(Press-News.org) When a coastline undergoes massive erosion, like a hurricane flattening a beach and its nearby environments, it has to rebuild itself - relying on the resilience of its natural coastal structures to begin piecing itself back together in a way that will allow it to survive the next large phenomena that comes its way.
Drs. Orencio Duran Vinent, assistant professor, and Ignacio Rodriguez-Iturbe, Distinguished University Professor and Wofford Cain Chair I Professor, in the Department of Ocean Engineering at Texas A&M University, are investigating the resilience of barrier islands and coastal dunes after high-water events and storms. In doing so, they are helping engineers and researchers assess the vulnerability of coastal landscapes.
Their full findings were published as related articles in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences titled "Probabilistic structure of events controlling the after-storm recovery of coastal dunes" and "Stochastic dynamics of barrier island elevation."
"If you understand how dunes grow, then you can take action, for example, in terms of vegetation or artificial barriers, to protect the coastline," Rodriguez-Iturbe said. "But you cannot protect or manage, in this case, dunes and barrier islands if you don't first understand the dynamics taking place."
In general, there are two types of high-water events along the coast: natural disasters like hurricanes and tsunamis, which cause waves that devastate the shoreline, and lesser storm surges, which do not cause widescale damage but still affect the coastal environment. As Duran Vinent explained, it is these smaller, routine events that control the post-storm resiliency of dunes and barrier islands that play a key role in protecting coastal communities by absorbing some of the impact from surges.
"Those events are not really strong enough to erode a mature dune completely, but they are strong enough to prevent one from growing in the first place after a storm that erodes the dunes and the vegetation ecosystem," he said.
With that in mind, the research team first studied the structure and properties of such smaller high-water events from around the world, utilizing buoy and other data to calculate characteristics like beach elevation, wave runup and water level to analyze them.
Their findings were twofold: first, they confirmed that the high-water events happen randomly and unrelatedly to one another. Then the team discovered that high-water events around the world shared the same general characteristics and had the same typical frequency per year with a given intensity when measured at beach level.
"This means that we can actually say something about the typical size of these nuisance flooding events or the typical size and frequency of events affecting the recovery of the coastal environment," Duran Vinent said. "Regardless of location, we have a unified description. And this simplifies the work for policymakers or managers a lot because then they don't need complex calculations."
The team took their newly discovered information and applied it to developing a model that would determine the elevation of a barrier island and, ultimately, whether or not a dune would be able to succeed. Additionally, this model provides a valuable tool in rebuilding coastlines that have been broken down and deteriorated over time, as it gives engineers a way to see how tall a dune or barrier island needs to be in order to prevent frequent overwashes and, thus, ensure ecosystem survival.
"The dynamic between high-water events and the geomorphology of barrier islands is complicated because the impact of any high-water event depends on how big the dunes are," Rodriguez-Iturbe said.
"And then while the dune is growing, you have these high-water events randomly interrupting its growth," Duran Vinent said. "This means that there is a competition between the frequency of the high-water erosional event and how fast the dune is growing."
This competition became the base of their analytical equation developed to determine whether or not a dune would be able to succeed, mathematically mapping in which conditions a barrier island would be resilient or vulnerable.
Dunes on barrier islands are vitally important, Duran Vinent explained, because they prevent water events from breaching the island and protect the vegetation on the back of the island from flooding, allowing a diverse set of vegetation to grow that is otherwise intolerant to seawater.
INFORMATION:
The research team also included ocean engineering graduate students Tobia Rinaldo and Kiran Adhithya Ramakrishnan, as well as collaboration with Dr. Benjamin E. Schaffer, research associate at Princeton University.
You're going at the speed limit down a two-lane road when a car barrels out of a driveway on your right. You slam on the brakes, and within a fraction of a second of the impact an airbag inflates, saving you from serious injury or even death.
The airbag deploys thanks to an accelerometer -- a sensor that detects sudden changes in velocity. Accelerometers keep rockets and airplanes on the correct flight path, provide navigation for self-driving cars, and rotate images so that they stay right-side up on cellphones and tablets, among other essential tasks.
Addressing the increasing ...
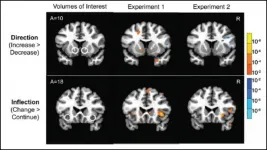
Forecasting changes in stock prices may be possible with the help of brain activity in regions associated with how people feel before making investment choices. Scientists could accurately forecast market price changes based on the average brain activity among a group but failed when using only prior stock trends or people's investment choices, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
Scientists have used the average brain activity among a group to predict which videos will go viral and which crowdfunding campaigns will receive funding. In a new study, Stallen et al. investigated if this relationship extends to a more ...
