INFORMATION:
Hybrid microbes: Genome transfer between different bacteria strains explored
2021-03-08
(Press-News.org) Bacteria integrate genetic material from other bacterial strains more easily than previously thought, which can lead to improved fitness and accelerated evolution. This is shown in a recent study by biophysicists at the University of Cologne. The team analysed genome transfer between bacteria of different lineages. The study was published in the journal PNAS.
In the experiment, the team brought one strain of bacteria into contact with DNA fragments from another strain. The uptake of foreign genetic material is known as horizontal gene transfer -- in contrast to vertical gene transfer, by which genes are inherited from a parent cell of the same lineage. The results show that laboratory evolution through horizontal gene transfer can rapidly produce hybrid organisms of different lineages with extensive genomic and functional changes. "It is a bit like interbreeding modern humans and Neandertals'", says Dr. Fernanda Pinheiro of the Institute of Biological Physics at the University of Cologne and author of the study. The bacteria readily integrated foreign DNA at many sites in the genome. Within 200 generations, the research team observed the exchange of up to 14 percent of the bacterium's core genes.
Horizontal gene transfer is an important factor in bacterial evolution that can operate across species boundaries. "Yet we know little about the rate and genomic targets of cross-strain gene transfer. Also, little is known so far about the effects on the physiology and fitness of the recipient organism", says Pinheiro. From a scientific perspective, hybrid creatures whose parents belong to different species raise fundamental evolutionary biology questions: What combinations of traits yield viable organisms? What are the limits of evolutionary processes when more than one species is involved in reproduction? "Our study makes an important contribution here," Pinheiro adds.
Is the uptake of genes random or does it follow a definite pattern? As the researchers observed, some functional units of the foreign genome were repeatedly imported and the resulting hybrid bacteria had higher growth rates. "This implies that cross-lineage gene exchange drives evolution very efficiently," Pinheiro says. Integrating foreign genes through horizontal gene transfer produces new combinations of genes yet preserves essential structures that make a cell viable. Thus, the study opens new perspectives for future work: to combine transfer evolution experiments and synthetic biology methods to engineer functional innovations.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Hospital-based violence intervention program engages vulnerable populations
2021-03-08
DES PLAINES, IL - A Boston violence intervention advocacy program is effectively engaging the client population that hospital-based violence intervention programs (HVIPs) have been designed to support. This is the conclusion of a study titled Boston Violence Intervention Advocacy Program: Challenges and Opportunities for Client Engagement and Goal Achievement, to be published in the March 2021 issue of Academic Emergency Medicine (AEM), a journal of the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine (SAEM).
According to the study, HVIPs should consider which types of client needs prove most challenging to address and which novel strategies will engage vulnerable populations not typically targeted by intervention programs. ...
Unique sensor network for measuring greenhouse gases
2021-03-08
The sensor network MUCCnet (Munich Urban Carbon Column network) consists of five high-precision optical instruments that analyze the sun's light spectra. They measure the concentration of the gases carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and carbon monoxide (CO). Since each gas has its own unique spectral "fingerprint", concentrations of these gases can be determined in the columns of air between the instruments and the sun.
"By measuring a vertical column of the atmosphere, local disturbances, such as the disproportionate influence of neighboring stacks, can be removed. Therefore, this type of greenhouse gas balancing is considered particularly robust and accurate," says Prof. Jia Chen.
Measurements at five locations in and around Munich
One of MUCCnet's measurement devices is ...
Study highlights barriers for women and marginalized groups in supramolecular chemistry
2021-03-08
A new study by the international network Women In Supramolecular Chemistry (WISC) has highlighted the equality, diversity and inclusion (EDI) issues faced by women and marginalised groups working within that field.
The network has also set out a 'calling in' approach to address these issues.
The study, led by Dr Jennifer Leigh and Dr Jennifer Hiscock (both University of Kent) alongside WISC's wider team of international researchers, found that both men and women in the supramolecular community wanted to see more mentoring opportunities and more visibility for women and marginalised groups. There is a desire for more guidance during the transition from postdoctoral researcher to independent Principal Investigator, to ensure women can be retained ...
No more sitting in the dark?
