Researchers develop a new, efficient tin monosulfide solar cell prototype
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) A team of researchers from Tohoku University have created a tin monosulfide (SnS) solar cell that boasts attractive performance levels, promoting affordable and clean energy and moving society closer to achieving the UN's sustainable development goals.
Their results were published in the journal Solar RRL on February 25, 2021.
Current thin film solar cells often use cadmium telluride and copper indium gallium selenide to induce the photovoltaic effect. However, these materials contain rare and toxic elements. In contrast, tin and sulfur are abundant, easy to refine and non-toxic.
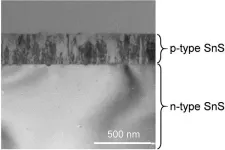
The key to high efficiency SnS solar cells lies within the p-n homojunction. P-type SnS is easy to fabricate, but the same cannot be said of n-type SnS. The complexity of fabricating n-type SnS has stalled the manufacturing of the p-n homojunction for SnS solar cells.
However, the team, led by Sakiko Kawanishi and Issei Suzuki from Tohoku University's Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, overcame this barrier and fabricated a p-n homojunction by using a large n-type SnS single crystals. The large crystals were grown using an original technique released in August 2020.
The newly created solar cell's open circuit voltage, which contributes to the conversion efficiency, recorded 360 mV even with no device optimization.
"This is remarkable since this is only our first prototype, yet it still recorded the comparable open circuit voltage as previously reported heterojunction SnS-based devices," said Kawanishi.
Although the conversion efficiency of the "first" device is still 1.4%, it is expected to surpass the best efficiency of the heterojunction devices (?5%) rapidly through device optimization.
Kawanishi adds, "Our group believes this significant first achievement further accelerates the future development for SnS solar cells' practical application."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-10
Photosynthetic organisms harvest light from the sun to produce the energy they need to survive. A new paper published by University of Chicago researchers reveals their secret: exploiting quantum mechanics.
"Before this study, the scientific community saw quantum signatures generated in biological systems and asked the question, were these results just a consequence of biology being built from molecules, or did they have a purpose?" said Greg Engel, Professor of Chemistry and senior author on the study. "This is the first time we are seeing biology actively exploiting quantum effects."
The scientists studied a type of microorganism called green sulfur bacteria. These bacteria need light to survive, but even small amounts of oxygen can damage their delicate photosynthetic equipment. ...
2021-03-10
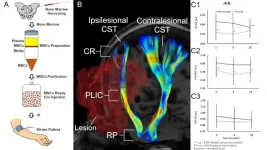
Durham, NC - Results of a clinical trial released in STEM CELLS Translational Medicine provide evidence that treating patients with an injection of bone marrow cells may lead to a reduction in brain injury after a stroke.
The study was conducted by Muhammad E. Haque, Ph.D., Sean I. Savitz, M.D., and colleagues from the Institute for Stroke and Cerebrovascular Disease at The University of Texas Health Science Center in Houston. "Nearly 90 percent of patients who suffer an ischemic stroke - the most common type of stroke - exhibit weakness or paralysis to one side of the body," Dr. Haque said. "Injuries to the corticospinal tract (CST), which is ...
2021-03-10
NASA's Perseverance Rover recently made a successful landing on Mars, embarking on a two-year mission to seek signs of ancient life and collect samples. Because Mars is extremely cold -- nighttime temperatures can drop below -112 F -- heaters are required to keep the rover's battery system from freezing. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Nano Letters have 3D printed porous carbon aerogels for electrodes in ultralow-temperature supercapacitors, reducing heating needs for future space and polar missions.
Jennifer Lu, Yat Li and colleagues wanted to develop an energy storage system that could operate at very low temperatures without heating units, which add weight and energy requirements ...
2021-03-10
A recent study on spectacular fossil plants preserved in a volcanic ash fall deposit--known as China's "vegetational Pompeii," in Inner Mongolia, China--has resolved a mystery that puzzled palaeontology for over a century: What are Noeggerathiales?
The study, published in PNAS on March 8, was led by Prof. WANG Jun from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) and by Prof. David Dilcher from Indiana University (USA). Researchers from the UK, Czech Republic and Austria were also involved.
The researchers confirmed that Noeggerathiales had the spore propagation mode of ferns and the vascular tissue of seed plants. They belonged to a sister group of seed plants, the former gymnosperm.
Noeggerathiales ...
2021-03-10
Poor oral hygiene produces gum-disease bacteria and accelerates oral microbiome aging faster than previously thought.
A new study shows that within 24-72 hours of the interruption of oral hygiene, there was a steep decrease in the presence of 'good oral bacteria' and the beneficial anti-inflammatory chemicals they are associated with. An increase of 'bad bacteria' typically present in the mouths of patients with periodontitis, a severe gum disease which can lead to tooth damage or loss, was also discovered.
The research team, led by scientists from Single-Cell Center, Qingdao Institute of BioEnergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and Procter & Gamble Company (P&G), published their findings in the journal mBio on Mar. 9, 2021.
The ...
2021-03-10
Material behaviors depend on many things including not just the composition of the material but also the arrangement of its molecular parts. For the first time, researchers have found a way to coax carbon nanotubes into creating moiré patterns. Such structures could be useful in materials research, in particular in the field of superconducting materials.
Professor Hiroyuki Isobe from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Tokyo, and his team create nanoscopic material structures, primarily from carbon. Their aim is to explore new ways to create carbon nanostructures and to find useful applications for them. The most recent breakthrough from their lab is a new form of carbon nanotube with a very specific arrangement ...
2021-03-10
The slowdown in global warming that was observed at the end of last century was reflected by a decrease in malaria transmission in the Ethiopian highlands, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by "la Caixa" Foundation, and the University of Chicago. The results, published in Nature Communications, underscore the close connection between climate and health.
For several years there has been a heated debate on the impact of global warming on malaria incidence. It is believed that the largest effect could occur in the highlands, where lower temperatures ...
2021-03-10
The human brain is less accessible than other organs because it is covered by a thick, hard skull. As a result, researches have been limited to low-resolution imaging or analysis of brain signals measured outside the skull. This has proved to be a major hindrance in brain research, including research on the different developmental stages, causes of diseases, and their treatments. Recently, studies have been performed using primary neurons from rats or human-derived *induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to create artificial brain models that have been applied to investigate brain developmental ...
2021-03-10
First grade teachers can find out who is on track with math and who is lagging, using an accurate diagnostic test that they can administer in the classroom.
After Covid-19 school reopening, or during catch-up sessions in the holidays, this is instrument can also be useful, especially in large, multilingual classrooms.
The test is supplemented by a 15-week 1-hour-a week "maths boost" invention program for first graders.
The program provides teachers good instructional material to support children in an efficient way.
Uniquely, the test measures numeracy skills along with listening comprehension and executive functions, pinpointing additional reasons why students improve ...
2021-03-10
Researchers from University of Texas-Arlington, University of Virginia, Sun Yat-Sen University, and University of Washington published a new paper in the Journal of Marketing that seeks to advance the discipline of avatar-based marketing.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled "An Emerging Theory of Avatar Marketing" and is authored by Fred Miao, Irina Kozlenkova, Haizhong Wang, Tao Xie, and Robert Palmatier.
In 2020, Samsung's Star Labs brought digital avatars to CES 2020. However, this promotion was burned by its own fanfare. The avatars looked realistic ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop a new, efficient tin monosulfide solar cell prototype