INFORMATION:
The expanding possibilities of bio-based polymers
Researchers from the Kleij group present a new route to prepare biobased polyesters with tuneable properties
2021-03-02
(Press-News.org) Finding innovative and sustainable solutions to our material needs is one of the core objectives of green chemistry. The myriad plastics that envelop our daily life - from mattresses to food and cars - are mostly made from oil-based monomers which are the building blocks of polymers. Therefore, finding bio-based monomers for polymer synthesis is attractive to achieve more sustainable solutions in materials development.
In a paper published in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, researchers from the Kleij group present a new route to prepare biobased polyesters with tuneable properties. The researchers are building upon the multifunctional structure of the terpene β-elemene: three double bonds which have distinct reactivity, allowing to selectively transform these bonds and thus tweaking the functionalities in the backbone of the polymer. "This multi-functional terpene scaffold is rather unique and allows to fine-tune structural diversity and prospectively to modulate polymer and material properties," explains Arjan Kleij, ICIQ group leader and ICREA professor.
In collaboration with the company Isobionics, the researchers utilised β-elemene obtained through an innovative sugar-fermentation route. This process has proved to be a promising start for the use of β-elemene as a raw material for polymerisation. "Isobionic's sugar-fermentation route completely changes the scale of β-elemene availability, which now can be used in polymer production," explains Francesco Della Monica, postdoctoral researcher in the Kleij group working in the European SUPREME project, an MSCActions Individual Fellowship and first author of the paper.
Via a ring-opening copolymerisation reaction (ROCOP), the researchers combined β-elemene oxides and phthalic anhydride (a common monomer used in the preparation of polyesters) to create the biobased linear polymer poly(BEM-alt-PA) and its related structure, crosslinked-poly(BED-alt-PA). These transformations were achieved with catalytic systems (iron and aluminium aminotriphenolate complexes combined with bis-(triphenylphosphine) iminium chloride) developed previously by the group using non-critical, abundant elements for catalytic polymerisation.
Once the polyester is prepared, there are two remaining double bonds from the original terpene building block that can be easily and selectively addressed and functionalised, allowing to tailor the final polyester. "These post-modification reactions on a biobased polymer are quite rare. Most of the biobased monomers that are available don't present functionalities," remarks Della Monica.
The paper is a starting point for further development of β-elemene based polymers that allow tailoring the properties of the final material (depending on its use) through easy post-polymerisation modifications. The paper does not address the biodegradation of the material, although for Della Monica, "depending on the final use, the ideal thing may not be biodegradation but to create a recyclable polymer: i.e., take a starting material, create the polymer, use it, recover it, and then degrade it in a controlled fashion and reuse that material. Now that we have the idea of a circular economy within grasp, we need circular processes," concludes the scientist.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Here's how insects coax plants into making galls
2021-03-02
Insects can reprogram plant growth, transforming ordinary plant parts into intricately patterned shelters that are safe havens for feeding and reproduction.
These structures, called galls, have fascinated biologists for centuries. They're crafted by a variety of insects, including some species of aphids, mites, and wasps. And they take on innumerable forms, each specific in shape and size to the insect species that's created it - from knobs to cone-shaped protrusions to long, thin spikes. Some even resemble flowers.
Insects create galls by manipulating the development of plants, but figuring out exactly how they perform this feat "feels like ...
Mammal ancestors moved in their own unique way
2021-03-02
The backbone is the Swiss Army Knife of mammal locomotion. It can function in all sorts of ways that allows living mammals to have remarkable diversity in their movements. They can run, swim, climb and fly all due, in part, to the extensive reorganization of their vertebral column, which occurred over roughly 320 million years of evolution.
Open any anatomy textbook and you'll find the long-standing hypothesis that the evolution of the mammal backbone, which is uniquely capable of sagittal (up and down) movements, evolved from a backbone that functioned ...
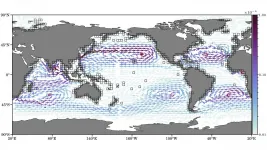
How does plastic debris make its way into ocean garbage patches?
