(Press-News.org) On Earth, plate tectonics is not only responsible for the rise of mountains and earthquakes. It is also an essential part of the cycle that brings material from the planet's interior to the surface and the atmosphere, and then transports it back beneath the Earth's crust. Tectonics thus has a vital influence on the conditions that ultimately make Earth habitable.
Until now, researchers have found no evidence of global tectonic activity on planets outside our solar system. A team of researchers led by Tobias Meier from the Center for Space and Habitability (CSH) at the University of Bern and with the participation of ETH Zurich, the University of Oxford and the National Center of Competence in Research NCCR PlanetS has now found evidence of the flow patterns inside a planet, located 45 light-years from Earth: LHS 3844b. Their results were published in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
An extreme contrast and no atmosphere
"Observing signs of tectonic activity is very difficult, because they are usually hidden beneath an atmosphere", Meier explains. However, recent results suggested that LHS 3844b probably does not have an atmosphere. Slightly larger than Earth and likely similarly rocky, it orbits around its star so closely that one side of the planet is in constant daylight and the other in permanent night - just like the same side of the Moon always faces the Earth. With no atmosphere shielding it from the intense radiation, the surface gets blisteringly hot: it can reach up to 800°C on the dayside. The night side, on the other hand, is freezing. Temperatures there might fall below minus 250°C. "We thought that this severe temperature contrast might affect material flow in the planet's interior", Meier recalls.
To test their theory, the team ran computer simulations with different strengths of material and internal heating sources, such as heat from the planet's core and the decay of radioactive elements. The simulations included the large temperature contrast on the surface imposed by the host star.
Flow inside the planet from one hemisphere to the other
"Most simulations showed that there was only upwards flow on one side of the planet and downwards flow on the other. Material therefore flowed from one hemisphere to the other", Meier reports. Surprisingly, the direction was not always the same. "Based on what we are used to from Earth, you would expect the material on the hot dayside to be lighter and therefore flow upwards and vice versa", co-author Dan Bower at the University of Bern and the NCCR PlanetS explains. Yet, some of the teams' simulations also showed the opposite flow direction. "This initially counter-intuitive result is due to the change in viscosity with temperature: cold material is stiffer and therefore doesn't want to bend, break or subduct into the interior. Warm material, however, is less viscous - so even solid rock becomes more mobile when heated - and can readily flow towards the planet's interior", Bower elaborates. Either way, these results show how a planetary surface and interior can exchange material under conditions very different from those on Earth.
A volcanic hemisphere
Such material flow could have bizarre consequences. "On whichever side of the planet the material flows upwards, one would expect a large amount of volcanism on that particular side", Bower points out. He continues "similar deep upwelling flows on Earth drive volcanic activity at Hawaii and Iceland". One could therefore imagine a hemisphere with countless volcanoes - a volcanic hemisphere so to speak - and one with almost none.
"Our simulations show how such patterns could manifest, but it would require more detailed observations to verify. For example, with a higher-resolution map of surface temperature that could point to enhanced outgassing from volcanism, or detection of volcanic gases. This is something we hope future research will help us to understand", Meier concludes.
Bernese space exploration: With the world's elite since the first moon landing
When the second man, "Buzz" Aldrin, stepped out of the lunar module on July 21, 1969, the first task he did was to set up the Bernese Solar Wind Composition experiment (SWC) also known as the "solar wind sail" by planting it in the ground of the moon, even before the American flag. This experiment, which was planned and the results analysed by Prof. Dr. Johannes Geiss and his team from the Physics Institute of the University of Bern, was the first great highlight in the history of Bernese space exploration.
Ever since Bernese space exploration has been among the world's elite. The numbers are impressive: 25 times were instruments flown into the upper atmosphere and ionosphere using rockets (1967-1993), 9 times into the stratosphere with balloon flights (1991-2008), over 30 instruments were flown on space probes, and with CHEOPS the University of Bern shares responsibility with ESA for a whole mission.
The successful work of the Department of Space Research and Planetary Sciences (WP)from the Physics Institute of the University of Bern was consolidated by the foundation of a university competence center, the Center for Space and Habitability (CSH). The Swiss National Fund also awarded the University of Bern the National Center of Competence in Research (NCCR) PlanetS, which it manages together with the University of Geneva.
INFORMATION:
Female gannets travel further than male gannets to find fish for their chicks in some years but not others, new research shows.
Scientists tracked breeding gannets from Grassholm Island in Wales over 11 years with tiny GPS devices and by measuring isotopic signatures in their blood.
Male gannets flew an average of 220km to forage for their chicks, while females averaged 260km. Some birds travelled 1,000km on a single trip.
The scientists also found that the two sexes selected different habitats and foraged at different times of day, but some years ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Putting a price on producing carbon is the cheapest, most efficient policy change legislators can make to reduce emissions that cause climate change, new research suggests.
