Addressing a complex world of pain in a single gene difference
2021-03-01
(Press-News.org) A single letter difference in a single gene, inherited from both parents, spells a lifetime of anemia and pain for 20 million people, mostly of African ancestry, worldwide. Sickle cell disease (SCD) causes red blood cells to assume a sickle shape and jam in capillaries, cutting off oxygen to lungs, brain, bones and other organs. Despite the single genetic origin of SCD, each person's disease experience and even life expectancy depend upon where they live, and the social, physical and environmental factors they encounter.
Now, a new review published by Wiley in the journal Advanced Genetics proposes that it is not only possible and necessary to analyze all these influences to understand disparities in experience and treatment of this disease, but that this approach will advance understanding and healthcare for all diseases with a hereditary component. The research and this new perspective stems from review of existing research on SCD together with preliminary data collected by an international collaboration studying the relationships of sociodemographic, clinical, genetic, and environmental factors to pain among adults with SCD from three countries in Africa and the African Diaspora - Cameroon, Jamaica, and the United States.
SCD is the first molecular disease and may become the first to have an approved molecular cure from gene editing. In the meantime, we must continue to scale up efforts to develop new tools and techniques for reducing and preventing complications in the millions of people worldwide suffering from SCD, most of whom are unlikely to have immediate access to high-tech cures when they become available. The unmet needs of people with SCD are prevalent, even in European and North American countries. The authors write, "large national and multinational integrative studies are needed to better understand SCD globally and catalyze the development, translation, and implementation of locally-appropriate interventions and policies."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-01
The rapid loss of variation within species is a hidden biodiversity crisis, according to the authors of a new study looking at how this variation supports essential ecological functions and the benefits nature provides for people.
Published March 1 in Nature Ecology and Evolution, the study highlights the need to better understand and conserve variation within species in order to safeguard nature's contributions to people.
"Biodiversity means more than the number of species, and when we focus on species-level extinctions we are missing part of the story," said corresponding author Eric Palkovacs, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz. "Intraspecific variation is a neglected aspect of biodiversity, ...
2021-03-01
ITHACA, N.Y. - The expansion of charter schools in the 2000s led to an increase in school segregation and a slight decline in residential segregation, according to new research from Cornell University providing the first national estimates of the diverging trends.
According to the study, the average district to expand charter school enrollment between 2000 and 2010 experienced a 12% increase in white-Black school segregation and a 2% decrease in white-Black residential segregation.
The patterns moved in opposite directions, the research found, because charter ...
2021-03-01
Scientists from the Stanley Manne Children's Research Institute at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children's Hospital of Chicago found that a region within the DNA of the cancer-promoting GLI1 gene is directly responsible for regulating this gene's expression. These findings, published in the journal Stem Cells, imply that this region within GLI1 could potentially be targeted as cancer treatment, since turning off GLI1 would interrupt excessive cell division characteristic of cancer.
"From previous research, we know that GLI1 drives the unrelenting cell proliferation that is responsible for many cancers, and that this gene also stimulates its own expression," says co-senior author Philip Iannaccone, MD, PhD, Professor Emeritus at the Manne Research Institute at Lurie Children's and Northwestern ...
2021-03-01
Scientists from Far Eastern Federal University (FEFU) together with Russian and German colleagues, continue studying antitumor compounds synthesized based on bioactive molecules isolated from a sea sponge. One of them fights cancer cells resistant to standard chemotherapy, and at the same time has an interesting dual mechanism of action. A related article appears in Marine Drugs.
Scientists have tested the biological effect of the marine alkaloid 3,10-dibromofascaplysin on various prostate cancer cells, including those resistant to standard docetaxel-based chemotherapy. ...
2021-03-01
CORVALLIS, Ore. - In tropical oceans, a combination of sunlight and weak winds drives up surface temperatures in the afternoon, increasing atmospheric turbulence, unprecedented new observational data collected by an Oregon State University researcher shows.
The new findings could have important implications for weather forecasting and climate modeling, said Simon de Szoeke, a professor in OSU's College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences and the lead author of the study.
"The ocean warms in the afternoon by just a degree or two, but it is an effect that has largely been ignored," said de Szoeke. ...
2021-03-01
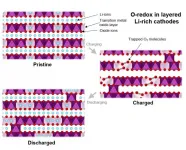
HARWELL, UK (1 March 2021) Scientists based at the University of Oxford as part of the Faraday Institution CATMAT project researching next-generation cathode materials have made a significant advance in understanding oxygen-redox processes involved in lithium-rich cathode materials. The paper, published in Nature Energy, proposes strategies that offer potential routes to increase the energy density of lithium-ion batteries.
"In the ever more difficult quest to make incremental improvements to Li-ion battery energy density, being able to harness the potential of oxygen-redox cathodes and the bigger improvements they offer relative to the nickel rich cathodes in commercial use today is potentially significant," Prof Peter Bruce, University ...
2021-03-01
Childhood cancer and its treatment can result in cognitive struggles. Scientists atSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital are studying the risk factors. They looked at social and economic issues in children with brain tumors treated with radiation.
These patients have the greatest risk of cognitive problems. Scientists followed a group of St. Jude patients for 10 years. The children all had conformal radiation therapy.
For each patient, researchers looked at certain factors. These included the parent's job, education level, and whether it was a single parent home. The children were from different backgrounds.
The findings show social and economic status is linked to IQ, academics, attention ...
2021-03-01
Amsterdam, March 1, 2021 - Comfort is a daily human experience central to the perception of our environment and the continuous processing of sensory input. Environmental factors such as smell, temperature and light can influence comfort, as can our interaction with products, such as the design of a chair or a mattress. Increasingly, researchers investigating the science of comfort and discomfort are focusing on the role of human behavior. A special supplement to the journal WORK presents the latest advances, from optimal seat design in offices and transportation to the influence of smell on comfort and the interaction between time and comfort.
"This special supplement adds unique findings to comfort knowledge. ...
2021-03-01
A novel targeted immunotherapy approach developed by researchers at the Ludwig Center, the Lustgarten Laboratory, and Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center employs new antibodies against genetically altered proteins to target cancers.
The researchers targeted their immunotherapy approach to alterations in the common cancer-related p53 tumor suppressor gene, the RAS tumor-promoting oncogene or T-cell receptor genes. They also tested the therapy on cancer cells in the laboratory and in animal tumor models. Their findings are reported in three related studies published March 1 in Science Immunology, Science and Science Translational Medicine.
Two ...
2021-03-01
Scientists have identified that the COVID-19 virus could be transmitted through faecal contaminated river water.
A team of researchers, including water quality, epidemiology, remote sensing and modelling experts, led by Dr Jamie Shutler at the University of Exeter, have developed a fast and simple way to assess the potential risk of water-borne transmission of the COVID-19 virus, posed by sewage spills into open and closed freshwater networks.
The new study, published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology - Water, identifies the relative risk of viral transmission by sewerage spills, across 39 different counties.
The study used information on the environment, a population's infection rate, and water usage to calculate the potential potency of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Addressing a complex world of pain in a single gene difference