University launches isolated power supply chip with new design
2021-03-02
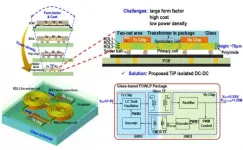
(Press-News.org) Recently, research group led by Professor CHENG Lin from School of Microelectronics, University of science and technology of China has made significant achievements in the field of fully integrated isolated power chip design. They proposed a chip based on glass fan-out wafer-level package (FOWLP), achieving 46.5% peak transformation efficiency and 50mW/mm2 power density.
Compared with the traditional isolated power supply chip, this new design interconnects the receiving and transmitting chips through the micro transformer made of the rewiring layer, showing no need of additional transformer chips. In this way, it lowered the need for three or even four chips in the existing chip design, so as to greatly improve the efficiency of isolated power supply.
In addition, they proposed a grid voltage control technology with variable capacitor, which maintains the grid peak voltage in the best safe voltage range even in a wider supply voltage range.
This design improves the conversion efficiency and power density of the chip effectively, providing a new solution for the design of isolated power chip in the future.
INFORMATION:
This work is published at IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), known as the Olympic Games in the field of integrated circuit design, and selected as demo demonstration at the meeting.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-02
The pandemic has impacted significantly on people who suffer chronic pain. A study performed by the eHealth Lab, a research group affiliated with the Faculty of Health Sciences and the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya's eHealth Center, has shown that 70% of the people with chronic pain have seen their condition worsen in terms of severity, frequency of episodes and interference in their daily activities.
A total of 502 patients took part in the study; 88% were women aged between 30 and 59, with long-duration chronic pain (mean duration, 7 years). Most participants (87.6%) had pain in more than one point; the most frequent locations were the abdomen, lower back and neck. The participants answered online surveys, designed in accordance with ...
2021-03-02
Organometallic reagents are essential tools in synthetic chemistry. They work even better and more effectively in combination with alkali alkoxides. The exact nature of this effect has never been well understood. A team based in Switzerland has now performed a detailed study of the mechanism of reaction of aryl bromides with organo-magnesium reagents and lithium alkoxides. As reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie, a complex equilibrium of bimetallic intermediates plays a key role.
Substituted aromatic ring systems are an important class of building block for the synthesis of many products, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and ...
2021-03-02
Recently, the Laboratory of Micro and Nano Engineering, School of Engineering Science, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) has made important progress in the field of structural chirality detection research using vortex light and found that photon orbital angular momentum can efficiently detect the optical chiral signal of structures.
The achievement was published in an international well-known journal PNAS.
Chiral structures are widely found in nature, such as DNA double helix structures, plant tendrils and shells. In addition to observing the geometry of objects, their chirality can also be distinguished by the interaction of light with matter. For example, the detection of circular ...
2021-03-02
Aqueous free-radical precipitation polymerization is one of the most useful methods to prepare the uniformly sized hydrogel microspheres (microgels), and an understanding of the polymerization mechanism is crucial to control the structure or physicochemical properties of microgels. However, the details of the mechanism of precipitation polymerization remain unclear.
Thus, first author Yuichiro Nishizawa, Prof. Daisuke Suzuki of the Graduate School of Textile Science & Technology, Shinshu University and Prof. Takayuki Uchihashi of Nagoya University set out to clarify the formation mechanism of microgels during precipitation polymerization by evaluating structural evolution and thermoresponsiveness of developing microgels during ...
2021-03-02
The study examined the gender and affiliations of 1051 top-authors, those scientists with the most publications in 13 leading ecology and conservation journals. The results show that women and the Global South are barely represented on this list. "The overall list of top authors included only 11% women, while 75% of the articles were related to just five countries in the Global North," says Bea Maas, lead author from the University of Vienna. "This massive imbalance in scientific authorship is extremely concerning, especially in the field of ecology and conservation, ...
2021-03-02
The formation of double bonds between two carbon atoms (C=C) is of central significance in natural organisms. The vast majority of natural substances therefore contain one or more of these double bonds. Compounds with C=C double bonds, the alkenes or olefins, also play a prominent role in the organic chemical industry. A great many chemical processes have therefore been developed over the years to control the formation of C=C bonds.
One such process, olefin metathesis, has received particular attention over the last few decades and the 2005 Nobel Prize for Chemistry was awarded in recognition of its significance.
Despite the many ...
2021-03-02
A technological and biological development that is unprecedented in Israel and the world has been achieved at Tel Aviv University. For the first time, the ear of a dead locust has been connected to a robot that receives the ear's electrical signals and responds accordingly. The result is extraordinary: When the researchers clap once, the locust's ear hears the sound and the robot moves forward; when the researchers clap twice, the robot moves backwards.
The interdisciplinary study was led by Idan Fishel, a joint master student under the joint supervision of Dr. Ben M. Maoz of the Iby and Aladar Fleischman ...
2021-03-02
Removal of pollutants from the air, or atmospheric deposition, is a natural cleaning mechanism. However, the removed toxic matters don't just disappear on the Earth. China's Soil Pollution Survey released in 2014 shows that 19.4% of the Chinese farmland soil was polluted and 82% of pollutant was toxic heavy metals such as cadmium, which can cause chronic health problems.
Atmospheric deposition is an important source of these heavy metals in the soil but it tends to be neglected. Unlike sources from irrigation water, sewage sludge, fertilizers and livestock manures, atmospheric deposition can't easily be perceived. And the paucity of measurements also makes it difficult to track what ...
2021-03-02
Currently, the roles of free D-amino acids and D-amino acid residues in proteins are garnering extensive attention in biological fields such as molecular biology, physiology, microbiology, and pathophysiology. Because it is crucial to analyze these materials rapidly and accurately, many methods have been employed. However, samples for measurement are currently limited to solutions containing target molecules in the pure form. Hence, there is need for an analytical method for the in situ measurement of biological samples placed on a solid support.
We report the construction of a multidimensional ...
2021-03-02
Earth's surface environments are highly oxygenated - from the atmosphere to the deepest reaches of the oceans, representing a hallmark of active photosynthetic biosphere. However, the fundamental timescale of the oxygen-rich atmosphere on Earth remains uncertain, particularly for the distant future. Solving this question has great ramifications not only for the future of Earth's biosphere but for the search for life on Earth-like planets beyond the solar system.
A new study published in Nature Geoscience this week tackles this problem using a numerical model of biogeochemistry and climate and reveals that the future lifespan ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] University launches isolated power supply chip with new design