Mechanistic understanding of oxygen-redox processes in lithium-rich battery cathodes
Informing practical strategies towards higher energy density batteries
2021-03-01
(Press-News.org) HARWELL, UK (1 March 2021) Scientists based at the University of Oxford as part of the Faraday Institution CATMAT project researching next-generation cathode materials have made a significant advance in understanding oxygen-redox processes involved in lithium-rich cathode materials. The paper, published in Nature Energy, proposes strategies that offer potential routes to increase the energy density of lithium-ion batteries.
"In the ever more difficult quest to make incremental improvements to Li-ion battery energy density, being able to harness the potential of oxygen-redox cathodes and the bigger improvements they offer relative to the nickel rich cathodes in commercial use today is potentially significant," Prof Peter Bruce, University of Oxford and Chief Scientist of the Faraday Institution. "The deeper understanding of the fundamental mechanisms of oxygen-redox is an important step in informing strategies to mitigate the current limitations of such materials, bringing their potential commercial use a step closer to reality."
"Finding pioneering solutions in the UK's race to electrification needs large-scale, focused research effort targeted at industry relevant goals," said Pam Thomas, CEO of the Faraday Institution. This is one example of Faraday Institution researchers achieving a significant scientific milestone, one that unlocks and accelerates multiple new avenues of research in the quest towards battery materials and that could increase the range of future electric vehicles. The breakthrough was facilitated by use of state-of-the-art facilities provided by Diamond Light Source and Royce Institute, demonstrating the importance of maintaining the strength of the UK's research infrastructure."
Increasing the range of electric vehicles demands battery materials that can store more charge at higher voltages in order to achieve a higher "energy density". There are a limited number of ways to increase the energy density of lithium-ion cathode materials. Most current cathode materials are layered transition metal oxides incorporating, e.g. cobalt, nickel and manganese. One research route involves storing charge on the oxide ions as well as on the transition metal ions.
Use of such oxygen-redox materials to increase cathode energy density has been promising for some years, but realising their full potential in commercial batteries has been hampered by the structural changes they experience during their first charge, which are predominantly irreversible, and which give rise to a significant drop in the voltage available on subsequent discharge and future cycles.
A significant research effort has been underway for some time around the world to uncover a mechanism for oxygen-redox that explains these structural changes, but a clear understanding of the nature of oxidised oxygen remains a key part of the puzzle.
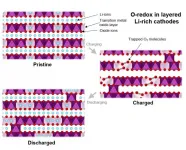
Techniques such as RIXS (resonant inelastic X-ray scattering) have been used with success in the past to probe the changes to the oxygen. But by collaborating with researchers at the state-of-the art, I21 beamline at Diamond Light Source, Faraday Institution researchers have successfully resolved these RIXS features that indicate that the oxidised oxygen species in the bulk of the material is molecular oxygen rather than peroxide or other species.
"Moreover, computational modelling has demonstrated that the evolution of molecular oxygen explains both the observed electrochemical response - the reduction in voltage on first discharge - and the observed structural changes - explained by the accommodation of the molecular oxygen within the bulk of the material," said Prof Saiful Islam, University of Bath and CATMAT Principal Investigator. "This single unified model tying molecular oxygen and voltage loss together allows researchers to propose practical strategies for avoiding oxygen-redox-induced instability, offering potential routes towards more reversible high energy density Li-ion cathodes."
Six such strategies are proposed in the paper, of varying novelty, all of which are promising and are being explored by the CATMAT project. The mechanistic understanding developed will speed up research in each of these areas, offering an alternative to iterative, trial and error approaches. In one novel research direction, researchers are investigating the development of a unique "superstructure" where control is exerted over the ordering of lithium atoms in the transition metal layer, giving more stability to the structure and reducing voltage loss.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-01
Childhood cancer and its treatment can result in cognitive struggles. Scientists atSt. Jude Children's Research Hospital are studying the risk factors. They looked at social and economic issues in children with brain tumors treated with radiation.
These patients have the greatest risk of cognitive problems. Scientists followed a group of St. Jude patients for 10 years. The children all had conformal radiation therapy.
For each patient, researchers looked at certain factors. These included the parent's job, education level, and whether it was a single parent home. The children were from different backgrounds.
The findings show social and economic status is linked to IQ, academics, attention ...
2021-03-01
Amsterdam, March 1, 2021 - Comfort is a daily human experience central to the perception of our environment and the continuous processing of sensory input. Environmental factors such as smell, temperature and light can influence comfort, as can our interaction with products, such as the design of a chair or a mattress. Increasingly, researchers investigating the science of comfort and discomfort are focusing on the role of human behavior. A special supplement to the journal WORK presents the latest advances, from optimal seat design in offices and transportation to the influence of smell on comfort and the interaction between time and comfort.
