Ultrasonic cleaning of salad could reduce instances of food poisoning
2021-03-02
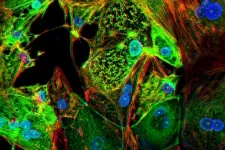
(Press-News.org) A new study has shown that gentle streams of water carrying sound and microscopic air bubbles can clean bacteria from salad leaves more effectively than current washing methods used by suppliers and consumers. As well as reducing food poisoning, the findings could reduce food waste and have implications for the growing threat of anti-microbial resistance.
Salad and leafy green vegetables may be contaminated with harmful bacteria during growing, harvesting, preparation and retail leading to outbreaks of food poisoning which may be fatal in vulnerable groups.
Because there is no cooking process to reduce the microbial load in fresh salads, washing is vital by the supplier and the consumer.
Washing with soap, detergent bleach or other disinfectants is not recommended and the crevices in the leaf surface means washing with plain water may leave an infectious dose on the leaf. Even if chemicals are used, they may not penetrate the crevices.
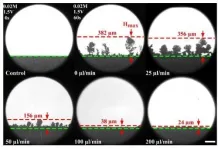
In this new study, published in the journal Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, scientists used acoustic water streams to clean spinach leaves directly sourced from the field crop, then compared the results with leaves rinsed in plain water at the same velocity.
Professor Timothy Leighton of the University of Southampton, who invented the technology and led this research, explains: "Our streams of water carry microscopic bubbles and acoustic waves down to the leaf. There the sound field sets up echoes at the surface of the leaves, and within the leaf crevices, that attract the bubbles towards the leaf and into the crevices. The sound field also causes the walls of the bubbles to ripple very quickly, turning each bubble into a microscopic 'scrubbing' machine. The rippling bubble wall causes strong currents to move in the water around the bubble, and sweep the microbes off the leaf. The bacteria, biofilms, and the bubbles themselves, are then rinsed off the leaf, leaving it clean and free of residues."
The results showed that the microbial load on samples cleaned with the acoustic streams for two minutes was significantly lower six days after cleaning than on those treated without the added sound and bubbles. The acoustic cleaning also caused no further damage to the leaves and demonstrated the potential to extend food shelf life, which has important economic and sustainability implications.
Improving how food providers clean fresh produce could have a major role to play in combating the threat of anti-microbial resistance. In 2018 and 2019, there were fatal outbreaks of different strains of E. coli on romaine lettuce in the USA and Canada and samples from humans infected showed strains that are resistant to antibiotics.
University of Southampton PhD student Weng Yee (Beverly) Chong, who was part of the research team added: "I am very grateful to Vitacress and EPSRC for funding my PhD. I came from an engineering background, and took Professor Leighton's classes, but he told me that I could be a trans-disciplinary PhD student, and become a microbiologist whilst increasingmy engineering skills. I am also very grateful to Sloan Water Technology Ltd.: They opened up their laboratories for use by students like me, so that I can keep working on my experiments. It is an exciting environment to work in because they are doing so much inventive work to combat the pandemic and infections as a whole."
Previously as part of her PhD Beverly has studied how the technology could reduce the infection risk to horses and other livestock through hay cleaning.
The work was sponsored by Vitacress, whose Group Technical Director Helen Brierley said: "Ensuring food safety for our products is an essential requirement. At Vitacress, we wash our produce in natural spring water, and this type of ground-breaking new technology helps to enhance our process whilst ensuring our commitment to protect the environment is maintained. We are always interested in new developments and are excited to see the results of this research".
INFORMATION:
The research project was a collaboration between Sloan Water Technology Limited, Vitacress and the University of Southampton, a collaboration formed and supported by Global-NAMRIP (the Global Network for Antimicrobial Resistance and Infection Prevention).
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-02
Healthcare sex discrimination protections for the LGBTQ community may be expanded under the Biden Administration, including safeguards against verbal abuse, physical abuse and the denial of bedside care, according to West Virginia University College of Law experts.
In a report published in California Law Review, Professor Valarie Blake and students Ashley Stephens and Amy Post examined whether gender identity and sexual orientation should be included in healthcare sex discrimination laws, on the heels of the historic 2020 Supreme Court case Bostock v. Clayton County.
In that case, the Court ruled that sex discrimination includes gender identity and sexual orientation when it comes to employment standards. Yet the interpretation of whether ...
2021-03-02
Scientists at the University of Bath in the UK have found a way to bind together two photons of different colours, paving the way for important advancements in quantum-electrodynamics - the field of science that describes how light and matter interact. In time, the team's findings are likely to impact developments in optical and quantum communication, and precision measurements of frequency, time and distances.
