(Press-News.org) Plants grow towards the light. This phenomenon, which already fascinated Charles Darwin, has been observed by everyone who owns houseplants. Thus, the plant ensures that it can make the best use of light to photosynthesize and synthesize sugars. Similarly, the roots grow into the soil to ensure that the plant is supplied with water and nutrients.
These growth processes are controlled by a hormone called "auxin", which plays a key role in the formation of polarity in plants. To do this, auxin is transported in the plant body polar, from the shoot through the plant body into the roots. In this process, a family of polar transport proteins distributes the auxin throughout the plant. To better understand this process, the research team investigated it in more detail with the help of a chemical.
How the herbicide naptalam works
Scientists around the world are studying transporter proteins in more detail due to their central role in plant development processes. Naptalam (NPA) is an important tool to elucidate the structure of the transporters.
Naptalam is the registered name of Napthylphphthalic acid. It inhibits the directional flow of auxin, thus severely inhibiting plant growth. It was used in in the European Union until 2002, and the sodium salt of naptalam is still used in the USA as a pre-emergence herbicide to control broadleaf weed in cucurbits and nursery stock.
"We wanted to know how naptalam exerts its effects," says PD Dr. Ulrich Hammes, the study's principal investigator. "Our studies show that the activity of the auxin transporters is really completely shut down by the inhibitor." When NPA binds to the transporter proteins, auxin can no longer get out of the cell, and thus the plant is no longer able to grow polarly. The roots no longer grow to the center of the earth, and flowers and seed formations are massively disrupted.
An effect of the inhibitor NPA on the activators of the transporters, known as kinases, could be ruled out through collaboration with Claus Schwechheimer, Professor of Plant Systems Biology of at the TUM, where the work was carried out. He explains, "This makes it clear that the inhibitor NPA acts directly on the transport proteins."
How transport proteins contribute to plant development
"We can now clearly explain the molecular mechanism by which polar plant growth can be disrupted pharmacologically," says Ulrich Hammes.
The research groups in Vienna were able to show that naptalam not only binds the transporters, but also prevents the transporters from binding to each other. "This mechanism of binding to each other seems to apply universally in the family of auxin transporters, as we observed the effect in all transporters studied," says Martina Kolb, first author of the study.
Better understanding of molecular relationships
Overall, the study provides a significant step forward in understanding the mechanism of the molecular machinery of plant polarity. The new findings make it possible to study polar growth more precisely and to understand the molecular mechanism of auxin transport.
INFORMATION:
At the TUM School of Life Sciences in Weihenstephan, researchers are therefore now working further in depth to caracterize polar auxin transport processes. "We hope to be able to better understand plant growth movements through this mechanism," says Ulrich Hammes.
The cover for issue 49 of Oncotarget features Figure 4, "CART-Tree analysis for overall survival in IMDC intermediate risk group," by Guida, et al.recently published in "Identification of international metastatic renal cell carcinoma database consortium (IMDC) intermediate-risk subgroups in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma" which reported that as these patients have different prognosis, the aim of this study is to better characterize IR patients in order to better tailor the treatment.
A multivariable Cox model with backward selection procedure and a Classification and Regression Tree analysis were performed to identify which prognostic factors were associated to OS in IR patients.
Median OS for patients with ...
Oncotarget recently published "Exploiting the metabolic dependencies of the broad amino acid transporter SLC6A14" which reported that Tumor cells typically enhance their metabolic capacity to sustain their higher rate of growth and proliferation.
One way to elevate the nutrient intake into cancer cells is to increase the expression of genes encoding amino acid transporters, which may represent targetable vulnerabilities.
The Oncotarget authors analyze the pattern of transcriptional changes in a panel of breast cancer cell lines upon metabolic stress and found that SLC6A14 expression levels are increased in the absence of methionine.
Methionine deprivation, which can be achieved via modulation of dietary methionine intake in tumor cells, in turn leads to a heightened ...
