(Press-News.org) Since 1970, bird populations in North America have declined by approximately 2.9 billion birds, a loss of more than one in four birds. Factors in this decline include habitat loss and ecosystem degradation from human actions on the landscape.
At the same time, enthusiasm for bird-watching has grown, with more than 45 million recreational participants in the United States alone. Now, researchers are looking into how to mobilize these bird enthusiasts to help limit bird population declines.
Enter bird-friendly coffee.
Bird-friendly coffee is certified organic, but its impact on the environment goes further than that: it is cultivated specifically to maintain bird habitats instead of clearing vegetation that birds and other animals rely on.
Researchers from Virginia Tech's College of Natural Resources and Environment, Cornell University, and Columbia University explored whether bird-friendly coffee is on the radar of bird-watchers: are they drinking it and, if not, why not? The study results published in the journal People and Nature.
"We know bird-watchers benefit from having healthy, diverse populations of birds, and they tend to be conservation-minded folks," explained Assistant Professor Ashley Dayer of Virginia Tech's Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation. "My colleagues and I wanted to dig into this key audience to determine their interest in bird-friendly coffee."
Bird-friendly coffee is shade-grown, meaning that it is grown and harvested under the canopy of mature trees, a process that parallels how coffee was historically grown. But with most farms in Central and South America and the Caribbean converting to full-sun operations, crucial bird habitats for migrating and resident bird species are being lost.
"Over recent decades, most of the shade coffee in Latin America has been converted to intensively managed row monocultures devoid of trees or other vegetation," explained Amanda Rodewald, the Garvin Professor and senior director of the Center for Avian Population Studies at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology. "As a result, many birds cannot find suitable habitats and are left with poor prospects of surviving migration and successfully breeding."
Purchasing shade-grown coffee is one of seven simple actions that people can take as a step toward returning bird populations to their previous numbers. "But even simple actions are sometimes not taken by people who you would expect to be on board. Human behavior is complex -- driven by knowledge, attitudes, skills, and many other factors," explained Dayer, an affiliate of the Global Change Center housed in Virginia Tech's Fralin Life Sciences Institute.
The research team surveyed more than 900 coffee-drinking bird-watchers to understand bird-friendly coffee behavior among bird-watchers.
"One of the most significant constraints to purchasing bird-friendly coffee among those surveyed was a lack of awareness," said Alicia Williams, lead author and former research assistant at the Cornell Lab of Ornithology and Virginia Tech. "This includes limits on understanding what certifications exist, where to buy bird-friendly coffee, and how coffee production impacts bird habitat."
"I was surprised to see that only 9 percent of those surveyed purchased bird-friendly coffee and less than 40 percent were familiar with it," Williams added. "It was also interesting, though not surprising, that a large number of our respondents reported that the flavor or aroma of coffee was an important consideration in their coffee purchases, which could be a useful attribute of bird-friendly coffee to stress going forward."
The next step to increasing awareness about shade-grown coffee and its potential impact on bird populations may include increased advertising for bird-friendly coffee, more availability of bird-friendly coffee, and collaborations between public-facing conservation organizations and coffee distributors.
INFORMATION:
A new paper in Oxford Open Materials Science, published by Oxford University Press, presents low cost modifications to existing N95 masks that prolongs their effectiveness and improves their reusability post disinfectants.
The COVID-19 crisis has increased demand for respiratory masks, with various models of DIY masks becoming popular alongside the commercially available N95. The utility of such masks is primarily based on the size of aerosols that they are capable of filtering out and how long they can do so effectively.
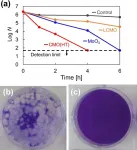
Conventional masks like the N95 use a layered system and have an efficiency ...
Researchers at Tokyo Institute of Technology working in collaboration with colleagues at the Kanagawa Institute of Industrial Science and Technology and Nara Medical University in Japan have succeeded in preparing a material called cerium molybdate (γ-Ce2Mo3O13 or CMO), which exhibits high antiviral activity against coronavirus.
The ongoing coronavirus pandemic has highlighted the urgency not only of vaccine development and rollout but also of developing innovative materials and technologies with antiviral properties that could play a vital role in helping to contain the spread of the virus.
Conventional inorganic antimicrobial materials are often prepared with metals such as copper or photocatalysts ...
Peer Reviewed
Experimental
Animals
Consumption of a high fat diet may be activating a response in the heart that is causing destructive growth and lead to greater risk of heart attacks, according to new research.
