Universal prosodic cues facilitate learning in both animals and humans
Elements of oral expression such as pitch, tone and intonation, highlight important parts of speech, and not only humans benefit. According to a study on the evolution of language published in the journal Cognition
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) Prosody is a branch of linguistics that analyses and formally represents the elements of oral expression such as pitch, tones and intonation. A study published in Cognition on 5 February shows that there are universal prosodic cues that help with learning in humans and in animals.
This study, published by Juan Manuel Toro, ICREA research professor and Paola Crespo-Bojorque, researchers of the Center for Brain and Cognition (CBC) of the UPF Department of Information and Communication Technologies (DTIC), is part of the research into language evolution that is being conducted thanks to a European Research Council Starting Grant.
Some of the mechanisms we humans use to learn language are based on general principles we inherited from other species
The prosodic contour is universal
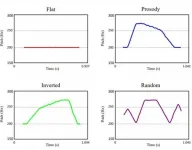
When we speak, we pronounce words more intensely at first and lengthen them slightly more at the end of the sentence. This is known as the prosodic contour. This contour is universal, in the sense that it not only defines the way in which speech occurs in humans, but also in birdsong and probably any other animal vocalization. "This occurs because the prosodic contour appears as a result of how humans and animals produce sounds by expelling air through the larynx", Toro and Crespo Bojorque explain.
And they add: "In our study, we showed that this prosodic contour facilitates the learning of words not only in humans but also in other animals (in our experiment, rats)".
Through various experiments, the researchers found that animals learned to recognize nonsense words when they had a natural prosodic contour. Conversely, they could not learn them when they had a flat or random contour.
Thus, the authors conclude that there are universal cues that facilitate learning, and both humans and other non-human animals benefit from them. In general terms, "this suggests that some of the mechanisms humans use to learn language are based on general principles we inherited from other species", the study researchers conclude.
INFORMATION:
Related work:
Juan Manuel Toro, Paola Crespo-Bojorque (2021), "Arc-shaped pitch contours facilitate item recognition in non-human animals", Cognition, 5 february, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cognition.2021.104614
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-09
Long life is common among bird parents that get help with childcare. This finding comes from researchers at the universities of Lund and Oxford who reviewed data from more than 9,000 studies.
Being a parent can be tough. In general, animals that care for many offspring die young, at least in species where parents are not helped by others. However, in some species things are different and parents recruit 'helpers' to assist with childcare. In such group-living species, parents often produce lots of young and also live an exceptionally long time. This new research ...
2021-03-09
Thrombotic occlusion of blood vessels, which leads to myocardial infarctions, strokes and venous thromboembolisms, is the major cause of death in the western hemisphere. Therefore, it is of critical importance to understand mechanisms preventing thrombus formation. A new study by the research group of Christoph Binder, Principal Investigator at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences and Professor at the Medical University of Vienna, now explains the important role of immunoglobulin-M (IgM) antibodies in preventing thrombosis. The study published in the journal Blood shows that these antibodies recognize microvesicles, which are ...
2021-03-09
Spiders from the genus Phoneutria - also known as banana spiders - are considered aggressive and among the most venomous spiders in the world, with venom that has a neurotoxic action. These large nocturnal spiders usually inhabit environments disturbed by humans and are often found in banana plantations in the Neotropical region.
One of these spiders, P. boliviensis, is a medically important species widely distributed in Central and South America, whose behaviour, habitat, venom composition, toxicity and bites on humans have already been paid considerable attention in previous research work. Nevertheless, after examining a large pool of museum specimens, biologists from The George Washington University (N. Hazzi and G. Hormiga) began to ...
2021-03-09
Tsukuba, Japan - Because human females have two X chromosomes and males have one X and one Y, somatic cells have special mechanisms that keep expression levels of genes on the X chromosome the same between both sexes. This process is called dosage compensation and has been extensively studied in the fruit fly Drosophila. Now, researchers at the University of Tsukuba (UT) continued work with Drosophila to show that dosage compensation does not occur in the germ cells of male flies.
In an article published in Scientific Reports, the UT researchers investigated this phenomenon in fly primordial germ cells (PGCs), which are present in embryos and are the precursor cells to what ultimately become ...
2021-03-09
Pierfranco Demontis said in 1988, "Ice becomes a fast-ion conductor at high pressure and high temperatures," but his prediction was only hypothetical until recently. After 30 years of study, superionic water ice was verified experimentally in 2018. Superionicity may eventually explain the strong magnetic field in giant planetary interiors.
What about Earth, whose interiors are also under extreme pressure and temperature conditions? Although three-quarters of Earth's surface is covered by water, standalone water or ice rarely exists in Earth's interiors. The most common unit of "water" is hydroxyl, which is associated with host minerals to make ...
2021-03-09
The melting of the Earth's ice cover intensified in the 20th century, with glaciers and sea ice in the Arctic and Antarctic regions melting at alarming speeds. In fact, The Antarctic Peninsula (AP), which is the only landmass of Antarctica extending out past the Antarctic Circle, was found to be one of the most rapidly warming regions on the planet during the second half of the 20th century. This rapid change in climate has raised serious concerns of rising sea levels the world over.
Multiple factors have been associated with the melting of the ice cover: the primary factor being the greenhouse gas emissions from human activities that cause ...
2021-03-09
Anxiety levels in the United States are rising sharply and have especially intensified in younger populations. According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America, anxiety disorders affect 31.9 percent of children ages 13 to 18 years old. Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, children and adolescents have experienced unprecedented interruptions to their daily lives and it is expected that these disruptions may precipitate mental illness, including anxiety, depression, and/or stress related symptoms.
Traditional anxiety and depression treatments include ...
2021-03-09
A critical ingredient for auroras exists much higher in space than previously thought, according to new research in the journal Scientific Reports. The dazzling light displays in the polar night skies require an electric accelerator to propel charged particles down through the atmosphere. Scientists at Nagoya University and colleagues in Japan, Taiwan and the US have found that it exists beyond 30,000 kilometres above the Earth's surface - offering insight not just about Earth, but other planets as well.
The story of aurora formation begins with supersonic plasma propelled from the Sun into space as high-speed, charged particles. When these charged particles get close to Earth, they are ...
2021-03-09
Scientists at the University of Virginia School of Medicine have developed a tool to monitor communications within the brain in a way never before possible, and it has already offered an explanation for why Alzheimer's drugs have limited effectiveness and why patients get much worse after going off of them.
The researchers expect their new method will have tremendous impact on our understanding of depression, sleep disorders, autism, neurological diseases and major psychiatric conditions. It will speed scientific research into the workings of the brain, they say, and facilitate the development of new treatments.
"We can now 'see' how brain cells communicate in sharp detail in both the healthy and diseased brains," said lead researcher J. Julius Zhu, PhD, of UVA's Department ...
2021-03-09
(LOS ANGELES) - Recent advances in technology have opened many possibilities for using wearable and implantable sensors to monitor various indicators of patient health. Wearable pressure sensors are designed to respond to very small changes in bodily pressure, so that physical functions such as pulse rate, blood pressure, breathing rates and even subtle changes in vocal cord vibrations can be monitored in real time with a high degree of sensitivity.
Such responses occur when a substance in the sensor "gates," or allows selected pressure signals to pass to a transistor, which then conducts and amplifies these signals for detection. A recent type of transistor, organic electrochemical transistors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Universal prosodic cues facilitate learning in both animals and humans
Elements of oral expression such as pitch, tone and intonation, highlight important parts of speech, and not only humans benefit. According to a study on the evolution of language published in the journal Cognition