Study: Increase in taking HIV meds using Amazon Prime model
Study took place in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa, among 162 people living with HIV; findings presented at Virtual CROI 2021
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) Home delivery of HIV medicines in South Africa significantly increased viral suppression compared to those who received clinical care, according to a study by researchers at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The study, conducted with Amazon.com guidance during COVID-19 restrictions in South Africa, showed that among study participants, paying a fee for home delivery and monitoring of antiretroviral therapy (ART) was highly acceptable in the context of low income and high unemployment, and improved health outcomes as a result.
The researching findings were presented March 8 at Virtual Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI) 2021.
The one-time fee for home delivery was tiered based on participant income (US $2, $4, $6). Working with a Amazon.com routing scientist, the team developed an algorithm to support efficient delivery of medication that chose a route dependent on the remaining ART supply and location of the client. The study team delivered the medication following the algorithm.
After 47 weeks, the study found that compared to standard clinic care, fee for home delivery of ART significantly increased viral suppression from 74% in the clinic group to 88% in the home delivery group.
"It was reassuring to see that the clinic services were able to move to fast-track pick-up of medication with maintenance of viral suppression, but overall the paid home delivery model worked significantly better particularly among men who can be harder to reach with clinic-based services," said lead investigator Ruanne Barnabas, a professor of global health at the University of Washington School of Medicine.
The study team conducted the randomized trial October 2019 to December 2021 in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa among 162 people living with HIV. They were randomized to one of two groups: Fee for home delivery and monitoring of ART or clinic-based ART (standard of care).
The study provides evidence that home delivery and monitoring of ART is convenient, overcomes logistic barriers, and could increase ART adherence and viral suppression particularly among men who engage less in clinic-based HIV care than women. If clients pay for this service and the benefits are sufficient, it could be a scalable strategy.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-09
Researchers at the Buck Institute analyzed data from the COVID-19 Symptom Tracker app used by 3 million people in the United Kingdom, adding the use of immunosuppressant medication, use of a mobility aid, shortness of breath, fever, and fatigue to the list of symptoms and comorbidities that increase the risk for severe COVID-19. Results are published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research.
"Even though there are established risk factors for severe COVID-19 there are no good predictors that enable healthcare providers, or even those who have tested positive, to assess who should seek advanced medical care," says Buck Institute ...
2021-03-09
TAMPA, Fla. (March 8, 2021) -- Preterm birth is a END ...
2021-03-09
Recently, Prof. CHEN Gao from Institute of Geometry and Physics of the University of Science and Technology of China has made breakthrough in the field of complex differential geometry. Using mathematical invention, he buildt a new bridge between the relativity of Einstein and quantum mechanics. This work was published in Inventiones Mathematicae.
In the field of complex differential geometry, there are two crucial physical equations: the Hermitian-Yang-Mills equation, which became the standard model of quantum mechanics, and the Kähler-Einstein equation, which is closely related to relativity. To stably solve these two equations ...
2021-03-09
A team of researchers led by Professor Yaakov Nahmias, director of the Grass Center for Bioengineering at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and founder of Tissue Dynamic, introduced a new technological approach that has the potential to rapidly develop new drugs without the need for animal experiments.
According to Professor Nahmias, "Drug development is a long and expensive endeavor that is defined by multiple failures. The main reason for this failure is that clinical experiments are ultimately based on minimal information gained from animal experiment which often fail to replicate the human response."
The primary animals used in drug development ...
2021-03-09
For decades, there has been a trend in microelectronics towards ever smaller and more compact transistors. 2D materials such as graphene are seen as a beacon of hope here: they are the thinnest material layers that can possibly exist, consisting of only one or a few atomic layers. Nevertheless, they can conduct electrical currents - conventional silicon technology, on the other hand, no longer works properly if the layers become too thin.
However, such materials are not used in a vacuum; they have to be combined with suitable insulators - in order to seal them off from unwanted environmental influences, and ...
2021-03-09
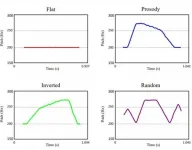
Prosody is a branch of linguistics that analyses and formally represents the elements of oral expression such as pitch, tones and intonation. A study published in Cognition on 5 February shows that there are universal prosodic cues that help with learning in humans and in animals.
This study, published by Juan Manuel Toro, ICREA research professor and Paola Crespo-Bojorque, researchers of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) of the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), is part of the research into language evolution that is being conducted thanks to a European Research Council Starting Grant.
Some of the mechanisms we humans use to learn language are based on general principles ...
2021-03-09
Long life is common among bird parents that get help with childcare. This finding comes from researchers at the universities of Lund and Oxford who reviewed data from more than 9,000 studies.
Being a parent can be tough. In general, animals that care for many offspring die young, at least in species where parents are not helped by others. However, in some species things are different and parents recruit 'helpers' to assist with childcare. In such group-living species, parents often produce lots of young and also live an exceptionally long time. This new research ...
2021-03-09
Thrombotic occlusion of blood vessels, which leads to myocardial infarctions, strokes and venous thromboembolisms, is the major cause of death in the western hemisphere. Therefore, it is of critical importance to understand mechanisms preventing thrombus formation. A new study by the research group of Christoph Binder, Principal Investigator at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and Professor at the Medical University of Vienna, now explains the important role of immunoglobulin-M (IgM) antibodies in preventing thrombosis. The study published in the journal Blood shows that these antibodies recognize microvesicles, which are ...
2021-03-09
Spiders from the genus Phoneutria - also known as banana spiders - are considered aggressive and among the most venomous spiders in the world, with venom that has a neurotoxic action. These large nocturnal spiders usually inhabit environments disturbed by humans and are often found in banana plantations in the Neotropical region.
One of these spiders, P. boliviensis, is a medically important species widely distributed in Central and South America, whose behaviour, habitat, venom composition, toxicity and bites on humans have already been paid considerable attention in previous research work. Nevertheless, after examining a large pool of museum specimens, biologists from The George Washington University (N. Hazzi and G. Hormiga) began to ...
2021-03-09
Tsukuba, Japan - Because human females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y, somatic cells have special mechanisms that keep expression levels of genes on the X chromosome the same between both sexes. This process is called dosage compensation and has been extensively studied in the fruit fly Drosophila. Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba (UT) continued work with Drosophila to show that dosage compensation does not occur in the germ cells of male flies.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, the UT researchers investigated this phenomenon in fly primordial germ cells (PGCs), which are present in embryos and are the precursor cells to what ultimately become ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study: Increase in taking HIV meds using Amazon Prime model
Study took place in KwaZulu Natal, South Africa, among 162 people living with HIV; findings presented at Virtual CROI 2021