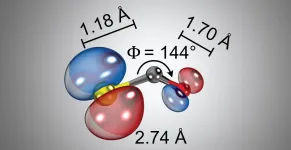(Press-News.org) The efficient provision of medical care is integral to society. Over time, the healthcare industry has tapped into modern technology in order to keep up its quality of service. This has, unsurprisingly, led to huge volumes of patient data. But it's not just patients whose data need to be stored; doctors, physicians, clinical staff, and even smart wearable gadgets are contributing to what is coming to be known as "healthcare big data."
Big data analytics (BDA), which involves the use of special design architectures to manage, store, and analyze complex data, is an important tool in healthcare. But it is hard to implement, owing to its high failure rate, resource-intensive process, and--most importantly--a lack of a clear guideline to aid practitioners.
In a recent study published in IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica (Volume 8, Issue 1, January 2021), researchers from Pakistan and Australia addressed this issue, offering a roadmap for the successful implementation of BDA in healthcare. They proposed a standard architecture that promises to solve all the challenges currently associated with BDA. Prof. Tariq Mahmood from Institute of Business Administration (IBA), Pakistan, lays down his motivation behind the study, "In reality, healthcare analytics has been in use for more than two decades but has not yet catered for healthcare big data. In our study, we proposed an architecture that has the potential to solve a large number of healthcare analytics problems in the next 5 years."
In the past, researchers have attempted to summarize the research work on BDA applications to improve patient healthcare. The summarization is ideally accomplished through a systematic and standardized review of published academic research papers. In the present study, the team took this approach to the next level by conducting the review through five different activities: 1) focusing on the use of all big data technologies, 2) identifying all limitations and challenges mentioned in previous studies, 3) proposing a novel, state-of-the-art design architecture called "Med-BDA" to solve these challenges, 4) identifying strategies for its successful implementation in the healthcare domain, and 5) comparing their work with all previously published studies.
The new Med-BDA architecture uses "Apache Spark technology" to analyze not only data in real time but also non-real-time data along with social network data to understand the bottlenecks of treatment process and make critical predictions regarding, for instance, in-patient cost estimates and expected mortality. Doctors can use these predictions to anticipate the patient's condition in real time and provide them with better and effective treatments. Moreover, by comparing their work with selected papers, the researchers confirmed that their Med-BDA architecture was unique, with no similar strategies proposed previously.
The research team is excited about the future prospects of Med-BDA. Prof. Mahmood says, "Med-BDA can digest gigabytes of information collectively from different sources and analyze them concurrently to build a clear picture of the patients' treatment processes for both real-time and batch-level analyses. Moreover, with the increasing popularity of 'Internet-of-Things' (IoT) in healthcare, Med-BDA will have the potential to digest big IoT data and thus improve BDA."
Perhaps, we're on the brink of a "big" revolution in healthcare!
INFORMATION:
Reference
S. Imran, T. Mahmood, A. Morshed, and T. Sellis, "Big data analytics in healthcare -- A systematic literature review and roadmap for practical implementation," IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sinica, vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 1-22, Jan. 2021.
Fulltext of the paper is available:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9205683
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica aims to publish high-quality, high-interest, far-reaching research achievements globally, and provide an international forum for the presentation of original ideas and recent results related to all aspects of automation.
The first Impact Factor of IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica is 5.129, ranking among Top 17% (11/63, SCI Q1) in the category of Automation & Control Systems, according to the latest Journal Citation Reports released by Clarivate Analytics in 2020. In addition, its latest CiteScore is 8.3, and has entered Q1 in all three categories it belongs to (Information System, Control and Systems Engineering, Artificial Intelligence) since 2018.
Why publish with us: Fast and high quality peer review; Simple and effective online submission system; Widest possible global dissemination of your research; Indexed in SCIE, EI, IEEE, Scopus, Inspec.
JAS papers can be found at http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/mostRecentIssue.jsp?punumber=6570654
Light microscopes have revolutionized our understanding of the microcosmos, but their resolution is limited to about 100 nanometers. To see how molecules bond, break, or change their structure, we need at least 1000 times better resolution.
Laser induced electron diffraction (LIED) is a technique which allows to pinpoint the individual atoms inside a single molecule, and to see where each atom moves when the molecule undergoes a reaction. This technique proved to be an amazing tool for the imaging molecules, such as water, carbonyl sulfide or carbon disulfide. However, using a strong laser field to generate the electron diffraction presented challenges in retrieving the exact structure, since the structural resolution depended on exact knowledge of the ...
New Haven, Conn. -- Mailing a package of SARS-CoV-2 tests to every household in America and asking people to use them once a week could greatly reduce total infections and mortality at a justifiable cost, a new study led by the Yale School of Public Health finds.