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- Tons of plastic debris get released into the ocean every day, and most of it accumulates within the middle of garbage patches, which tend to float on the oceans' surface in the center of each of their regions. The most infamous one, known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, is in the North Pacific Ocean.
Researchers in the U.S. and Germany decided to explore which pathways transport debris from the coasts to the middle of the oceans, as well as the relative strengths of different subtropical gyres in the oceans and how they influence long-term accumulation of debris.
In Chaos, from AIP Publishing, Philippe Miron, Francisco Beron-Vera, Luzie Helfmann, and Peter Koltai report creating a Markov chain ...
Association between COVID-19 lockdown measures, ED visits for violence-related injuries in Wales
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: This study investigates emergency department visits for violence-related injuries occurring at home and outside the home in Cardiff, Wales, before and after COVID-19 lockdown measures were instituted in March 2020.
Authors: Jonathan P. Shepherd, Ph.D., Crime and Security Research Institute at Cardiff University in Wales, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.25511)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Belly fat resistant to every-other-day fasting: study
2021-03-02
In a mouse study, Australian researchers have mapped out what happens behind the scenes in fat tissue during intermittent fasting, showing that it triggers a cascade of dramatic changes, depending on the type of fat deposits and where they are located around the body.
Using state-of-the-art instruments, University of Sydney researchers discovered that fat around the stomach, which can accumulate into a 'protruding tummy' in humans, was found to go into 'preservation mode', adapting over time and becoming more resistant to weight loss.
The findings are published today in Cell Reports.
A research team led by Dr Mark Larance examined fat tissue types from different locations to understand their role during every-other-day fasting, ...
Study reveals impact of lockdown on violence in a UK capital city
2021-03-02
The first UK COVID-19 lockdown saw a "rapid and sustained" fall in violence outside the home in the Welsh capital city, a new study led by Cardiff University has shown.
Researchers from Cardiff University's Crime and Security Research Institute (CSRI) and the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention studied data from Cardiff's sole emergency department (ED) from March to June 2020 and compared it to weekly data from January 2019 onwards.
They found there were almost 60% fewer attendances per week for violent injury outside the home in the first lockdown during ...
Complex fluid dynamics may explain hydroplaning
2021-03-02
WASHINGTON, March 2, 2021 -- When a vehicle travels over a wet or flooded road, water builds up in front of the tire and generates a lift force. In a phenomenon known as hydroplaning, this force can become large enough to lift the vehicle off the ground.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, scientists from the CNRS, the University of Lyon, and The Michelin Group use a laser imaging technique to study water flow in front of and through tire grooves.
To counteract hydroplaning, tread designs are chosen to drain water from the front of the tire without decreasing its ability to adhere to the road. Very few quantitative experimental studies of the movement of water through tire grooves have been done, so little is known about the exact flow patterns in ...
Assessment of hotel-based COVID-19 isolation, quarantine strategy for people experiencing homelessness
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: This study suggests that, during the COVID-19 pandemic, a hotel- based isolation and quarantine strategy that delivers integrated medical and behavioral health support to people experiencing homelessness can be done safely outside the hospital setting.
Authors: Jonathan D. Fuchs, M.D., M.P.H., of the San Francisco Department of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0490)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest ...
Assessment of respiratory function in infants, young children wearing face masks during COVID-19 pandemic
2021-03-02
What The Study Did: Wearing surgical face masks for 30 minutes was not associated with changes in respiratory parameters or clinical signs of respiratory distress in this study of 47 infants and young children in Italy.
Authors: Silvia Bloise, M.D., of Sapienza University of Rome in Italy, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0414)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and ...
Requests for brand name over generic prescription drugs cost the Medicare program $1.7 billion in a single year, study finds
2021-03-02
The Medicare Part D program would have saved $977 million in a single year if all branded prescription drugs requested by prescribing clinicians had been substituted by a generic option, according to a new study by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. And if Medicare patients had requested generic drugs instead of brand name drugs, the Medicare Part D program would have saved an additional $673 million in one year, for a total savings of $1.7 billion.
Medicare Part D offers supplemental outpatient drug coverage plans for seniors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] The expanding possibilities of bio-based polymersResearchers from the Kleij group present a new route to prepare biobased polyesters with tuneable properties