Recyclable bioplastic membrane to clear oil spills from water
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) Polymer scientists from the University of Groningen and NHL Stenden University of Applied Sciences, both in the Netherlands, have developed a polymer membrane from biobased malic acid. It is a superamphiphilic vitrimer epoxy resin membrane that can be used to separate water and oil. This membrane is fully recyclable. When the pores are blocked by foulants, it can be depolymerized, cleaned and subsequently pressed into a new membrane. A paper describing the creation of this membrane was published in the journal Advanced Materials on 7 March 2021.
How do you clean up an oil spill in water? This is quite a challenge. Superamphiphilic membranes, that 'love' both oil and water, are a promising solution but not yet a very practical one. These membranes are often not robust enough for use outside the laboratory environment and the membrane pores can clog up as a result of fouling by algae and sand. Chongnan Ye and Katja Loos from the University of Groningen and Vincent Voet and Rudy Folkersma from NHL Stenden used a relatively new type of polymer to create a membrane that is both strong and easy to recycle.
Dynamic network
In recent years, the researchers from both institutes have joined forces to investigate vitrimer plastics, polymer materials that have the mechanical properties and chemical resistance of a thermoset plastic. However, vitrimer plastics can also behave like a thermoplastic, since they can be depolymerized and reused. This means that a vitrimer plastic has all the qualities to make a good membrane for oil spill remediation. 'Furthermore, it was made from malic acid, a natural monomer,' adds Loos.
'The polymers in the vitrimer are crosslinked in a reversible manner,' explains Voet. 'They form a dynamic network, which enables recycling of the membrane.' The vitrimer is produced through base-catalysed ring-opening polymerization between pristine and epoxy-modified biobased malic acid. The polymers are ground into a powder by ball milling and turned into a porous membrane through the process of sintering.
Pores
Both water and oil will spread out on the resulting superamphiphilic membrane. In an oil spill, much more water is present than oil, which means that the membrane is covered by water that can then pass through the pores. Voet: 'The water film on the membrane's surface keeps the oil out of the pores so that it is separated from the water.'
The membrane is firm enough to filter oil from the water. When sand and algae clog up the pores, the membrane can be depolymerized and recreated from the building blocks after removal of the pollutants. 'We have tested this on a laboratory scale of a few square centimetres,' says Loos. 'And we are confident that our methods are scalable, both for the polymer synthesis and for the production and recycling of the membrane.' The scientists are hoping that an industrial partner will take up further development.
Applications
Creating this new membrane for oil spill remediation shows the power of cooperation between a research university and an applied university. 'A while ago, we decided that the polymer groups at the two institutes should become one, by sharing students, staff and facilities. We recently started the first hybrid research group in the Netherlands,' explains Loos. This makes it easier to find applications for newly designed materials. Voet: 'Polymer chemists strive to link molecular structures to material properties and applications. Our hybrid research team has the experience to do just that.'
INFORMATION:
Reference: Chongnan Ye, Vincent S. D. Voet, Rudy Folkersma and Katja Loos: Robust Superamphiphilic Membrane with a Closed-loop Life Cycle. Advanced Materials, 7 March 2021.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-09
Study Reveals New Hope for Men With Common Urinary Issues
A new systematic review of evidence recommends the use of behavioral self-management treatments for common urinary issues experienced by upwards of 70 percent of older men. Common symptoms include trouble urinating, increased frequency and incontinence. These symptoms can have a substantial negative impact on sleep, social functioning and quality of life. Several guidelines recommend self-management techniques like health education, advice on fluid intake, and bladder retraining; however, in practice, self-management is often excluded from the menu of treatment options that include medication and surgery.
Researchers at Bond University's Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare found that ...
2021-03-09
What would a truly progressive city look like? A city that pays more than lip service to issues that directly affect low-income residents, seniors, marginalized communities and others whom neoliberal policies have seemingly left behind? ...
2021-03-09
Since 1983, the bacteria Pantoea ananatis has been known to infect several important crops including onions, rice, and corn. It was unclear, however, what molecules were involved. A new study, published in mBio, has identified one of the culprits: pantaphos. Intriguingly, the researchers have discovered that pantaphos can also act as an herbicide and it is toxic to glioblastoma cells, making it an exciting candidate for agricultural and biomedical applications.
