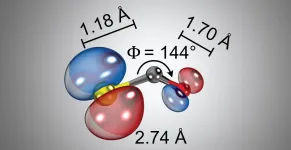(Press-News.org) Light microscopes have revolutionized our understanding of the microcosmos, but their resolution is limited to about 100 nanometers. To see how molecules bond, break, or change their structure, we need at least 1000 times better resolution.
Laser induced electron diffraction (LIED) is a technique which allows to pinpoint the individual atoms inside a single molecule, and to see where each atom moves when the molecule undergoes a reaction. This technique proved to be an amazing tool for the imaging molecules, such as water, carbonyl sulfide or carbon disulfide. However, using a strong laser field to generate the electron diffraction presented challenges in retrieving the exact structure, since the structural resolution depended on exact knowledge of the laser field itself.
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, ICFO researchers Aurelien Sanchez, Kasra Amini, Tobias Steinle, Xinyao Liu, led by ICREA Prof. at ICFO Jens Biegert, in collaboration with researchers from Kansas State University, Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt, and Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, have reported on an alternative and novel approach that retrieves accurate and precise information about the atomic structure without exact knowledge over the laser field. They successfully applied the method to imaging gas-phased molecule Carbonyl Sulfide (OCS), in particular on the bond lengths between the constituent atoms, showing a significant bent and asymmetrically stretched configuration of the ionized OCS+ structure.
Determining the atomic bonds of Carbonyl Sulfide
In their experiment, the scientists took a gas mixture of 1% OCS in helium and expanded it supersonically to create a molecular beam of the gas with a temperature below 90K. They then took a 3.2?m laser and exposed the molecule to the strong laser field. The interaction between the laser and the molecule produced an accelerated electron, which was released from the molecule, accelerated into the laser field and returned back to the target ion by the electric field of the laser; the re-collision of the electron with the ion structure generated a molecular imprint of the structure and, by extracting this information from the electron interference pattern and the scattering angle analysis, the scientists were capable of determining the proper structure of the molecule.
Novelty of the approach
Named ZCP-LIED, the novelty of this approach resides in the fact that the scientists came up with a very clever way to retrieve the atomic information by using the full 2D electron scattering information, mainly the energy and scattering angle spectra of the electron in the laboratory frame instead of the laser frame, which drastically improved the statistics of the results. Alongside to using 2D data instead of 1D information, they also identified a distinctive feature in spectra related to what they called the zero crossing point (ZCP) positions (where the interference signal showed a null value). By carrying out the analysis over these critical points, the scientists were able to obtain from a much smaller data set more precise information on the bond lengths of the atoms that make up the molecule, reducing quite considerably the calculation time.
For validation of their approach, they used various methods, compared them to quantum chemistry theoretical simulations and prove that their ZCP-LIED technique could obtain inter-nuclear distances with a much higher precision, could measure bond distances of similar length (something rather impossible to do with previous methods), that it avoided converting frames of reference, and was able to determine the molecular structure in environments where the background noise could be considerable. Taking all this into account, they reported obtaining the molecular information of 10-atom molecules, and in particular, for the carbonyl sulfide, where they saw that the molecule OCS+ had a significantly bent and asymmetrically stretched structure, different to what previous studies had determined for this molecule.
The results obtained by this study have demonstrated that the ZCP-LIED technique could be a very powerful tool to determine the molecular structure of large and more complex molecules. It could also be extended to ultrafast electron diffraction (UED) and even ultrafast X-ray diffraction (UXD) to track the geometric structure molecules in a transient phase.
INFORMATION:
Reference: Molecular structure retrieval directly from laboratory-frame photoelectron spectra in laser-induced electron diffraction, A. Sanchez, K. Amini, S.-J. Wang, T. Steinle, B. Belsa, J. Danek, A.T. Le, X. Liu, R. Moshammer, T. Pfeifer, M. Richter, J. Ullrich, S. Gräfe, C.D. Lin, J. Biegert, Nature Communications, 10.1038/s41467-021-21855-4.
New Haven, Conn. -- Mailing a package of SARS-CoV-2 tests to every household in America and asking people to use them once a week could greatly reduce total infections and mortality at a justifiable cost, a new study led by the Yale School of Public Health finds.
The research, published today in Annals of Internal Medicine, considers rapid antigen tests that warn people, in real-time, that they are potentially contagious and that they should isolate themselves before unknowingly spreading the disease to others. Investigators, led by Professor A. David Paltiel, assembled data on the epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 and the natural history of COVID-19. They then used a mathematical model to estimate how many infections, hospitalizations, and deaths could be averted - and at what cost - by providing ...
