Study reveals process to explain how maternal stress triggers idiopathic preterm birth
A University of South Florida Health preclinical study indicates that FKBP51-progesterone receptor binding plays a critical role in stress-induced preterm birth
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) TAMPA, Fla. (March 8, 2021) -- Preterm birth is a END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Bridge built between Kähler-Einstein and Chen-Ning Yang's Equations
2021-03-09
Recently, Prof. CHEN Gao from Institute of Geometry and Physics of the University of Science and Technology of China has made breakthrough in the field of complex differential geometry. Using mathematical invention, he buildt a new bridge between the relativity of Einstein and quantum mechanics. This work was published in Inventiones Mathematicae.
In the field of complex differential geometry, there are two crucial physical equations: the Hermitian-Yang-Mills equation, which became the standard model of quantum mechanics, and the Kähler-Einstein equation, which is closely related to relativity. To stably solve these two equations ...
Can chips replace animal testing?
2021-03-09
A team of researchers led by Professor Yaakov Nahmias, director of the Grass Center for Bioengineering at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem and founder of Tissue Dynamic, introduced a new technological approach that has the potential to rapidly develop new drugs without the need for animal experiments.
According to Professor Nahmias, "Drug development is a long and expensive endeavor that is defined by multiple failures. The main reason for this failure is that clinical experiments are ultimately based on minimal information gained from animal experiment which often fail to replicate the human response."
The primary animals used in drug development ...
Microchips of the future: Suitable insulators are still missing
2021-03-09
For decades, there has been a trend in microelectronics towards ever smaller and more compact transistors. 2D materials such as graphene are seen as a beacon of hope here: they are the thinnest material layers that can possibly exist, consisting of only one or a few atomic layers. Nevertheless, they can conduct electrical currents - conventional silicon technology, on the other hand, no longer works properly if the layers become too thin.
However, such materials are not used in a vacuum; they have to be combined with suitable insulators - in order to seal them off from unwanted environmental influences, and ...
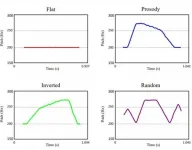
Universal prosodic cues facilitate learning in both animals and humans
2021-03-09
Prosody is a branch of linguistics that analyses and formally represents the elements of oral expression such as pitch, tones and intonation. A study published in Cognition on 5 February shows that there are universal prosodic cues that help with learning in humans and in animals.
This study, published by Juan Manuel Toro, ICREA research professor and Paola Crespo-Bojorque, researchers of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) of the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), is part of the research into language evolution that is being conducted thanks to a European Research Council Starting Grant.
Some of the mechanisms we humans use to learn language are based on general principles ...
Bird parents that receive help live longer
2021-03-09
Long life is common among bird parents that get help with childcare. This finding comes from researchers at the universities of Lund and Oxford who reviewed data from more than 9,000 studies.
Being a parent can be tough. In general, animals that care for many offspring die young, at least in species where parents are not helped by others. However, in some species things are different and parents recruit 'helpers' to assist with childcare. In such group-living species, parents often produce lots of young and also live an exceptionally long time. This new research ...
New therapeutic approach discovered for reducing the risk of thrombosis
2021-03-09
Thrombotic occlusion of blood vessels, which leads to myocardial infarctions, strokes and venous thromboembolisms, is the major cause of death in the western hemisphere. Therefore, it is of critical importance to understand mechanisms preventing thrombus formation. A new study by the research group of Christoph Binder, Principal Investigator at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and Professor at the Medical University of Vienna, now explains the important role of immunoglobulin-M (IgM) antibodies in preventing thrombosis. The study published in the journal Blood shows that these antibodies recognize microvesicles, which are ...
Two species and a single name: 'Double identity' revealed in a venomous banana spider
2021-03-09
Spiders from the genus Phoneutria - also known as banana spiders - are considered aggressive and among the most venomous spiders in the world, with venom that has a neurotoxic action. These large nocturnal spiders usually inhabit environments disturbed by humans and are often found in banana plantations in the Neotropical region.
One of these spiders, P. boliviensis, is a medically important species widely distributed in Central and South America, whose behaviour, habitat, venom composition, toxicity and bites on humans have already been paid considerable attention in previous research work. Nevertheless, after examining a large pool of museum specimens, biologists from The George Washington University (N. Hazzi and G. Hormiga) began to ...
X marks the spot: How genes on the sex chromosomes are controlled
2021-03-09
Tsukuba, Japan - Because human females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y, somatic cells have special mechanisms that keep expression levels of genes on the X chromosome the same between both sexes. This process is called dosage compensation and has been extensively studied in the fruit fly Drosophila. Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba (UT) continued work with Drosophila to show that dosage compensation does not occur in the germ cells of male flies.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, the UT researchers investigated this phenomenon in fly primordial germ cells (PGCs), which are present in embryos and are the precursor cells to what ultimately become ...
Earth's deep mantle may have proton rivers made of superionic phases
2021-03-09
Pierfranco Demontis said in 1988, "Ice becomes a fast-ion conductor at high pressure and high temperatures," but his prediction was only hypothetical until recently. After 30 years of study, superionic water ice was verified experimentally in 2018. Superionicity may eventually explain the strong magnetic field in giant planetary interiors.
What about Earth, whose interiors are also under extreme pressure and temperature conditions? Although three-quarters of Earth's surface is covered by water, standalone water or ice rarely exists in Earth's interiors. The most common unit of "water" is hydroxyl, which is associated with host minerals to make ...
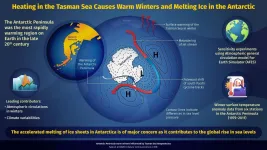
Antarctic Peninsula warming up due to heat in Tasman sea
2021-03-09
The melting of the Earth's ice cover intensified in the 20th century, with glaciers and sea ice in the Arctic and Antarctic regions melting at alarming speeds. In fact, The Antarctic Peninsula (AP), which is the only landmass of Antarctica extending out past the Antarctic Circle, was found to be one of the most rapidly warming regions on the planet during the second half of the 20th century. This rapid change in climate has raised serious concerns of rising sea levels the world over.
Multiple factors have been associated with the melting of the ice cover: the primary factor being the greenhouse gas emissions from human activities that cause ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
[Press-News.org] Study reveals process to explain how maternal stress triggers idiopathic preterm birthA University of South Florida Health preclinical study indicates that FKBP51-progesterone receptor binding plays a critical role in stress-induced preterm birth