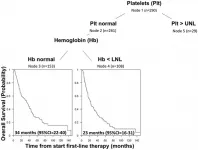
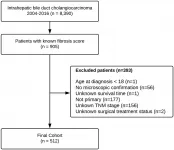
Oncotarget recently published "Effect of liver fibrosis on survival in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a SEER population-based study" which reported that the impact of fibrosis on overall and cancer-specific survival 12, 36, and 60 months following diagnosis, was evaluated in the entire cohort and in subgroups stratified according to treatment approach and the American Joint Committee on Cancer tumor stage using a Cox proportional-hazards model.
After adjusting for age, sex, race, year of diagnosis, AJCC stage, and surgical treatment strategy, advanced fibrosis was associated with worse cancer-specific survival across follow-up periods.
Similar effects were observed for overall survival.
Among patients that underwent surgical resection, ...
CHICAGO --- Public attitude toward COVID-19 and its treatments is more "infectious" than the disease itself, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to analyze tweets about the virus. Researchers studied the influence of Twitter on COVID-19 health beliefs as well as the competing influence of scientific evidence versus the speeches of politicians.
The study's key findings:
People's biases are magnified when they read tweets about COVID-19 from other users, and the more times it has been retweeted, the more they tend to believe it and retweet it themselves.
Scientific ...
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 1, 2021 - There is a growing recognition in health care that social factors such as racial bias, access to care and housing and food insecurity, have a significant impact on people's health. Compounding and amplifying those underlying inequalities are the ongoing disruptions related to the COVID-19 pandemic and social unrest in our country.
Although many health care organizations (National Academy of Medicine, American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Pediatrics) currently recommend that screening for social determinants of health (SDH) be included in clinical care, medical education has lagged ...
What The Study Did: Researchers assessed the recruitment and results reporting of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) to treat or prevent COVID-19 registered within 100 days of the first case reported to the World Health Organization.
Authors: Lars G. Hemkens, M.D., M.P.H., of the University Hospital Basel in Basel, Switzerland, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0330)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please ...
Researchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Nanjing Normal University recently reported a strategy for boosting the electrocatalytic performance of palladium (Pd) in ethanol oxidation reaction, the key anodic reaction of direct ethanol fuel cells (DEFCs), offering a rational concept for finely engineering the surface of electrocatalysts used in high-efficiency energy conversion devices and beyond.
The study was published in Cell Reports Physical Science on Mar. 1.
DEFCs, with ethanol as fuel, have the advantage of high energy density, low toxicity and easy operation. However, the lack of active and robust electrocatalysts ...
Rising temperatures could reduce the efficiency of food chains and threaten the survival of larger animals, new research shows.
Scientists measured the transfer of energy from single-celled algae (phytoplankton) to small animals that eat them (zooplankton).
The study - by the University of Exeter and Queen Mary University of London, and published in the journal Nature - found that 4°C of warming reduced energy transfer in the plankton food webs by up to 56%.
Warmer conditions increase the metabolic cost of growth, leading to less efficient energy flow through the ...
Researchers in the Muir Lab at Princeton University's Department of Chemistry have completed the first comprehensive analysis of cancer-associated histone mutations in the human genome, featuring both biochemical and cellular characterizations of these substrates. Their study reports that histone mutations that perturb nucleosome remodeling may contribute to the development or progression of a wide range of human cancers.
Within the human genome, DNA is wrapped around disc-shaped structures made up of eight histone proteins, each forming nucleosomes. Repeating nucleosome units comprise chromatin, a storehouse of genetic information that is both structured and dynamic. Broadly, the Muir Lab seeks to understand how chromatin controls genetic processes in the cell and how disruption ...
MADISON, Wis. -- Grafting neurons grown from monkeys' own cells into their brains relieved the debilitating movement and depression symptoms associated with Parkinson's disease, researchers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison reported today.
In a study published in the journal Nature Medicine, the UW team describes its success with neurons made from induced pluripotent stem cells from the monkeys' own bodies. This approach avoided complications with the primates' immune systems and takes an important step toward a treatment for millions of human Parkinson's patients.
"This result in primates is ...