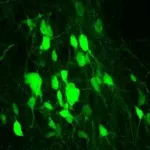
(Press-News.org) Using genetic engineering, researchers at UT Southwestern and Indiana University have reprogrammed scar-forming cells in mouse spinal cords to create new nerve cells, spurring recovery after spinal cord injury. The findings, published online today in Cell Stem Cell, could offer hope for the hundreds of thousands of people worldwide who suffer a spinal cord injury each year.
Cells in some body tissues proliferate after injury, replacing dead or damaged cells as part of healing. However, explains study leader END
Putting a protein into overdrive to heal spinal cord injuries
Scar-forming cells that overproduce the protein SOX2 made new neurons, improving recovery in mice
2021-03-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Outcomes, mortality among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 at US medical centers
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: The objectives of this study were to examine the characteristics and outcomes among adults hospitalized with COVID-19 at U.S. medical centers and analyze changes in mortality over the initial six months of the pandemic.
Authors: Ninh T. Nguyen, M.D., of the University of California, Irvine Medical Center, in Orange, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0417)
Editor's Note: The article includes ...
Racial/ethnic disparities in autism
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: Survey data were used to estimate changes in racial/ethnic disparities in rates of autism spectrum disorder among U.S. children and adolescents from 2014 through 2019.
Authors: Z. Kevin Lu, Ph.D., of the University of South Carolina in Columbia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0771)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed ...
Health care use among undocumented patients
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: Researchers examined the association of increased anti-immigrant rhetoric during the 2016 presidential campaign with changes in the use of health care services among undocumented patients.
Authors: Joseph Nwadiuko, M.D., M.P.H., M.S.H.P., of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0763)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article ...
Neurologic involvement in children, adolescents hospitalized in US for COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome
2021-03-05
What The Study Did: In this study, many children and adolescents hospitalized for COVID-19 or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children had neurologic involvement, mostly transient symptoms. A range of life-threatening and fatal neurologic conditions associated with COVID-19 infrequently occurred. Effects on long-term neurodevelopmental outcomes are unknown.
Authors: Adrienne G. Randolph, M.D., of Boston Children's Hospital, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2021.0504)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest ...
Antibiotic-resistant strains of staph bacteria may be spreading between pigs raised in factory farms
2021-03-05
DNA sequencing of bacteria found in pigs and humans in rural eastern North Carolina, an area with concentrated industrial-scale pig-farming, suggests that multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains are spreading between pigs, farmworkers, their families and community residents, and represents an emerging public health threat, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
S. aureus is commonly found in soil and water, as well as on the skin and in the upper respiratory tract in pigs, other animals, and people. It can cause medical problems from minor skin infections to serious surgical wound infections, pneumonia, and the often-lethal blood-infection condition known as sepsis. The findings provide evidence that multidrug-resistant ...
Cultural values and demographics impact COVID-19 pandemic
2021-03-05
Researchers from the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, have collaborated on two studies examining the socioeconomic factors involved in the spread of COVID-19.
Professor Alex Bentley and postdoctoral fellow Damian Ruck, both from the Department of Anthropology, joined Josh Borycz, a librarian at Vanderbilt University, to conduct the studies.
"One of our studies considers the global scale of nations and the other uses the national scale for US counties to analyze results during 2020," explained Bentley.
The studies show that the numbers of COVID-19 cases and deaths are significantly affected ...
Research identifies impact of teenage screen use
2021-03-05
Two thirds of children use more than one screen at the same time after school, in the evenings and at weekends as part of increasingly sedentary lifestyles, according to new research at the University of Leicester.
An NIHR study of more than 800 adolescent girls between the ages of 11 and 14 identified worrying trends between screen use and lower physical activity - including higher BMI - as well as less sleep.
The use of concurrent screens (termed 'screen stacking') grew over the course of the week - with 59% of adolescents using two or more screens after school, 65% in the evenings, and 68% at weekends.
Some teens reporting using as many as four screens at one time.
But further analysis showed the use of any screen was still detrimental to the indicators ...
Research may offer another avenue to tackling sexually aggressive behavior
2021-03-05
A new study from the University of Iowa sought to begin development of a possible approach to reduce the risk that college-aged men engage in sexually aggressive acts or risky sexual behavior.
The study authors, led by Teresa Treat, professor in the Department of Psychological and Brain Sciences at Iowa, developed a 12-point list of sexual assault prevention strategies. The list was created by the researchers based on previous research into risk factors that are associated with sexually aggressive acts--such as heavy alcohol consumption, difficulties reading women's cues, and not seeking consent for sexual activity.
The authors found that 71% of the college-aged men surveyed used the sexual assault prevention strategies on a regular basis over the past year. Yet 15% of the ...
Researchers find AI can predict new atrial fibrillation, stroke risk
2021-03-05
DANVILLE, Pa. - A team of scientists from Geisinger and Tempus have found that artificial intelligence can predict risk of new atrial fibrillation (AF) and AF-related stroke.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common cardiac arrhythmia and is associated with numerous health risks, including stroke and death. The study, published in Circulation, used electrical signals from the heart--measured from a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG)--to identify patients who are likely to develop AF, including those at risk for AF-related stroke.
"Each year, over 300 million ...
Eight ways chemical pollutants harm the body
2021-03-05
A new review of existing evidence proposes eight hallmarks of environmental exposures that chart the biological pathways through which pollutants contribute to disease: oxidative stress and inflammation, genomic alterations and mutations, epigenetic alterations, mitochondrial dysfunction, endocrine disruption, altered intercellular communication, altered microbiome communities, and impaired nervous system function.
The study by researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health, Ludwig Maximilian University, and Hasselt University is published in the journal Cell.
"Every day we learn ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
Tibet ASγ experiment sheds new light on cosmic rays acceleration and propagation in Milky Way
AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Hope for Rett syndrome: New research may unlock treatment pathway for rare disorder with no cure
How some skills become second nature
SFU study sheds light on clotting risks for female astronauts
UC Irvine chemists shed light on how age-related cataracts may begin
Machine learning reveals Raman signatures of liquid-like ion conduction in solid electrolytes
Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia researchers emphasize benefits and risks of generative AI at different stages of childhood development
Why conversation is more like a dance than an exchange of words
With Evo 2, AI can model and design the genetic code for all domains of life
Discovery of why only some early tumors survive could help catch and treat cancer at very earliest stages
Study reveals how gut bacteria and diet can reprogram fat to burn more energy
Mayo Clinic researchers link Parkinson's-related protein to faster Alzheimer's progression in women
Trends in metabolic and bariatric surgery use during the GLP-1 receptor agonist era
Loneliness, anxiety symptoms, depressive symptoms, and suicidal ideation in the all of us dataset
A decision-support system to personalize antidepressant treatment in major depressive disorder
Thunderstorms don’t just appear out of thin air - scientists' key finding to improve forecasting
Automated CT scan analysis could fast-track clinical assessments
New UNC Charlotte study reveals how just three molecules can launch gene-silencing condensates, organizing the epigenome and controlling stem cell differentiation
Oldest known bony fish fossils uncover early vertebrate evolution
High‑performance all‑solid‑state magnesium-air rechargeable battery enabled by metal-free nanoporous graphene
[Press-News.org] Putting a protein into overdrive to heal spinal cord injuriesScar-forming cells that overproduce the protein SOX2 made new neurons, improving recovery in mice