After old age, intellectual disability is greatest risk factor for death from COVID-19
A study of national data shows the devastating impact the pandemic has had on those with intellectual disabilities and their caregivers.
2021-03-05
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA - Intellectual disability puts individuals at higher risk of dying earlier in life than the general population, for a variety of medical and institutional reasons. A new study from Jefferson Health examined how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected this group, which makes up 1-3% of the US population. The study, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) Catalyst, found that intellectual disability was second only to older age as a risk factor for dying from COVID-19.
"The chances of dying from COVID-19 are higher for those with intellectual disability than they are for people with congestive heart failure, kidney disease or lung disease," says lead author Jonathan Gleason, MD, the James D. and Mary Jo Danella Chief Quality Officer for Jefferson Health. "That is a profound realization that we have not, as a healthcare community, fully appreciated until now."
The authors examined 64 million patient records from 547 healthcare organizations between January 2019 to November 2020 to understand the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on patients with intellectual disabilities. They identified variables such as COVID-19, intellectual disability or other health conditions, as well as demographic factors such as age.
The results showed that those with intellectual disabilities were 2.5 times more likely to contract COVID-19, were about 2.7 times more likely to be admitted to the hospital and 5.9 times more likely to die from the infection than the general population.
"Our failure to protect these deeply vulnerable individuals is heart-breaking," says co-author Wendy Ross, MD, a developmental and behavioral pediatrician and director for the Center for Autism and Neurodiversity at Jefferson Health. "I believe that if we can design a system that is safe and accessible for people with intellectual disabilities, it will benefit all of us."
The authors write that patients with intellectual disabilities may have less ability to comply with strategies that reduce the risk of infection, such as masking and social distancing. In addition, the researchers showed that these patients are more likely to have additional health conditions that contribute to a more severe course of COVID-19 disease. The results of the study highlight how these issues become compounded in this population.
"We need to understand more about what is happening with these patients," says Dr. Gleason. "I do believe these patients and their caregivers should be prioritized for vaccination and healthcare services. We should reflect on why we have failed this vulnerable population, and how we can better serve them during this health crisis, and into the future," Dr. Gleason says. "Even prior to the pandemic, individuals with intellectual disabilities have had poor health outcomes. We need to do much better."
The authors suggest key action steps that require a rapid response. "First, those with intellectual disabilities and their caregivers should be prioritized for vaccines by organizations that set federal guidelines, including the CDC," says Dr. Gleason. "Second, federal and state healthcare regulatory offices should measure access, quality and safety in this population in order to track our ability to improve health outcomes for these patients. Finally, the United States should redesign the care model for individuals with intellectual disabilities."
"As an organization deeply committed to advocating for the health of one of the most marginalized populations - those with intellectual disabilities (ID) - we have seen the need for people with ID to be prioritized as a high-risk group during this pandemic. It's devastating to hear that people with ID are almost six times more likely to die from COVID-19," said Alicia Bazzano, MD, PhD, MPH, Chief Health Officer of the Special Olympics. "Most health authorities do not recognize that people with ID who get COVID-19 have a much higher risk of dying. Special Olympics is grateful to the Jefferson team for shining a spotlight on these devastating numbers."
INFORMATION:
Article Reference: Jonathan Gleason, Wendy Ross, Alexander Fossi, Heather Blonsky, Jane Tobias, Mary Stephens, "The Devastating Impact of COVID-19 on individuals with intellectual disabilities in the United States," NEJM Catalyst, DIO: 10.1056/CAT.21.0051, 2021.
Media Contact:
Edyta Zielinska,
267-234-3553,
edyta.zielinska@jefferson.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-05
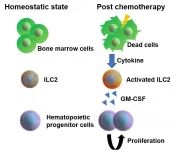
Osaka, Japan - Chemotherapy has a damaging effect on hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) in bone marrow. However, once chemotherapy ends, HSPCs regenerate, a process that has remained unknown--until now. In a new study, researchers from Osaka University have identified the molecular mechanism by which HSPCs recover after injury.
HSPCs reside in the bone marrow and give rise to several types of blood cells, such as red blood cells (which carry oxygen), some white blood cells (which are important for the immune system) and platelets (which are necessary to stop bleeding). Because HSPCs constantly divide to generate new cells, they are particularly sensitive to injury induced by, for example, chemotherapy. ...
2021-03-05
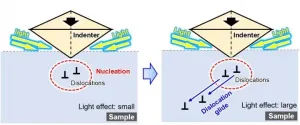
Semiconductor materials play an indispensable role in our modern information-oriented society. For reliable performance of semiconductor devices, these materials need to have superior mechanical properties: they must be strong as well as resistant to fracture, despite being rich in nanoscale structures.
Recently, it has become increasingly clear that the optical environment affects the structural strength of semiconductor materials. The effect can be much more significant than expected, especially in light-sensitive semiconductors, and particularly since due to technological constraints ...
2021-03-05
Background: Although caregivers of patients with eating disorders usually experience a heavy caregiving burden, the effects of social support on caregivers of patients with eating disorders are unknown. This study aimed to investigate how social support for mothers who are caregivers of patients with an eating disorder improves the mothers' mental status and, consequently, the symptoms and status of the patients.