APPLE AND WAVE: THEY BOTH HAVE A MASS
An apple falling from a tree has velocity and mass, which together give it momentum. 'Apple energy' derived from motion depends on the fruit's momentum and mass.
Most people find ...
2021-03-02
Volcanic basalt rocks in the Black Rock Desert, Utah.
If you drive south through central Utah on Interstate 15 and look west somewhere around Fillmore, you'll see smooth hills and fields of black rock. The area is, aptly, named the Black Rock Desert. It may not look like much, but you're looking at some of Utah's volcanoes.
A pair of earthquake sequences, in September 2018 and April 2019, focused scientists' attention on the Black Rock Desert. The sequences, which included the main quakes and their aftershocks, were very different from the Magna earthquake that shook the Wasatch Front in 2020 and other Utah earthquakes. The Black Rock sequences were captured ...
2021-03-02
Since early in the pandemic, COVID-19 has been associated with heart problems, including reduced ability to pump blood and abnormal heart rhythms. But it's been an open question whether these problems are caused by the virus infecting the heart, or an inflammatory response to viral infection elsewhere in the body. Such details have implications for understanding how best to treat coronavirus infections that affect the heart.
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis provides evidence that COVID-19 patients' heart damage ...
2021-03-02
Positive psychological effects associated with taking small doses of psychedelic drugs are likely the result of users' expectations, suggests a study published today in eLife.
The study - the largest placebo-controlled trial on psychedelics to date - used an innovative 'self-blinding citizen science' approach, where members of the public who were already microdosing implemented their own placebo control following online instructions. The results from the trial may influence future studies in real-world settings.
There has been renewed interest in studying whether psychedelic drugs may be a useful treatment for depression, addiction, obsessive-compulsive disorders and other conditions. Few small studies have previously suggested that microdoses ...
2021-03-02
A new paper from associate professor Jiandi Wan's group in the UC Davis Department of Chemical Engineering, published in Science Advances, proposes a potential solution to dendrite growth in rechargeable lithium metal batteries. In the paper, Wan's team prove that flowing ions near the cathode can potentially expand the safety and lifespans of these next-generation rechargeable batteries.
Lithium metal batteries use lithium metal as the anode. These batteries have a high charge density and potentially double the energy of conventional lithium ion batteries, but safety is a big concern. When they charge, some ions are reduced to lithium ...
2021-03-02
In a new study from Shiley Eye Institute at UC San Diego Health, researchers have identified a potential new marker that shows cardiovascular disease may be present in a patient using an optical coherence tomography (OCT) scan -- a non-invasive diagnostic tool commonly used in ophthalmology and optometry clinics to create images of the retina. The finding suggests it may be possible to detect heart disease during an eye examination.
In the paper published March 2, 2021 in EClinical Medicine by The Lancet, the research team examined lesions of the retina, the inner-most, light-sensitive layer of the eye, to determine if a cardiovascular disorder may be present.
"The eyes are a window into our health, and many diseases can manifest in the eye; cardiovascular ...
2021-03-02
NEW YORK, NY--March 2, 2021--In March and April 2020, mental health claim lines for individuals aged 13-18, as a percentage of all medical claim lines, approximately doubled over the same months in the previous year. At the height of the spring wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, this rise in mental health claim lines amounted to 97.0 percent in March and 103.5 percent in April. These are among the many findings in FAIR Health's new white paper, the seventh in its COVID-19 studies, The Impact of COVID-19 on Pediatric Mental Health: A Study of Private Healthcare Claims.
In those same months of March and April 2020, all medical claim lines (including mental health claim lines) decreased by approximately ...
2021-03-02
When it comes to the evolution of the mammal spine -- think of animals whose backbone allows them to gallop, hop, swim, run, or walk upright -- a key part of the tale is quite simple.
Because nonmammalian synapsids, the extinct forerunners to mammals, had similar traits to living reptiles (like having their limbs splayed out to the side instead of tucked into their body like today's mammals), the strongheld belief was that they must have also moved in similar ways. Primarily, their backbones must have moved side-to-side, bending like those of modern lizards, instead of the up-and-down bending motion mammal spines are known for. It's believed over time, and in response to selective pressures, the mammal spine evolved from that lizard like side-to-side bending ...
2021-03-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- By modeling wolves in Yellowstone National Park, researchers have discovered that how a population is organized into social groups affects the spread of infectious diseases within the population. The findings may be applicable to any social species and could be useful in the protection of endangered species that suffer from disease invasion.
Like other social carnivores, wolves tend to form territorial social groups that are often aggressive toward each other and may lead to fatalities. During these encounters, infectious diseases -- like mange and canine distemper -- can spread between groups, which can further reduce the number of individuals in a group.
"Previous social group-disease models have assumed that groups do not change ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ultrasonic cleaning of salad could reduce instances of food poisoning