"This special supplement adds unique findings to comfort knowledge. ...
2021-03-01
A novel targeted immunotherapy approach developed by researchers at the Ludwig Center, the Lustgarten Laboratory, and Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center employs new antibodies against genetically altered proteins to target cancers.
The researchers targeted their immunotherapy approach to alterations in the common cancer-related p53 tumor suppressor gene, the RAS tumor-promoting oncogene or T-cell receptor genes. They also tested the therapy on cancer cells in the laboratory and in animal tumor models. Their findings are reported in three related studies published March 1 in Science Immunology, Science and Science Translational Medicine.
Two ...
2021-03-01
Scientists have identified that the COVID-19 virus could be transmitted through faecal contaminated river water.
A team of researchers, including water quality, epidemiology, remote sensing and modelling experts, led by Dr Jamie Shutler at the University of Exeter, have developed a fast and simple way to assess the potential risk of water-borne transmission of the COVID-19 virus, posed by sewage spills into open and closed freshwater networks.
The new study, published in the journal Environmental Science and Technology - Water, identifies the relative risk of viral transmission by sewerage spills, across 39 different counties.
The study used information on the environment, a population's infection rate, and water usage to calculate the potential potency of ...
2021-03-01
Plants grow towards the light. This phenomenon, which already fascinated Charles Darwin, has been observed by everyone who owns houseplants. Thus, the plant ensures that it can make the best use of light to photosynthesize and synthesize sugars. Similarly, the roots grow into the soil to ensure that the plant is supplied with water and nutrients.
These growth processes are controlled by a hormone called "auxin", which plays a key role in the formation of polarity in plants. To do this, auxin is transported in the plant body polar, from the shoot through the plant body into the roots. In this process, a family of polar transport proteins distributes the auxin throughout the plant. To ...
2021-03-01
The cover for issue 49 of Oncotarget features Figure 4, "CART-Tree analysis for overall survival in IMDC intermediate risk group," by Guida, et al.recently published in "Identification of international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium (IMDC) intermediate-risk subgroups in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma" which reported that as these patients have different prognosis, the aim of this study is to better characterize IR patients in order to better tailor the treatment.
A multivariable Cox model with backward selection procedure and a Classification and Regression Tree analysis were performed to identify which prognostic factors were associated to OS in IR patients.
Median OS for patients with ...
2021-03-01
Oncotarget recently published "Exploiting the metabolic dependencies of the broad amino acid transporter SLC6A14" which reported that Tumor cells typically enhance their metabolic capacity to sustain their higher rate of growth and proliferation.
One way to elevate the nutrient intake into cancer cells is to increase the expression of genes encoding amino acid transporters, which may represent targetable vulnerabilities.
The Oncotarget authors analyze the pattern of transcriptional changes in a panel of breast cancer cell lines upon metabolic stress and found that SLC6A14 expression levels are increased in the absence of methionine.
Methionine deprivation, which can be achieved via modulation of dietary methionine intake in tumor cells, in turn leads to a heightened ...
2021-03-01
Oncotarget recently published "Effect of liver fibrosis on survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a SEER population-based study" which reported that the impact of fibrosis on overall and cancer-specific survival 12, 36, and 60 months following diagnosis, was evaluated in the entire cohort and in subgroups stratified according to treatment approach and the American Joint Committee on Cancer tumor stage using a Cox proportional-hazards model.
After adjusting for age, sex, race, year of diagnosis, AJCC stage, and surgical treatment strategy, advanced fibrosis was associated with worse cancer-specific survival across follow-up periods.
Similar effects were observed for overall survival.
Among patients that underwent surgical resection, ...
2021-03-01
CHICAGO --- Public attitude toward COVID-19 and its treatments is more "infectious" than the disease itself, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to analyze tweets about the virus. Researchers studied the influence of Twitter on COVID-19 health beliefs as well as the competing influence of scientific evidence versus the speeches of politicians.
The study's key findings:
People's biases are magnified when they read tweets about COVID-19 from other users, and the more times it has been retweeted, the more they tend to believe it and retweet it themselves.
Scientific ...
2021-03-01
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 1, 2021 - There is a growing recognition in health care that social factors such as racial bias, access to care and housing and food insecurity, have a significant impact on people's health. Compounding and amplifying those underlying inequalities are the ongoing disruptions related to the COVID-19 pandemic and social unrest in our country.
Although many health care organizations (National Academy of Medicine, American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Pediatrics) currently recommend that screening for social determinants of health (SDH) be included in clinical care, medical education has lagged ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mechanistic understanding of oxygen-redox processes in lithium-rich battery cathodes
Informing practical strategies towards higher energy density batteries