The research, published today in Annals of Internal Medicine, considers rapid antigen tests that warn people, in real-time, that they are potentially contagious and that they should isolate themselves before unknowingly spreading the disease to others. Investigators, led by Professor A. David Paltiel, assembled data on the epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 and the natural history of COVID-19. They then used a mathematical model to estimate how many infections, hospitalizations, and deaths could be averted - and at what cost - by providing ...
As much as a year's worth of past academic progress made by disadvantaged children in the Global South may have been wiped out by school closures during the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers have calculated.
The research, by academics from the University of Cambridge and RTI International, attempts to quantify the scale of learning loss that children from poor and marginalised communities in the Global South may have experienced, and the extent to which home support and access to learning resources could ameliorate it. While it is known that the education of these children has suffered disproportionately during the pandemic, it is much harder to measure exactly how much their academic progress has ...
Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are at a significantly increased risk of contracting COVID-19 than women without the condition, new research led by the University of Birmingham has revealed.
Researchers are now calling for healthcare policy to specifically encourage women with PCOS to adhere to COVID-19 infection control measures while the global pandemic continues.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common condition affecting around one in 10 women in the UK. The three main symptoms are irregular periods, high levels of "male" hormones which may cause physical signs such as excess facial or body hair, and a cystic appearance on an ultrasound or MRI scan of the ovaries which is caused by follicles becoming increasingly fluid filled as they fail to develop and ...
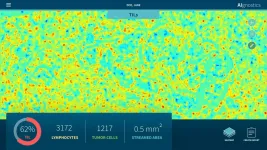
Researchers at Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin and TU Berlin as well as the University of Oslo have developed a new tissue-section analysis system for diagnosing breast cancer based on artificial intelligence (AI). Two further developments make this system unique: For the first time, morphological, molecular and histological data are integrated in a single analysis. Secondly, the system provides a clarification of the AI decision process in the form of heatmaps. Pixel by pixel, these heatmaps show which visual information influenced the AI decision process and to what extent, thus enabling doctors to understand and assess the plausibility of the results of the AI analysis. This represents ...
People with unhealthy heart structures and poorer functioning hearts have a significantly higher risk of being diagnosed with COVID-19 infection, according to research by Queen Mary University of London, in collaboration with the Medical Research Council Lifecourse Epidemiology Unit (The University of Southampton).
The researchers made use of the comprehensive and internationally unique UK Biobank database, which includes health and genetic information from over half a million participants from across the UK, including detailed magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of their hearts as well as linkages to COVID-19 test results from Public Health England.
The team investigated records from 310 Biobank participants to see whether pre-existing features of the heart ...
In light of the United Nations (UN) declaration that 2021-2030 is the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, a group of scientists voice concerns about restoration in heavily fragmented landscapes under a hotter and drier future scenario.
Poor recovery of small fragments will end up costing management and wider society later down the line. Millions are invested in setting aside patches, but management is then weak and costly.
Rainforests turn into oil palm plantations
The past 40 years in Southeast Asia have seen about 50% of lowland rainforests converted to oil palm and other plantations, and much of the remaining forest heavily logged.
Little is known about how fragmentation influences recovery and whether climate change will hamper restoration.
"Here, we use repeat airborne ...
Scientists have pinpointed the location of an essential enzyme in plant cells involved in photosynthesis, according to a study published today in eLife.
The findings overturn conventional thinking about where the enzyme resides in plant cells and suggest a probable role in regulating energy processes as plants adapt from dark to light conditions.
During photosynthesis, plants convert carbon into energy stores through 'electron transport', involving an enzyme called ferredoxin:NADP(H) oxidoreductase, or FNR.
Plants can switch rapidly between two types of electron transport - linear electron flow (LEF) and cyclic electron ...
Gas and liquid separation processes in the chemical industry could be made more efficient and environmentally friendly by using substances known as intrinsically porous materials (IPMs). KAUST researchers review the prospects for IPMs in the journal Accounts of Chemical Research.
Niveen Khashab and her team are currently heavily involved in IPM research. "We focus on making materials that will have an impact on the chemical and petrochemical industries in Saudi Arabia and the world," says Niveen Khashab, the corresponding author of the review.
IPM materials can separate gases and liquids without using traditional ...
The annually occurring algal spring blooms play an important role for our climate, as they remove large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, they are an ephemeral phenomenon. Most of the carbon is released into the water once the algae die. There, bacteria are already waiting to finish them off and consume the algal remains.
Previous studies have shown that in these blooms, different algae can come out on top each year. However, within the bacteria subsequently degrading the algae, the same specialised groups prevail year after year. Apparently not the algae themselves but rather their components ...