In a paper published in Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, researchers looked at the effect of feeding mice a high fat diet on oxidative stress levels on heart cells. The team from the University of Reading found that cells from the mice had twice the amount of oxidative stress, and led to heart cells being up to 1.8 times bigger due to cardiac hypertrophy which is associated with heart disease.
Named first author Dr Sunbal Naureen ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New technology from Purdue University innovators may help improve tissue restoration outcomes for people with breast cancer and other diseases or traumatic injuries.
Purdue researchers, along with fellowship-trained breast surgeon Carla Fisher of Indiana University School of Medicine, teamed up with Purdue startup GeniPhys to develop and perform preclinical studies on a regenerative tissue filler.
This is a first-of-a-kind, in situ scaffold-forming collagen. When applied as a filler for soft tissue defects and voids, it shows promise for accelerating and improving tissue restoration outcomes. The team's work is published in Scientific Reports.
"It ...
The Acheulean was estimated to have died out around 200,000 years ago but the new findings suggest it may have persisted for much longer, creating over 100,000 years of overlap with more advanced technologies produced by Neanderthals and early modern humans.
The research team, led by Dr Alastair Key (Kent) alongside Dr David Roberts (Kent) and Dr Ivan Jaric (Biology Centre of the Czech Academy of Sciences), made the discovery whilst studying stone tool records from different regions across the world. Using statistical techniques new to archaeological science, the archaeologists and conservation experts were able to reconstruct the end of the Acheulean period and re-map the archaeological record.
Previously, a more rapid shift between the earlier Acheulean stone ...
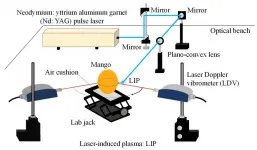
Most people are probably familiar with the unpleasant feeling of eating overripe or underripe fruit. Those who work in agriculture are tasked with ensuring a timely harvest so that ripeness is at an optimal point when the fruit is sold, both to minimize the amount of fruit that goes to waste and maximize the quality of the final product. To this end, a number of techniques to assess fruit ripeness have been developed, each with their respective advantages and disadvantages depending on the type of produce.
Although biochemical and optical methods exist, mechanical techniques are the most widely used. They indirectly assess ripeness based on the fruit's firmness. In turn, firmness ...
Scientists have discovered a previously unknown breeding site used by the world's rarest seal species.
The Mediterranean monk seal is classified as "endangered", with a total population of about 700.
The new study - by the University of Exeter and the Society for the Protection of Turtles (SPOT) - used camera-traps to confirm breeding in caves in northern Cyprus, with at least three pups born from 2016-19 at one cave.
Only certain caves are suitable for monk seal breeding and resting, so - although the numbers are small - the researchers say urgent action is needed to protect these caves.
"This area of coastline in being developed rapidly, especially for ...
The anti-inflammatory drug hydroxychloroquine should not be used to prevent infection in people who do not have covid-19, say a WHO Guideline Development Group (GDG) panel of international experts in The BMJ today.
Their strong recommendation is based on high certainty evidence from six randomised controlled trials involving over 6,000 participants with and without known exposure to a person with covid-19 infection.
High certainty evidence showed that hydroxychloroquine had no meaningful effect on death and admission to hospital, while moderate certainty evidence showed that hydroxychloroquine had no meaningful effect on laboratory confirmed covid-19 infection and it probably increases the risk of adverse effects.
As such, ...
LOS ANGELES -- COVID-19 has taken a huge medical, emotional and economic toll on Americans. Now, new Keck Medicine of USC research shows that the pandemic may also have harmful indirect consequences.
Alcohol and tobacco sales nationwide rose in the early months of COVID-19, according to a study appearing in the Annals of Internal Medicine today. From April - June 2020, researchers found that sales of these substances increased 34% and 13% respectively when compared to the same months in 2019.
"These are significant jumps, and show that the stress, boredom and loneliness caused by the pandemic may have led to increased alcohol and tobacco ...
GALVESTON, Texas -A team from The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston (UTMB) focused on drug addiction research have pioneered a new way to study frustration as a factor in substance use disorders. The study was published in the medical journal Psychopharmacology.
Traditional addiction research has focused on three aspects of substance use disorders: craving, impulsivity, or habit. Scientists hypothesized that a fourth factor, frustration, could also lead to escalation of drug use and addiction.
The Psychopharmacology paper noted that research into the role of frustration and substance use disorders ...