2021-03-08
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) - Concussion, a form of traumatic brain injury, is a common injury among children and teens. Concussions can have adverse effects on physical, cognitive, emotional and sleep health. Clinical guidelines for managing concussion in children and teens traditionally recommend complete physical and cognitive rest until symptom resolution, followed by a gradual return to activities like school and sports. These guidelines are often disputed and based on expert consensus as opposed to strong evidence. The challenge has been how to quantify the amount of physical and cognitive activity that children and teens should engage in during recovery. A new study by researchers at the Center for ...
Latest research delineates the effectiveness of "quitlines" for smoking cessation
2021-03-08
While cigarette smoking continues to be the leading cause of preventable disease, disability and death in the U.S., the evidence base for cessation support has revealed that telephone call centers, or "quitlines," have been a particularly successful intervention, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), which recently published a compilation of scientific research in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Titled "The Role of Quitlines in Tobacco Cessation," the supplement is composed of nine peer-reviewed articles and three commentaries presenting the latest science on quitlines' effectiveness for smoking termination. The compilation demonstrates the relevance and importance of call ...
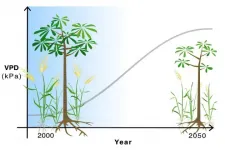
Atmospheric drying will lead to lower crop yields, shorter trees across the globe
2021-03-08
A global observation of an ongoing atmospheric drying -- known by scientists as a rise in vapor pressure deficit -- has been observed worldwide since the early 2000s. In recent years, this concerning phenomenon has been on the rise, and is predicted to amplify even more in the coming decades as climate change intensifies.
In a new paper published in the journal Global Change Biology, research from the University of Minnesota and Western University in Ontario, Canada, outlines global atmospheric drying significantly reduces productivity of both crops and non-crop plants, even under well-watered conditions. The new findings were established on a large-scale analysis covering 50 years of research and 112 plant species.
"When there ...
The impact of lockdown drives us to make poorer choices
2021-03-08
Lockdown and other restrictions imposed to control the COVID-19 pandemic have had unseen negative effects on the cognitive capacity and mental health of the population. A study led by the UOC's research group Open Evidence, in collaboration with international universities and BDI Schlseinger Group Market Research, has gauged the impact of the measures taken during the first and second waves of the virus on citizens of three European Union countries. The study concludes that the shock produced by the situation has reduced people's cognitive capacity, leading them to take more risks, ...
A giant, sizzling planet may be orbiting the star Vega
2021-03-08
Astronomers have discovered new hints of a giant, scorching-hot planet orbiting Vega, one of the brightest stars in the night sky.
The research, published this month in The Astrophysical Journal, was led by University of Colorado Boulder student Spencer Hurt, an undergraduate in the Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences.
It focuses on an iconic and relatively young star, Vega, which is part of the constellation Lyra and has a mass twice that of our own sun. This celestial body sits just 25 light-years, or about 150 trillion miles, from Earth--pretty close, astronomically speaking.
Scientists can also see Vega with telescopes even when it's light out, which makes ...
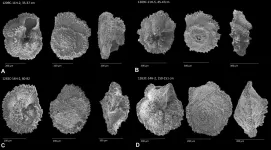
Oceans were stressed preceding abrupt, prehistoric global warming
2021-03-08
Microscopic fossilized shells are helping geologists reconstruct Earth's climate during the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), a period of abrupt global warming and ocean acidification that occurred 56 million years ago. Clues from these ancient shells can help scientists better predict future warming and ocean acidification driven by human-caused carbon dioxide emissions.
Led by Northwestern University, the researchers analyzed shells from foraminifera, an ocean-dwelling unicellular organism with an external shell made of calcium carbonate. After analyzing the calcium isotope composition of the fossils, the researchers concluded that massive volcanic activity injected large amounts of carbon dioxide into the Earth system, causing global warming and ocean acidification.
They ...
The amazing promise of artificial intelligence in health care
2021-03-08
Artificial intelligence can already scan images of the eye to assess patients for diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of vision loss, and to find evidence of strokes on brain CT scans. But what does the future hold for this emerging technology? How will it change how doctors diagnose disease, and how will it improve the care patients receive?
A team of doctors led by UVA Health's James H. Harrison Jr., MD, PhD, has given us a glimpse of tomorrow in a new article on the current state and future use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the field of pathology. Harrison and other members of the College of American Pathologists' Machine Learning ...