As much as a year's worth of past academic progress made by disadvantaged children in the Global South may have been wiped out by school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers have calculated.
The research, by academics from the University of Cambridge and RTI International, attempts to quantify the scale of learning loss that children from poor and marginalised communities in the Global South may have experienced, and the extent to which home support and access to learning resources could ameliorate it. While it is known that the education of these children has suffered disproportionately during the pandemic, it is much harder to measure exactly how much their academic progress has ...
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are at a significantly increased risk of contracting COVID-19 than women without the condition, new research led by the University of Birmingham has revealed.
Researchers are now calling for healthcare policy to specifically encourage women with PCOS to adhere to COVID-19 infection control measures while the global pandemic continues.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition affecting around one in 10 women in the UK. The three main symptoms are irregular periods, high levels of "male" hormones which may cause physical signs such as excess facial or body hair, and a cystic appearance on an ultrasound or MRI scan of the ovaries which is caused by follicles becoming increasingly fluid filled as they fail to develop and ...
Researchers at Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin and TU Berlin as well as the University of Oslo have developed a new tissue-section analysis system for diagnosing breast cancer based on artificial intelligence (AI). Two further developments make this system unique: For the first time, morphological, molecular and histological data are integrated in a single analysis. Secondly, the system provides a clarification of the AI decision process in the form of heatmaps. Pixel by pixel, these heatmaps show which visual information influenced the AI decision process and to what extent, thus enabling doctors to understand and assess the plausibility of the results of the AI analysis. This represents ...
People with unhealthy heart structures and poorer functioning hearts have a significantly higher risk of being diagnosed with COVID-19 infection, according to research by Queen Mary University of London, in collaboration with the Medical Research Council Lifecourse Epidemiology Unit (The University of Southampton).
The researchers made use of the comprehensive and internationally unique UK Biobank database, which includes health and genetic information from over half a million participants from across the UK, including detailed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of their hearts as well as linkages to COVID-19 test results from Public Health England.
The team investigated records from 310 Biobank participants to see whether pre-existing features of the heart ...
In light of the United Nations (UN) declaration that 2021-2030 is the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, a group of scientists voice concerns about restoration in heavily fragmented landscapes under a hotter and drier future scenario.
Poor recovery of small fragments will end up costing management and wider society later down the line. Millions are invested in setting aside patches, but management is then weak and costly.
Rainforests turn into oil palm plantations
The past 40 years in Southeast Asia have seen about 50% of lowland rainforests converted to oil palm and other plantations, and much of the remaining forest heavily logged.
Little is known about how fragmentation influences recovery and whether climate change will hamper restoration.
"Here, we use repeat airborne ...
Scientists have pinpointed the location of an essential enzyme in plant cells involved in photosynthesis, according to a study published today in eLife.
The findings overturn conventional thinking about where the enzyme resides in plant cells and suggest a probable role in regulating energy processes as plants adapt from dark to light conditions.
During photosynthesis, plants convert carbon into energy stores through 'electron transport', involving an enzyme called ferredoxin:NADP(H) oxidoreductase, or FNR.
Plants can switch rapidly between two types of electron transport - linear electron flow (LEF) and cyclic electron ...
Gas and liquid separation processes in the chemical industry could be made more efficient and environmentally friendly by using substances known as intrinsically porous materials (IPMs). KAUST researchers review the prospects for IPMs in the journal Accounts of Chemical Research.
Niveen Khashab and her team are currently heavily involved in IPM research. "We focus on making materials that will have an impact on the chemical and petrochemical industries in Saudi Arabia and the world," says Niveen Khashab, the corresponding author of the review.
IPM materials can separate gases and liquids without using traditional ...
The annually occurring algal spring blooms play an important role for our climate, as they remove large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, they are an ephemeral phenomenon. Most of the carbon is released into the water once the algae die. There, bacteria are already waiting to finish them off and consume the algal remains.
Previous studies have shown that in these blooms, different algae can come out on top each year. However, within the bacteria subsequently degrading the algae, the same specialised groups prevail year after year. Apparently not the algae themselves but rather their components ...
According to an international study published in Frontiers in Psychology, people around the world have reported changes in their physical activity levels, wellbeing, and eating habits during the first stages of the COVID-19 pandemic. A decrease in physical activity during the pandemic was associated with poorer perceived physical and mental health. Reduced exercise was also associated with perceptions of weight gain and decreased sleep.
More than a thousand individuals from several countries with different containment measures participated in an online survey that explored changes in physical activity, eating, sleep, physical and mental health, and wellbeing during the first lockdown phases ...