New teamwork model could improve patient health care
2021-03-08
(Press-News.org) HOUSTON - (March 8, 2021) - Health care teams must prepare for anything, including the unconventional work environments brought about by a global pandemic and social unrest.
Multiracial medical team having a discussion as they stand grouped together around a tablet computer on a stair well, overhead view
Open communication and trust are essential for successful teamwork in challenging health care situations, as detailed in "Building effective healthcare team development interventions in uncertain times: Tips for success." The paper was authored by researchers at Rice University, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and The Group for Organizational Effectiveness.
The study outlines a new model, developed at MD Anderson under the guidance of the researchers, with recommendations for health care team effectiveness. It can be implemented in different settings to improve a team's communication, coordination and attitudes toward one another, improving clinical care and patient outcomes.
Team effectiveness is based on an organization's culture, leadership support and a trained and capable workforce, the researchers write. In addition, all team members should have clearly defined roles and purposes, with a clear team direction. But leaders must also consider the way a team feels, how it functions in the workplace and the way its members think. This is known in team science as the ABCs: attitudes, behaviors and cognitions.
By considering all these factors, the researchers suggest teams can achieve what they call "ideal team states," which include psychological safety (the freedom to speak openly without fear of negative job consequences), trust, adaptability and resilience.
"Only after embracing these states will teams be able to reach their highest potential," said Stephanie Zajac, a leadership practitioner at MD Anderson and the study's lead author.
The researchers also offer tips for successfully implementing team development interventions (TDIs), exercises used to advance team effectiveness. They recommend team leaders actively engage and invest time in TDIs, and that the exercises be integrated with existing organizational efforts to support teams, such as individual leader and team coaching. Team leaders should also show care and concern for team members as they navigate these exercises together.
Finally, leaders are encouraged to communicate regularly with their employees, and reflect on and celebrate the progress they make.
As teams grow more diverse and face unexpected circumstances, including the health and social justice hurdles of the past year, these tips can make all the difference when running successful health care institutions, conducting innovative research and delivering high-quality and safe patient care, the researchers wrote.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors of the study include Courtney Holladay, executive director of the Leadership Institute at MD Anderson; Scott Tannenbaum, president of The Group of Organizational Effectiveness; and Eduardo Salas, the Allyn R. and Gladys M. Cline Professor and chair of the Department of Psychological Sciences at Rice.
The article is online at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0090261620300760.
This news release can be found online at news.rice.edu.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations on Twitter @RiceUNews.
Photo link: https://news-network.rice.edu/news/files/2021/03/54832423_l.jpg
Photo credit: 123rf.com
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,978 undergraduates and 3,192 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is just under 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for lots of race/class interaction and No. 1 for quality of life by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-08
Squids have long been a source of fascination for humans, providing the stuff of legend, superstition and myth. And it's no wonder -- their odd appearances and strange intelligence, their mastery of the open ocean can inspire awe in those who see them.
Legends aside, squids continue to intrigue people today -- people like UC Santa Barbara professor Daniel Morse -- for much the same, albeit more scientific, reasons. Having evolved for hundreds of millions of years to hunt, communicate, evade predators and mate in the vast, often featureless expanses of open water, squids have developed some of the most sophisticated skin in the animal kingdom.
"For centuries, people have been amazed at the ability of squids to change the color and patterns of their skin -- which they ...
2021-03-08
The perils of machine learning - using computers to identify and analyze data patterns, such as in facial recognition software - have made headlines lately. Yet the technology also holds promise to help enforce federal regulations, including those related to the environment, in a fair, transparent way, according to a new study by Stanford researchers.
The analysis, published this week in the proceedings of the Association of Computing Machinery Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency(link is external), evaluates machine learning techniques designed to support a U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) initiative to reduce ...
2021-03-08
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Evolutionary arms races between marine animals overhauled ocean ecosystems on scales similar to the mass extinctions triggered by global disasters, a new study shows.
Scientists at Umeå University in Sweden and the Florida Museum of Natural History used paleontological databases to build a multilayered computer model of the history of marine life over the last 500 million years. Their analysis of the fossil record closely echoed a seminal 1981 study by paleontologist J. John Sepkoski - with one key difference.
Sepkoski's ground-breaking statistical work showed abrupt ocean-wide changes in biodiversity about 490 and 250 ...
