(Press-News.org) In a study published online February 25, 2021 in The New England Journal of Medicine, a repurposed drug used to treat arthritis did not significantly improve the outcomes of patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia.
Results of the Phase III clinical trial, conducted by an international team led by senior author Atul Malhotra, MD, research chief of pulmonary, critical care and sleep medicine at UC San Diego Health, found that tocilizumab did not significantly improve clinical status or mortality rate at 28 days for participants who received it compared to a placebo.
"Although our trial was negative based on primary outcomes, we did see some benefits, including an improvement in length of stay of eight days with tocilizumab compared to placebo, as well as fewer days on the mechanical ventilator with our intervention," said Malhotra.
"Although it is important to be cautious in interpreting secondary outcomes, our trial helped in the design of subsequent studies which do show some improvement in outcomes with tocilizumab, particularly when given in combination with corticosteroids."
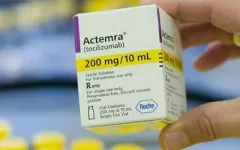
Marketed as Actemra, tocilizumab is an immunosuppressive drug used primarily to treat rheumatoid arthritis and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, a severe form of the disease in children. The therapy works by using humanized monoclonal antibodies to specifically target and block cellular receptors for interleukin-6 (IL-6), a small protein or cytokine that plays an important role in triggering inflammation as an early immune response to disease.
In some patients with COVID-19, the immune response runs amok, overexpressing IL-6 and generating a "cytokine storm," which can lead to potentially life-threatening damage to lungs and other organs. Cytokine storms have been linked to a number of inflammatory diseases, from respiratory conditions caused by coronaviruses such as SARS and MERS to some forms of influenza to non-infectious diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and pancreatitis.
Researchers hoped that the heightened role of IL-6 in respiratory diseases and the fact that many severe cases of COVID-19 involve respiratory failure, hospitalization and death pointed to tocilizumab as a potentially effective therapy. Early case reports and retrospective observational studies buttressed that optimism.
The Phase III clinical trial, which began April 2020 and was conducted in 62 hospitals in nine countries, involved 452 patients with confirmed cases of severe COVID-19 pneumonia, randomized into a group of 294 persons who would receive an intravenous infusion of tocilizumab and 144 persons who received a placebo. Malhotra expressed his gratitude to his team at UC San Diego as well as the countless individuals around the world who helped in the execution of a carefully done study.
The researchers found no significant difference in how the two groups fared, and no reduced mortality rate associated with tocilizumab, though they noted the trial was not designed to fully assess that outcome.
No safety issues arose regarding the use of tocilizumab, and the authors said study data suggested the treatment may have some therapeutic benefit during hospital stays and in shortening stays in intensive care units. In both cases, though, they said more research was required.
"Since this trial launched, a lot has been learned about the virus and about how COVID-19 manifests in different people, in different ways and stages," said Malhotra. "These findings need to be understood in that context. We looked at very sick patients. There are very few proven therapies for severe COVID-19. Tocilizumab and some monoclonal antibody treatments may still have utility in specific circumstances, but more work needs to be done.
"In fact, more work must be done. The need for effective treatments for patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia remains a major challenge of this pandemic. Each new study brings us one step closer to putting that challenge behind us."
INFORMATION:
In early 2020, daily life in Northern China slammed to a halt as the region entered a strict period of lockdown to slow the spread of COVID-19. Emissions from transportation and industry plummeted. Emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) from fossil fuels fell by 60 to 70 percent.
And yet, environmental researchers noticed that ground-level ozone pollution in Beijing and the Northern China Plain skyrocketed during this time period, despite the decrease of NOx, a component of ozone.
The region is no stranger to severe ozone pollution but until about five years ago, most ozone events occurred ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Oregon State University research has revealed a crucial mechanism behind one of humankind's most deadly physiological processes: the movement of malignant cells from one part of the body to another.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the study led by OSU biophysicist Bo Sun shows the role that tissues' microscopic geometry plays in cancer metastasis, the internal spreading of the disease that's responsible for 95% of all cancer deaths.