Methods: Fifty-seven pairs of participants were recruited from four family self-help groups and one university hospital in Japan. Recruitment was conducted from July 2017 to August 2018. Mothers were ...
2021-03-05
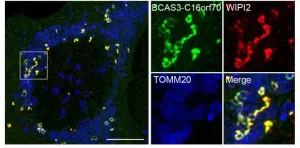
Autophagy is an intracellular degradation process of cytosolic materials and damaged organelles. Researchers at Ubiquitin Project of TMIMS have been studying the molecular mechanism of mitophagy, the selective autophagy process to eliminate damaged mitochondria. PINK1 (a serine/threonine kinase) and Parkin (a ubiquitin ligating enzyme: E3) work together to ubiquitylate the outer membrane proteins of damaged mitochondria, then ubiquitin chains are recognized as signals for autophagy degradation. Dysfunction of mitophagy causes a decrease in mitochondrial quality with overproduction of ROS, and is linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's disease.
In Autophagy machinery, cellular components targeted for degradation are engulfed by phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PI3P)-rich ...
2021-03-05
Frequently occurring chronic skin inflammation like in atopic dermatitis (AD or neurodermatitis) and psoriasis have different causes such as genetic predisposition, stress or allergens. These frequently occurring skin diseases are mostly attributed by biomedical scientists to a disturbed immune system, although the noticeable thickening and flaking of the epidermis, which is the outermost layer of skin, also indicates a disruption of the epithelial cells. A team of researchers from the University Clinic for Dermatology and the Clinical Institute for Laboratory Medicine at MedUni Vienna has now been able to identify new molecular ...
2021-03-05
WHO: Giovanni Traverso, MB, BChir, PhD, Associate Physician, Division of Gastroenterology, Brigham and Women's Hospital; corresponding author of a new article published in JAMA Network Open.
Peter Chai, MD, MMS, Assistant Professor, Department of Emergency Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital; first author.
WHAT: In the age of COVID-19, mobile robotic telehealth systems could help clinicians and patients interact without contact. Last spring, some health care systems deployed robotic systems within a hospital to evaluate and interact with patients. In a JAMA Network Open article, Traverso and colleagues report the results of a national survey and a cohort study in an emergency department (ED), which analyzed patients' satisfaction with an initial evaluation ...
2021-03-05
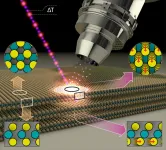
MoS2 thin films of superposed alternating layers of molybdenum and sulfur atoms form a two-dimensional semiconducting surface. However, even a surprisingly low-intensity blue light pulse is enough to alter the properties of the surface and make it metallic. This has now been demonstrated by a team at BESSY II.
The exciting thing is that the MoS2 layers in this metallic phase are also particularly active catalytically. They can then be employed, for example, as catalysts for splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen. As inexpensive catalysts, they could facilitate the production of hydrogen - an energy ...
2021-03-05
Approximately 15-to-30 percent of patients with metastatic breast cancer have brain metastasis (BM), with basal-like breast cancer (BLBC) metastasizing to the brain most frequently. The prognosis for BLBC-BM patients is poor, as the blood-brain barrier prevents most therapeutics from reaching the brain. Testing candidate therapies in clinical trials is also challenging because animal models that mimic BM are limited. In a new study, researchers from Brigham and Women's Hospital and collaborators engineered a bimodal tumor-suppressing and killing molecule that can be delivered to the brain by stem cells. They tested ...
2021-03-05
Beijing, 26 February 2021: the journal Cardiovascular Innovations and Applications (CVIA) has just published the third issue of Volume 5. This issue brings together important research from authors in the USA and China, including several important papers concerned with the various cardiological implications of COVID-19.
Papers in the issue are as follows.
RESEARCH PAPERS
Diyu Cui, Yimeng Liao, Jianlin Du and Yunqing Chen
A Meta-analysis of Major Complications between Traditional Pacemakers and Leadless Pacemakers
(http://ow.ly/CgYO30rz3eA)
Yue Wu, Guoyue Zhang, Rong Hu and Jianlin Du
Risk of Target Organ Damage in Patients with Masked Hypertension versus
Sustained Hypertension: A Meta-analysis (http://ow.ly/x63E30rzjEp)
Jing Li, Lijie Sun, Fang Wang, Bing Liu, Hui Li, Guodong ...
2021-03-05
If you stretch an elastic band, it becomes thinner - a physical behavior that applies to most "common" materials. Since the 20th century, an opposite behavior has been known in materials research: The so-called auxetic (from ancient Greek auxetos, meaning 'stretchable') materials expand in the direction orthogonal to the strain. Likewise, they shrink when they are compressed. Scientifically, they are characterized by a negative Poisson's ratio. Probably the best known and oldest application of unusual Poisson's ratios is the bottle cork, which has a Poisson's ratio of zero. This has the effect that the cork ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] After old age, intellectual disability is greatest risk factor for death from COVID-19
A study of national data shows the devastating impact the pandemic has had on those with intellectual disabilities and their caregivers.