2021-03-08
Oncotarget published "Chemotherapy sensitivity testing on ovarian cancer cells isolated from malignant ascites" which reported that the authors aim is to determine the feasibility of cell proliferation assays of tumor cells isolated from malignant ascites to predict in vitro chemotherapy sensitivity, and to correlate these results with clinical outcome.
Cell samples were enriched for tumor cells and EOC origin was confirmed by intracellular staining of CK7, surface staining of CA125 and EpCAM, and HE4 gene expression.
In vitro sensitivity to chemotherapy was determined in cell proliferation assays using intracellular ATP content as an indirect measure of cell number.
In twelve of ...
2021-03-08
Oncotarget published "High-fat diet-fed ovariectomized mice are susceptible to accelerated subcutaneous tumor growth potentially through adipose tissue inflammation, local insulin-like growth factor release, and tumor associated macrophages" which reported that the association between obesity and colorectal cancer (CRC) risk has been well established. This relationship appears to be more significant in men than in women, which may be attributable to sex hormones - controlled animal studies to substantiate these claims and the mechanisms involved are lacking. MC38 murine colon adenocarcinoma ...
2021-03-08
Oncotarget recently published "Estrogen receptor α polymorphism is associated with dementia in a Brazilian cohort" which reported that the growth of the elderly population is a worldwide phenomenon and it is associated with chronic diseases, including dementia.
In this scenario, the present study aimed to evaluate a possible association of estrogen receptor α polymorphisms with dementia in a Brazilian cohort.
The genotyping for the ERα PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms were performed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism.
The ERα PvuII pp genotype was associated with a higher odds ratio for dementia (OR = 3.42, 95% CI = 1.33-8.77, p = 0.01, ...
2021-03-08
Here is a link to a free Altmetric Report on this Research Output
Aging-US published "Hyperbaric oxygen therapy increases telomere length and decreases immunosenescence in isolated blood cells: a prospective trial" which reported that the aim of the current study was to evaluate whether hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) affects telomere length (TL) and senescent cell concentrations in a normal, non-pathological, aging adult population.
Thirty-five healthy independently living adults, aged 64 and older, were enrolled to receive 60 daily HBOT exposures.
Whole blood samples were collected at baseline, at the 30th and 60th session, and 1-2 weeks following the last HBOT session.
Telomeres ...
2021-03-08
Aging-US published "In search of preventive strategies: novel high-CBD Cannabis sativa extracts modulate ACE2 expression in COVID-19 gateway tissues" which reported that Cannabis sativa, especially those high in the anti-inflammatory cannabinoid cannabidiol, has been found to alter gene expression and inflammation and harbour anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory properties.
Working under a Health Canada research license, the Aging-US authors developed over 800 new C. sativa cultivars and hypothesized that high-CBD C. sativa extracts may be used to down-regulate ...
2021-03-08
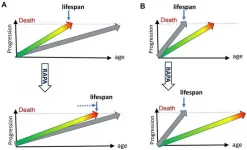
Aging-US published "DNA- and telomere-damage does not limit lifespan: evidence from rapamycin" which reported that failure of rapamycin to extend lifespan in DNA repair mutant and telomerase-knockout mice, while extending lifespan in normal mice, indicates that neither DNA damage nor telomere shortening limits normal lifespan or causes normal aging.
Dr. Mikhail V. Blagosklonny said, "As a provocative title has recently announced, 'rapamycin fails to extend lifespan in DNA repair -deficient mice' [1]. The word 'fails' implies bad news. Rapamycin tried but failed. Yet, it is expected that the anti-aging ...
2021-03-08
East Hanover, NJ. March 8, 2021. Kessler Foundation researchers have demonstrated changes in the functional connectivity within the 'fatigue network' in response to cognitive fatigue. This finding, the first of its kind, was reported in Scientific Reports on December 14, 2020 in the open access article, "Using functional connectivity changes associated with cognitive fatigue to delineate a fatigue network" (doi: 10.1038//s41598-020-78768-3).
The authors are Glenn Wylie, DPhil, Brian Yao, PhD, Helen M. Genova, PhD, Michele H. Chen, PhD, and John DeLuca, PhD, of Kessler Foundation. All have faculty appointments at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School. Dr. Wylie is also a research scientist at The Department of Veterans' Affairs War-related Injury and Illness ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New teamwork model could improve patient health care