To develop drugs that effectively combat metastasis, it's fundamentally important to understand what directs the metastatic process, Sun said.
"Our results show the level of tissue fiber alignment, particularly ...
A University of Melbourne led study has established how plants use their metabolism to tell time and know when to grow - a discovery that could help leverage growing crops in different environments, including different seasons, different latitudes or even in artificial environments and vertical gardens.
Published in the PNAS journal, Superoxide is promoted by sucrose and affects amplitude of circadian rhythms in the evening, details how plants use their metabolism to sense time at dusk and help conserve energy produced from sunlight during the day.
Lead ...
DURHAM, N.C. - Anyone who has ever developed a urinary tract infection (UTI) knows that it can be painful, pesky and persistent. UTIs have a high recurrence rate and primarily afflict women -- as many as 50% of women will experience at least one UTI during their lifetime.
However, what if patients could take a vaccine that would prevent future UTIs? In a March 1 study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Duke researchers describe a new vaccination strategy that they think could re-program the body to fight off the bacteria that cause urinary tract infections.
"Although several vaccines against UTIs have been investigated in clinical trials, they have so far had limited success," said Soman Abraham, Ph.D., Grace Kerby Distinguished Professor of Pathology, Immunology ...
A new study from Boston Children's Hospital and the Massachusetts Department of Health compared one of the latest rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 -- the Abbott BinaxNOW -- with a highly accurate PCR test in a high-volume, drive-thru testing environment. They found that the rapid test detected almost all adults who tested positive by PCR if they had had symptoms lasting seven days or less. In symptomatic children with less than seven days of symptoms, the test picked up about 85 percent of true positive cases.
But no matter the age, if the patient had high amounts of virus in their nose, the test caught it 99 percent of the time. It was also able to rule out COVID-19 ...
The human gut consists of a complex community of microbes that consume and secrete hundreds of small molecules--a phenomenon called cross-feeding. However, it is challenging to study these processes experimentally. A new study, published in END ...
Researchers from Skoltech and the University of Cambridge have shown that polaritons, the quirky particles that may end up running the quantum supercomputers of the future, can form structures behaving like molecules - and these "artificial molecules" can potentially be engineered on demand. The paper outlining these results was published in the journal Physical Review B Letters.
Polaritons are quantum particles that consist of a photon and an exciton, another quasiparticle, marrying light and matter in a curious union that opens up a multitude of possibilities in next-generation polaritonic devices. Alexander Johnston, Kirill Kalinin and Natalia Berloff, professor at the Skoltech Center for Photonics and Quantum Materials ...
A group of researchers representing four countries summed up the results of the Supertest, a large-scale study of the academic performance of engineering students in Russia, China, India, and the United States. It is the first study to track the progress of students in computer science and electrical engineering over the course of their studies with regard to their abilities in physics, mathematics, and critical thinking and compare the results among four countries. The article about study in Nature Human Behavior.
The HSE Institute of Education played a key role not only in collecting and analyzing data from Russia, ...
March 1, 2021 - Benign bone tumors may be present in nearly 20 percent of healthy children, based on a review of historical radiographs in The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio in partnership with Wolters Kluwer.
Although that may sound frightening, non-ossifying fibromas and other common benign bone tumors in symptom-free children are harmless and may resolve over time, reports the new study by Christopher D. Collier, MD, of Indiana University School of Medicine and colleagues. "These findings provide unique evidence to answer many commonly encountered questions when counseling patients and their families on benign bone tumors," the researchers write.
Study offers reassurance that benign ...
Blocking cell receptors for glucagon, the counter-hormone to insulin, cured mouse models of diabetes by converting glucagon-producing cells into insulin producers instead, a team led by UT Southwestern reports in a new study. The END ...