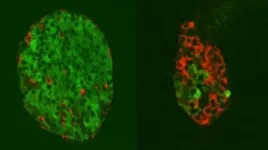
Goodbye UTIs: Duke scientists develop vaccine strategy for urinary tract infections
In tests in mice, the vaccine administered directly to the bladder cleared bacteria
2021-03-01
(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. - Anyone who has ever developed a urinary tract infection (UTI) knows that it can be painful, pesky and persistent. UTIs have a high recurrence rate and primarily afflict women -- as many as 50% of women will experience at least one UTI during their lifetime.
However, what if patients could take a vaccine that would prevent future UTIs? In a March 1 study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Duke researchers describe a new vaccination strategy that they think could re-program the body to fight off the bacteria that cause urinary tract infections.
"Although several vaccines against UTIs have been investigated in clinical trials, they have so far had limited success," said Soman Abraham, Ph.D., Grace Kerby Distinguished Professor of Pathology, Immunology and Molecular Genetics & Microbiology in the School of Medicine and senior author on the paper.
"There are currently no effective UTI vaccines available for use in the U.S. in spite of the high prevalence of bladder infections," Abraham said. "Our study describes the potential for a highly effective bladder vaccine that can not only eradicate residual bladder bacteria, but also prevent future infections."
The strategy, which the team showed to be effective in mouse models, involves re-programming an inadequate immune response that the team identified last year. They observed that when mouse bladders get infected with E. coli bacteria, the immune system dispatches repair cells to heal the damaged tissue, while launching very few warrior cells to fight off the attacker. This causes bacteria to never fully clear, living on in the bladder to attack again.
According to lead author Jianxuan Wu, Ph.D., who recently earned his doctorate from the Department of Immunology at Duke, "the new vaccine strategy attempts to 'teach' the bladder to more effectively fight off the attacking bacteria. By administering the vaccine directly into the bladder where the residual bacteria harbor, the highly effective vaccine antigen, in combination with an adjuvant known to boost the recruitment of bacterial clearing cells, performed better than traditional intramuscular vaccination."
The researchers reported that bladder-immunized mice effectively fought off infecting E. coli and eliminated all residual bladder bacteria, suggesting the site of administration could be an important consideration in determining the effectiveness of a vaccine.
"We are encouraged by these findings, and since the individual components of the vaccine have previously been shown to be safe for human use, undertaking clinical studies to validate these findings could be done relatively quickly," Abraham said.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Abraham and Wu, study authors include Chunjing Bao and R. Lee Reinhardt.
The study received funding support from the National Institutes of Health (R01DK121032 and R01DK121969).
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-01
A new study from Boston Children's Hospital and the Massachusetts Department of Health compared one of the latest rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 -- the Abbott BinaxNOW -- with a highly accurate PCR test in a high-volume, drive-thru testing environment. They found that the rapid test detected almost all adults who tested positive by PCR if they had had symptoms lasting seven days or less. In symptomatic children with less than seven days of symptoms, the test picked up about 85 percent of true positive cases.
But no matter the age, if the patient had high amounts of virus in their nose, the test caught it 99 percent of the time. It was also able to rule out COVID-19 ...
2021-03-01
The human gut consists of a complex community of microbes that consume and secrete hundreds of small molecules--a phenomenon called cross-feeding. However, it is challenging to study these processes experimentally. A new study, published in END ...
2021-03-01
Researchers from Skoltech and the University of Cambridge have shown that polaritons, the quirky particles that may end up running the quantum supercomputers of the future, can form structures behaving like molecules - and these "artificial molecules" can potentially be engineered on demand. The paper outlining these results was published in the journal Physical Review B Letters.
Polaritons are quantum particles that consist of a photon and an exciton, another quasiparticle, marrying light and matter in a curious union that opens up a multitude of possibilities in next-generation polaritonic devices. Alexander Johnston, Kirill Kalinin and Natalia Berloff, professor at the Skoltech Center for Photonics and Quantum Materials ...
2021-03-01
A group of researchers representing four countries summed up the results of the Supertest, a large-scale study of the academic performance of engineering students in Russia, China, India, and the United States. It is the first study to track the progress of students in computer science and electrical engineering over the course of their studies with regard to their abilities in physics, mathematics, and critical thinking and compare the results among four countries. The article about study in Nature Human Behavior.
The HSE Institute of Education played a key role not only in collecting and analyzing data from Russia, ...
2021-03-01
March 1, 2021 - Benign bone tumors may be present in nearly 20 percent of healthy children, based on a review of historical radiographs in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Although that may sound frightening, non-ossifying fibromas and other common benign bone tumors in symptom-free children are harmless and may resolve over time, reports the new study by Christopher D. Collier, MD, of Indiana University School of Medicine and colleagues. "These findings provide unique evidence to answer many commonly encountered questions when counseling patients and their families on benign bone tumors," the researchers write.
Study offers reassurance that benign ...
2021-03-01
Blocking cell receptors for glucagon, the counter-hormone to insulin, cured mouse models of diabetes by converting glucagon-producing cells into insulin producers instead, a team led by UT Southwestern reports in a new study. The END ...
2021-03-01
Boston, MA--Most pregnant women and mothers of children younger than 18 years old say they would receive a COVID-19 vaccine and vaccinate their children, according to a survey conducted by researchers at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. The research indicated that vaccine acceptance was highest in India, the Philippines, and all sampled countries in Latin America, and it was lowest in Russia, the U.S., and Australia.
The results will be published online on March 1, 2021 in the European Journal of Epidemiology.
Vaccines for COVID-19 are being distributed around the world, but until ...
2021-03-01
SILVER SPRING, Md. - A recent preclinical study by U.S. Military HIV Research Program (MHRP) researchers showed that an experimental therapy combining a TLR7 agonist and two broadly neutralizing antibodies delayed viral rebound in SHIV-infected macaques after antiretroviral therapy (ART) interruption.
The experimental combination therapy consisted of TLR7 agonist GS-986 and two broadly neutralizing antibodies (bnAbs), N6-LS and PGT121, targeting different regions of the HIV envelope. The rhesus macaques were initiated on viral suppressive antiretroviral therapy 14 days post infection, a timespan from infection to treatment which mirrors what is feasible in acute HIV infection. Researchers then administered the experimental combination ...
2021-03-01
NEW YORK, NY (March 1, 2021)--By harnessing the immune system against cancer, immunotherapies have revolutionized the way some types of cancer are treated. But most patients--across cancer types--do not respond, and in most cases, scientists are at a loss as to why.
Researchers at Columbia and MIT have created a new technique that can uncover nearly all of the tricks cancer cells use to evade immunotherapies, which could lead to the development of more effective treatments.
The researchers tested their new technique with cancer cells and matching immune cells from melanoma patients and identified previously unknown resistance mechanisms to immune checkpoint ...
2021-03-01
Black Americans have a high level of vaccine hesitancy and mistrust of COVID-19 vaccines, including among Black health care workers, according to a new RAND Corporation survey.
Those who expressed vaccine hesitancy also showed high levels of overall mistrust in the vaccine, concerns about potential harm and side effects, and lack of confidence in vaccine effectiveness and safety.
Participants in the RAND survey reported higher trust in COVID-19 information from health care providers and public health officials than from elected local and federal officials.
The findings are based on a survey ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Goodbye UTIs: Duke scientists develop vaccine strategy for urinary tract infections
In tests in mice, the vaccine administered directly to the bladder cleared bacteria