"Herbicide resistant weeds are an issue in agriculture," said William Metcalf (MMG leader), a professor of microbiology. "Unfortunately, there hasn't been a new class of herbicide ...
2021-03-09
CHAPEL HILL, NC -- A comprehensive review by University of North Carolina researchers and colleagues of hundreds of publications, incorporating more than two dozen articles on prevention screening for lung cancer with low-dose spiral computed tomography (LDCT), shows there are both benefits and harms from screening. The review is published in JAMA on March 9, 2021.
The results of the decadelong National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) showed that LDCT could detect lung cancer better than conventional X-rays in current or previous heavy smokers. Based on those results, the United States Preventive Services ...
2021-03-09
WASHINGTON, March 9, 2021 -- The University of Minnesota School of Music was concerned about one-on-one teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic and wondered if it should supplement its ventilation system with portable HEPA air purifiers.
So, school officials reached out to Suo Yang, a professor within the College of Science and Engineering, and his team to figure it out. In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Yang and the researchers describe their work to predict how virus particles spread within a music classroom.
"The airborne transmission of COVID-19 through ...
2021-03-09
By closely examining the jaw mechanics of juvenile and adult tyrannosaurids, some of the fiercest dinosaurs to inhabit earth, scientists led by the University of Bristol have uncovered differences in how they bit into their prey.
They found that younger tyrannosaurs were incapable of delivering the bone-crunching bite that is often synonymous with the Tyrannosaurus Rex and that adult specimens were far better equipped for tearing out chunks of flesh and bone with their massive, deeply set jaws.
The team also found that tension from the insertion of the lower pterygoid muscle is linked to decreasing stresses near the front of the typical tyrannosaur jaw, where the animals may have applied their highest impact bite ...
2021-03-09
WASHINGTON, March 9, 2021 -- One of the primary ways the COVID-19 virus is transmitted is via airborne diffusion of saliva microdroplets, so it is paramount to find methods to kill the virus in airborne microdroplets.
The extreme confusion that abounded at the beginning of the pandemic about safe social distances, mask wearing, and social behavior inspired Marche Polytechnic University researchers, who happen to be intrigued by saliva droplet diffusion, to search for answers and ways to help.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, Valerio D'Alessandro and colleagues describe using a supercomputer to do numerical modeling ...
2021-03-09
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) - To minimize transmission of COVID-19, in spring 2020, most U.S. states passed policies promoting social distancing through stay-at-home orders prohibiting non-essential travel. Vehicle-miles traveled in the U.S. decreased by 41% in April 2020 compared to 2019. A new study led by researchers at the Center for Injury Research and Policy at Nationwide Children's Hospital estimated associations between COVID-19-related social-distancing policies, traffic volume, and motor vehicle crash-related outcomes in Ohio.
The study, published today in JAMA, found the number of individuals involved in a motor vehicle crash, sustaining injury, sustaining ...
2021-03-09
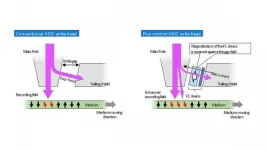
WASHINGTON, March 9, 2021 -- Researchers at Toshiba Corporation in Japan have studied the operation of a small device fabricated in the write gap of a hard disk drive's write head to extend its recording density. The device, developed by HWY Technologies, is based on a design concept known as microwave-assisted magnetic recording, or MAMR.
This technology, reported in the Journal of Applied Physics, by AIP Publishing, uses a microwave field generator known as a spin-torque oscillator. The spin-torque oscillator emits a microwave field causing the magnetic particles of the recording medium to wobble the way a spinning top does. This makes them much easier to flip over when the write head applies a recording magnetic ...
2021-03-09
People over 65 shouldn't take three or more medicines that act on their brain and nervous system, experts strongly warn, because the drugs can interact and raise the risk of everything from falls to overdoses to memory issues.
But a new study finds that 1 in 7 people with dementia who live outside nursing homes are taking at least three of these drugs.
Even if they received the drugs to calm some of dementia's more troubling behavioral issues, the researchers say, taking them in combination could accelerate their loss of memory and thinking ability, and raise their chance of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Recyclable bioplastic membrane to clear oil spills from water