The case study, published recently in the journal Current Sustainable/Renewable Energy Reports, analyzed the costs and effects that a variety of policy changes would have on reducing carbon dioxide emissions from electricity generation in Texas and found that adding a price, based on the cost of climate change, to carbon was the most effective.
"If the goal is reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, what we found is that putting a price on carbon and then letting suppliers and consumers make their ...
In order to show the clinical relevance of a difference between two treatment alternatives, in recent years, the manufacturer dossiers submitted in early benefit assessments of new drugs have increasingly contained responder analyses for patient-relevant outcomes. In such analyses, it is investigated whether the proportion of patients experiencing a noticeable change in the respective outcome differs between the two treatment groups in a study. This involves information on health-related quality of life or on individual symptoms such as pain or itching, which patients recorded with the help of scales in questionnaires.
But what difference makes a change relevant for the individual? That is, at what threshold can a response to an intervention be derived for ...
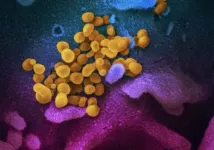
A deep sequencing study of 747 SARS-CoV-2 virus isolates has revealed mutant peptides derived from the virus that cannot effectively bind to critical proteins on the surface of infected cells and, in turn, hamper activation of CD8+ killer T cells that recognize and destroy these infected cells. These peptides, the authors say, represent one way the coronavirus subverts killer T cell responses and stymies immunity in the host. Their results may be of particular importance for SARS-CoV-2 subunit vaccines, such as the RNA vaccines currently in use, which induce responses against a limited number of viral ...
There are no therapeutics available that have been developed for COVID-19 treatment. Repurposing of already available medication for COVID-19 therapy is an attractive option to shorten the road to treatment development. The drug Camostat could be suitable. Camostat exerts antiviral activity by blocking the protease TMPRSS2, which is used by SARS-CoV-2 for entry into cells. However, it was previously unknown whether SARS-CoV-2 can use TMPRSS2-related proteases for cell entry and whether these proteases can be blocked by Camostat. Moreover, it was unclear whether metabolization of Camostat interferes with antiviral activity. An international team of researchers around Markus Hoffmann and Stefan Pöhlmann ...
Solving a Genetic Mystery at the Heart of the COVID-19 Pandemic
As the COVID-19 pandemic enters its second year, scientists are still working to understand how the new strain of coronavirus evolved, and how it became so much more dangerous than other coronaviruses, which humans have been living alongside for millennia.
Virologists and epidemiologists worldwide have speculated for months that a protein called ORF8 likely holds the answer, and a recent study by Berkeley Lab scientists has helped confirm this hypothesis.
In a paper published in mBio, lead author Russell Neches and his colleagues ...
By embedding a silver catalyst inside a porous crystal, KAUST researchers have improved a chemical reaction that converts carbon dioxide (CO2) into carbon monoxide (CO), which is a useful feedstock for the chemical industry.
Carbon monoxide is a building block for producing hydrocarbon fuels, and many researchers are searching for ways to produce it from CO2, a greenhouse gas emitted by burning fossil fuels. One strategy involves using electricity and a catalyst to drive a so-called CO2 reduction reaction. But this reaction typically produces a variety of other products, including methane, methanol and ethylene. Separating these products significantly raises the cost of the process, ...
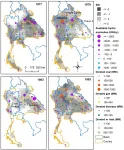
A study on big droughts in the Greater Mekong region revealed findings that can help reduce the carbon footprint of power systems while providing insights into better designed and more sustainable power plants.
The study, titled 'The Greater Mekong's climate-water-energy nexus: how ENSO-triggered regional droughts affect power supply and CO2 emissions', was published by researchers from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) and the University of California, Santa Barbara, in the journal Earth's Future.
Known as an important means to support economic growth in Southeast Asia, the hydropower resources of the Mekong River Basin have been largely exploited by the riparian countries. The researchers ...
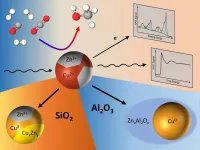
The current commercial production of methanol through the hydrogenation of the green-house gas CO2 relies on a catalyst consisting of copper, zinc oxide and aluminum oxide. Even though this catalyst has been used for many decades in the chemical industry, unknowns still remain. A team of researchers from the Interface Science Department of the Fritz-Haber-Institute of the Max Planck Society, the Ruhr-University Bochum, Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), FZ Juelich and Brookhaven National Laboratory have now elucidated the origin of intriguing catalytic activity and selectivity trends of complex nanocatalysts ...
In 2015, hackers infiltrated the corporate network of Ukraine's power grid and injected malicious software, which caused a massive power outage. Such cyberattacks, along with the dangers to society that they represent, could become more common as the number of cyber-physical systems (CPS) increases.
A CPS is any system controlled by a network involving physical elements that tangibly interact with the material world. CPSs are incredibly common in industries, especially those integrating robotics or similar automated machinery to the production line. However, as CPSs make their way into societal infrastructures such as public transport and energy management, it becomes even more important to ...