Study reveals new hope for men with common urinary issues
2021-03-09
(Press-News.org) A new systematic review of evidence recommends the use of behavioral self-management treatments for common urinary issues experienced by upwards of 70 percent of older men. Common symptoms include trouble urinating, increased frequency and incontinence. These symptoms can have a substantial negative impact on sleep, social functioning and quality of life. Several guidelines recommend self-management techniques like health education, advice on fluid intake, and bladder retraining; however, in practice, self-management is often excluded from the menu of treatment options that include medication and surgery.
Researchers at Bond University's Institute for Evidence-Based Healthcare found that self-management interventions reduced the severity of lower urinary tract symptoms. The reduction in symptoms appeared similar in groups receiving medications versus self-management interventions. However, compared with drugs alone, individuals who had both drug and self-management intervention experienced a small but meaningful reduction in symptom severity after six weeks. The authors recommend further research to determine the optimal components and delivery methods for self-management interventions so that these strategies can become standard options for men with lower urinary tract symptoms.
INFORMATION:
Self-Management for Men With Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Loai Albarqouni, MD, MSc, PhD, et al
Bond University, Queensland, Australia
https://www.annfammed.org/content/19/2/157
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-09
Wormholes play a key role in many science fiction films - often as a shortcut between two distant points in space. In physics, however, these tunnels in spacetime have remained purely hypothetical. An international team led by Dr. Jose Luis Blázquez-Salcedo of the University of Oldenburg has now presented a new theoretical model in the science journal Physical Review Letters that makes microscopic wormholes seem less far-fetched than in previous theories.
Wormholes, like black holes, appear in the equations of Albert Einstein's general theory ...
2021-03-09
A mobile app designed to help women manage urinary incontinence was as effective as usual, in-person treatment of incontinence in primary care, according to new research from the Netherlands. The study included 262 women with frequent stress incontinence, overactive bladder or a mix of symptoms. Participants were randomly assigned to use a standalone mobile app called URinControl, which offered pelvic floor muscle and bladder training exercises. Those in a control group received standard care and were referred to their own primary care doctors who were broadly advised to follow the Dutch guidelines for primary care. After four months, ...
2021-03-09
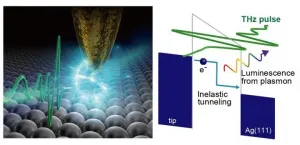
Since the early 2010s, ultrafast probing of materials at atomic-level resolution has been enabled by terahertz scanning tunneling microscopes (THz-STM). But these devices can't detect the dissipation of energy that happens during events such as when photons are emitted via recombination process of an electron-hole pair in a light emitting diode (LED). However, a new technique allows the tracking of just such energy dynamics alongside THz-STM, opening up new avenues of investigation for nanoscale science and technology.
Researchers in Japan have developed a microscopy technique that combines the ability to manipulate the motion of electrons on a femtosecond timescale ...
2021-03-09
According to two national surveys by researchers at the University of Michigan Medical School, US teens and young adults are engaged in the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic with most being knowledgeable about the disease, concerned about its impacts on others, and practicing social distancing. On March 6, 2020, 70 percent reported knowledge of the pandemic, with 46 percent noting they got information from news sources. By March 20, 2020, nearly all respondents, 95 percent, reported impact. Worry about the pandemic increased from 25 to 51 percent. For some young people who weren't worried early on about the pandemic, staying at home and engaging in other preventive public health guidelines made them feel safer. Between the two surveys, pandemic preparation seemed to shift. ...
2021-03-09
Evidence published in the Cochrane Library today will reassure people who want to stop smoking that quitting for at least 6 weeks may improve their mental wellbeing, by reducing anxiety, depression, and stress. People's social relationships are unlikely to suffer if they stop smoking.
Smoking is the world's leading cause of preventable illness and death. One in every two people who smoke will die of a smoking-related disease unless they quit. Some people believe that smoking helps reduce stress and other mental health symptoms, and that quitting smoking might make their mental health problems worse. People who smoke may also worry that stopping smoking will have a negative impact on their social lives and friendships.
The review found that people who stopped smoking for at least 6 weeks ...
2021-03-09
CHAPEL HILL, NC -- Calling the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force's newly released recommendation statement to expand eligibility for annual lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography a step forward, UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center researchers say future changes should address equity and implementation issues.
In an editorial published in JAMA, Louise M. Henderson, PhD, professor of radiology at UNC School of Medicine, M. Patricia Rivera, MD, professor of medicine at UNC School of Medicine, and Ethan Basch, MD, MSc, the Richard M. Goldberg Distinguished Professor in Medical Oncology and chief of oncology at the UNC School of Medicine, outlined their concerns and offered potential approaches to make the screening recommendation ...
2021-03-09
Researchers have come up with a better way to test which fabrics work best for masks that are meant to slow the spread of COVID-19. By testing those fabrics under conditions that mimic the humidity of a person's breath, the researchers have obtained measurements that more accurately reflect how the fabrics perform when worn by a living, breathing person.
The new measurements show that under humid conditions, the filtration efficiency -- a measure of how well a material captures particles -- increased by an average of 33% in cotton fabrics. Synthetic fabrics performed poorly relative to cotton, and their performance did not improve with humidity. The material from medical-procedure masks also did not improve with humidity, though it performed ...
2021-03-09
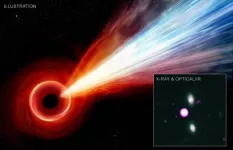
Astronomers have discovered evidence for an extraordinarily long jet of particles coming from a supermassive black hole in the early universe, using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory.
If confirmed, it would be the most distant supermassive black hole with a jet detected in X-rays. Coming from a galaxy about 12.7 billion light-years from Earth, the jet may help explain how the biggest black holes formed at a very early time in the universe's history.
The source of the jet is a quasar - a rapidly growing supermassive black hole - named PSO J352.4034-15.3373 (PJ352-15 for short), which sits ...
2021-03-09
Most teenagers don't remember life before the internet. They have grown up in a connected world, and being online has become one of their main sources of learning, entertaining and socializing.
As many previous studies have pointed out, and as many parents worry, this reality does not come risk-free. Whereas time on the internet can be informative, instructive and even pleasant, there is already significant literature on the potential harm caused by young children's problematic internet use (PIU).
However, a new study led by END ...
2021-03-09
"It was clear that the greater an individual's sensitivity to motion parallax cues, the more severe the motion sickness symptoms," says lead NYU Abu Dhabi researcher
Fast facts:
The visual system is often studied in relative isolation, but it has clear connections to other components of the nervous system.
A notable example of this is motion sickness, which affects certain people much more severely than others.
Motion sickness is typically associated with traveling in cars, boats, and airplanes, however discomfort or "cybersickness" also arises with technological use such as in virtual reality (VR).
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 9, 2021: A new study led by Head of the Rokers Vision Laboratory and NYUAD Associate Professor of Psychology Bas Rokers explored why ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reveals new hope for men with common urinary issues