Cultural values and demographics impact COVID-19 pandemic
2021-03-05
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, have collaborated on two studies examining the socioeconomic factors involved in the spread of COVID-19.
Professor Alex Bentley and postdoctoral fellow Damian Ruck, both from the Department of Anthropology, joined Josh Borycz, a librarian at Vanderbilt University, to conduct the studies.
"One of our studies considers the global scale of nations and the other uses the national scale for US counties to analyze results during 2020," explained Bentley.
The studies show that the numbers of COVID-19 cases and deaths are significantly affected by the cultural values and demographics of local or national populations.
"Local and national leaders have to work within the parameters set by the values and demographics of their constituents. Top-down government decisions are important, but bottom-up effects from the population matter too," added Ruck.
For the US, researchers were able to use the abundance of county-level data to help predict the true number of COVID-19 infections at a given time. This is important because cases were severely underestimated in early 2020. The model identifies the five most predictive factors as population size, population density, public transportation use, percentage of the population that is African American, and Democrat election vote share.
The researchers' work shows how measuring relatively stable features of society, such as culture and demographics, can help predict the spread of COVID-19. As such factors will change little over the course of a pandemic, this information could help in planning for the deployment of scarce resources in future pandemics.
INFORMATION:
The study "Cultural values predict national COVID-19 death rates" was published in Springer Nature Social Sciences. "Early warning of vulnerable counties in a pandemic using socio-economic variables" was published in Economics and Human Biology.
CONTACT
Amanda Womac (865-974-2992, awomac1@utk.edu)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-05
Two thirds of children use more than one screen at the same time after school, in the evenings and at weekends as part of increasingly sedentary lifestyles, according to new research at the University of Leicester.
An NIHR study of more than 800 adolescent girls between the ages of 11 and 14 identified worrying trends between screen use and lower physical activity - including higher BMI - as well as less sleep.
The use of concurrent screens (termed 'screen stacking') grew over the course of the week - with 59% of adolescents using two or more screens after school, 65% in the evenings, and 68% at weekends.
Some teens reporting using as many as four screens at one time.
But further analysis showed the use of any screen was still detrimental to the indicators ...
2021-03-05
A new study from the University of Iowa sought to begin development of a possible approach to reduce the risk that college-aged men engage in sexually aggressive acts or risky sexual behavior.
The study authors, led by Teresa Treat, professor in the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences at Iowa, developed a 12-point list of sexual assault prevention strategies. The list was created by the researchers based on previous research into risk factors that are associated with sexually aggressive acts--such as heavy alcohol consumption, difficulties reading women's cues, and not seeking consent for sexual activity.
The authors found that 71% of the college-aged men surveyed used the sexual assault prevention strategies on a regular basis over the past year. Yet 15% of the ...
2021-03-05
DANVILLE, Pa. - A team of scientists from Geisinger and Tempus have found that artificial intelligence can predict risk of new atrial fibrillation (AF) and AF-related stroke.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with numerous health risks, including stroke and death. The study, published in Circulation, used electrical signals from the heart--measured from a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG)--to identify patients who are likely to develop AF, including those at risk for AF-related stroke.
"Each year, over 300 million ...
2021-03-05
A new review of existing evidence proposes eight hallmarks of environmental exposures that chart the biological pathways through which pollutants contribute to disease: oxidative stress and inflammation, genomic alterations and mutations, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, endocrine disruption, altered intercellular communication, altered microbiome communities, and impaired nervous system function.
The study by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, Ludwig Maximilian University, and Hasselt University is published in the journal Cell.
"Every day we learn ...
2021-03-05
Patients' electronic health records convey crucial information. The application of natural language processing techniques to these records may be an effective means of extracting information that may improve clinical decision making, clinical documentation and billing, disease prediction and the detection of adverse drug reactions. Adverse drug reactions are a major health problem, resulting in hospital re-admissions and even the death of thousands of patients. An automatic detection system can highlight said reactions in a document, summarise them and automatically report them.
In this context, the Basurto University Hospital and the Galdakao ...
2021-03-05
A monoclonal antibody "cocktail" developed at Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) to neutralize the COVID-19 virus is effective against all known strains, or variants, of the virus, according to a report published in the journal Nature Medicine.
That was one of the findings reported by a multi-institutional team led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
In cell-culture studies, the researchers determined the ability of monoclonal antibodies as well as antibodies isolated from the "convalescent plasma" of previously infected people to neutralize highly transmissible variants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that have arisen in the United Kingdom, South Africa, Brazil and elsewhere.
In general, most of the monoclonal antibodies that have ...
2021-03-05
Can Switzerland, as planned, cut its CO2 emissions to zero by 2050? In a study, researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have investigated what measures would be necessary to achieve this reduction and how much it might cost per person.
In August 2019, the Swiss Federal Council decided on an ambitious target to limit climate change: From the year 2050 onward Switzerland should, on balance, discharge no further greenhouse gas emissions. With this commitment, Switzerland meets the internationally agreed goal of limiting global warming to a maximum of 1.5° C compared to the pre-industrial era.
Now a study by the Paul Scherrer Institute, ...
2021-03-05
Functioning ecosystems provide the basis for security, basic material needs, health, social interaction and individual liberty. This is how the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment 2005 described it, dividing ecosystem services into the following categories: The provisioning services; goods such as food, water, firewood and timber, the regulating services; pollination, water filtering function of the soil, flood and erosion protection, and the cultural services; recreation, places of inspiration, and education. Many of these services are indirectly and directly linked to the presence of species. For this reason, species conservation is often put forward as a measure for the conservation of vital natural services.
"However, most previous ...
2021-03-05
PHILADELPHIA - Intellectual disability puts individuals at higher risk of dying earlier in life than the general population, for a variety of medical and institutional reasons. A new study from Jefferson Health examined how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected this group, which makes up 1-3% of the US population. The study, published today in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) Catalyst, found that intellectual disability was second only to older age as a risk factor for dying from COVID-19.
"The chances of dying from COVID-19 are higher for those with intellectual disability than they are for people with congestive heart failure, kidney disease or lung disease," says lead author Jonathan Gleason, MD, the James D. and Mary Jo Danella ...
2021-03-05
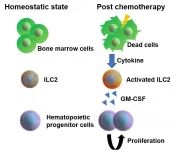
Osaka, Japan - Chemotherapy has a damaging effect on hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) in bone marrow. However, once chemotherapy ends, HSPCs regenerate, a process that has remained unknown--until now. In a new study, researchers from Osaka University have identified the molecular mechanism by which HSPCs recover after injury.
HSPCs reside in the bone marrow and give rise to several types of blood cells, such as red blood cells (which carry oxygen), some white blood cells (which are important for the immune system) and platelets (which are necessary to stop bleeding). Because HSPCs constantly divide to generate new cells, they are particularly sensitive to injury induced by, for example, chemotherapy. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cultural values and demographics impact COVID-19 pandemic