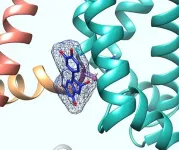
Irvine, CA - March 8, 2021 - A new study from the University of California, Irvine shows that compounds in both green and black tea relax blood vessels by activating ion channel proteins in the blood vessel wall. The discovery helps explain the antihypertensive properties of tea and could lead to the design of new blood pressure-lowering medications.
Published in Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, the discovery was made by the laboratory of Geoffrey Abbott, PhD, a professor in the Department of Physiology and Biophysics at the UCI School of Medicine. Kaitlyn Redford, a graduate student in the Abbott Lab, was first author of the study titled, "KCNQ5 potassium channel activation underlies vasodilation by tea."
Results from the research revealed that two catechin-type ...
HOUSTON - (March 8, 2021) - Health care teams must prepare for anything, including the unconventional work environments brought about by a global pandemic and social unrest.
Multiracial medical team having a discussion as they stand grouped together around a tablet computer on a stair well, overhead view
Open communication and trust are essential for successful teamwork in challenging health care situations, as detailed in "Building effective healthcare team development interventions in uncertain times: Tips for success." The paper was authored by researchers at Rice University, the University of Texas MD Anderson ...
Squids have long been a source of fascination for humans, providing the stuff of legend, superstition and myth. And it's no wonder -- their odd appearances and strange intelligence, their mastery of the open ocean can inspire awe in those who see them.
Legends aside, squids continue to intrigue people today -- people like UC Santa Barbara professor Daniel Morse -- for much the same, albeit more scientific, reasons. Having evolved for hundreds of millions of years to hunt, communicate, evade predators and mate in the vast, often featureless expanses of open water, squids have developed some of the most sophisticated skin in the animal kingdom.
"For centuries, people have been amazed at the ability of squids to change the color and patterns of their skin -- which they ...
The perils of machine learning - using computers to identify and analyze data patterns, such as in facial recognition software - have made headlines lately. Yet the technology also holds promise to help enforce federal regulations, including those related to the environment, in a fair, transparent way, according to a new study by Stanford researchers.
The analysis, published this week in the proceedings of the Association of Computing Machinery Conference on Fairness, Accountability and Transparency(link is external), evaluates machine learning techniques designed to support a U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) initiative to reduce ...
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Evolutionary arms races between marine animals overhauled ocean ecosystems on scales similar to the mass extinctions triggered by global disasters, a new study shows.
Scientists at Umeå University in Sweden and the Florida Museum of Natural History used paleontological databases to build a multilayered computer model of the history of marine life over the last 500 million years. Their analysis of the fossil record closely echoed a seminal 1981 study by paleontologist J. John Sepkoski - with one key difference.
Sepkoski's ground-breaking statistical work showed abrupt ocean-wide changes in biodiversity about 490 and 250 ...
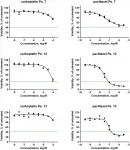
Oncotarget published "Chemotherapy sensitivity testing on ovarian cancer cells isolated from malignant ascites" which reported that the authors aim is to determine the feasibility of cell proliferation assays of tumor cells isolated from malignant ascites to predict in vitro chemotherapy sensitivity, and to correlate these results with clinical outcome.
Cell samples were enriched for tumor cells and EOC origin was confirmed by intracellular staining of CK7, surface staining of CA125 and EpCAM, and HE4 gene expression.
In vitro sensitivity to chemotherapy was determined in cell proliferation assays using intracellular ATP content as an indirect measure of cell number.
In twelve of ...
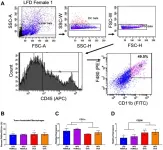
Oncotarget published "High-fat diet-fed ovariectomized mice are susceptible to accelerated subcutaneous tumor growth potentially through adipose tissue inflammation, local insulin-like growth factor release, and tumor associated macrophages" which reported that the association between obesity and colorectal cancer (CRC) risk has been well established. This relationship appears to be more significant in men than in women, which may be attributable to sex hormones - controlled animal studies to substantiate these claims and the mechanisms involved are lacking. MC38 murine colon adenocarcinoma ...
Oncotarget recently published "Estrogen receptor α polymorphism is associated with dementia in a Brazilian cohort" which reported that the growth of the elderly population is a worldwide phenomenon and it is associated with chronic diseases, including dementia.
In this scenario, the present study aimed to evaluate a possible association of estrogen receptor α polymorphisms with dementia in a Brazilian cohort.
The genotyping for the ERα PvuII and XbaI polymorphisms were performed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism.
The ERα PvuII pp genotype was associated with a higher odds ratio for dementia (OR = 3.42, 95% CI = 1.33-8.77, p = 0.01, ...