infection control practices related to COVID-19. In partnership, the American Dental Hygienists' Association (ADHA) and the American Dental Association (ADA) ...
The transition from single-celled organisms to multicellular ones was a major step in the evolution of complex life forms. Multicellular organisms arose hundreds of millions of years ago, but the forces underlying this event remain mysterious. To investigate the origins of multicellularity, Erika Pearce's group at the MPI of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg turned to the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum, which can exist in both a unicellular and a multicellular state, lying on the cusp of this key evolutionary step. These dramatically different states depend on just one thing - food.
A core question of Pearce's lab is to answer how changes in metabolism drive cell function and differentiation. Usually, they study immune cells ...
People who have had evidence of a prior infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, appear to be well protected against being reinfected with the virus, at least for a few months, according to a newly published study from the National Cancer Institute (NCI). This finding may explain why reinfection appears to be relatively rare, and it could have important public health implications, including decisions about returning to physical workplaces, school attendance, the prioritization of vaccine distribution, and other activities.
For the study, researchers at NCI, part of the National Institutes of Health, collaborated with ...