Reflecting on your own capabilities boosts resilience
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) The unpredictable nature of life during the coronavirus pandemic is particularly challenging for many people. Not everyone can cope equally well with the uncertainty and loss of control. Research has shown that while a large segment of the population turns out to be resilient in times of stress and potentially traumatic events, others are less robust and develop stress-related illnesses. Events that some people experience as draining seem to be a source of motivation and creativity for others.
These differing degrees of resilience demonstrate that people recover from stressful events at different rates, with psychosocial factors such as positivity, optimism, the ability to self-regulate, social skills, problem-solving skills and social support playing a role. A team from the Department of Psychology and the University Hospital of Psychiatry Zurich teamed up with researchers from New York to investigate how people can strengthen their psychological resilience when facing adversity.
Importance of believing in your own power
"Self-efficacy is a key element of resilience," explains Birgit Kleim, professor of psychology at UZH and director of the study. "By self-efficacy, I mean the belief that we have the ability to influence things to at least a small degree, even if some things are unchangeable." A self-efficacious person is convinced that they can draw on their own powers to overcome difficult and challenging situations. It doesn't matter whether this is actually the case, as Kleim explains: "Without believing in your own capabilities, you wouldn't take on any challenges in the first place." Self-efficacious people have stronger problem-solving abilities and a higher level of persistence. They also show changes in brain activation in regions linked to emotional regulation.
How might it be possible, then, to boost people's self-efficacy so that they can harness its positive powers in the coronavirus era? For the resilience study, a team of researchers examined 75 people who were distressed by a negative emotional memory. Before recalling and reassessing this distressing memory, one group of subjects was instructed to vividly recall a positive event such as a beautiful experience in nature or a joyful encounter with others. The others were instructed to think of a time in which they felt they were particularly self-efficacious: situations such as having a successful conversation, passing a difficult exam or giving a presentation. In many cases, doing this exercise just once was already enough to achieve a positive effect.
Recalling autobiographical self-efficacy yields dramatic effects
"Recalling a specific instance of one's own self-efficacy proved to have a far greater impact than recalling a positive event," says Kleim. People who actively recalled their own self-efficacious behavior found it easier to reassess a negative situation and view it in a different light. They perceived the negative experience as less distressing than the subjects who were instructed to reflect on a positive memory unconnected to self-efficacy.
"Our study shows that recalling self-efficacious autobiographical events can be used as a tool both in everyday life and in clinical settings to boost personal resilience," explains the research team. It may be possible to strategically use memories of overcoming past challenges as a way of coping with crisis situations. This also applies to the coronavirus crisis, where these memories can be used to shield against the negative impacts of the pandemic.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-10
In a study recently published in Nature Communications, scientists from The Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Biosustainability (DTU) and Yale University have investigated how bacteria that are commonly found in sugarcane ethanol fermentation affect the industrial process. By closely studying the interactions between yeast and bacteria, it is suggested that the industry could improve both its total yield and the cost of the fermentation processes by paying more attention to the diversity of the microbial communities and choosing between good and bad bacteria.
The scientists dissected yeast-bacteria interactions in sugarcane ethanol fermentation by reconstituting every possible combination ...
2021-03-10
Fuel cells, which are attracting attention as an eco-friendly energy source, obtain electricity and heat simultaneously through the reverse reaction of water electrolysis. Therefore, the catalyst that enhances the reaction efficiency is directly connected to the performance of the fuel cell. To this, a POSTECH-UNIST joint research team has taken a step closer to developing high-performance catalysts by uncovering the ex-solution and phase transition phenomena at the atomic level for the first time.
A joint research team of Professor Jeong Woo Han and Ph.D. candidate Kyeounghak Kim of POSTECH's Department of Chemical Engineering, and Professor Guntae Kim of UNIST have uncovered the mechanism by which PBMO - a catalyst used ...
2021-03-10
Italian and Russian researchers confirmed the hypothesis that the self-maintaining order in eukaryotic cells (cells with nuclei) is a result of two spontaneous mechanisms' collaboration. Similar molecules gather into 'drops' on the membrane and then leave it as tiny vesicles enriched by the collected molecules. The paper with the research results was published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
The research was carried out by an international interdisciplinary team of biologists (from Polytechnic University of Turin, Italian Institute for Genomic Medicine of the University of Turin and Candiolo Cancer Institute) and ...
2021-03-10
Variant B.1.1.7 of COVID-19 associated with a significantly higher mortality rate, research shows
The highly infectious variant of COVID-19 discovered in Kent, which swept across the UK last year before spreading worldwide, is between 30 and 100 per cent more deadly than previous strains, new analysis has shown.
A pivotal study, by epidemiologists from the Universities of Exeter and Bristol, has shown that the SARS-CoV-2 variant, B.1.1.7, is associated with a significantly higher mortality rate amongst adults diagnosed in the community compared to previously circulating strains.
The study compared death rates among people infected ...
2021-03-10
Newly published research has revealed a close link between proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease and age-related sight loss. The findings could open the way to new treatments for patients with deteriorating vision and through this study, the scientists believe they could reduce the need for using animals in future research into blinding conditions.
Amyloid beta (AB) proteins are the primary driver of Alzheimer's disease but also begin to collect in the retina as people get older. Donor eyes from patients who suffered from age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the most common cause of blindness amongst adults in the UK, have been shown to contain high levels of AB in their retinas.
This new study, published in the journal Cells, builds on previous ...
2021-03-10
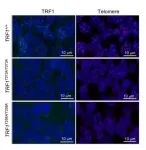
The Telomeres and Telomerase Group led by Maria A. Blasco at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) continues to make progress in unravelling the role that telomeres -the ends of chromosomes that are responsible for cellular ageing as they shorten- play in cancer. The CNIO team was among the first to propose that shelterins, proteins that wrap around telomeres and act as a protective shield, might be therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. Subsequently, they found that eliminating one of these shelterins, TRF1, blocks the initiation and progression of lung cancer and glioblastoma in mouse models and prevents glioblastoma stem cells from forming secondary tumours. Now, in a study published in PLOS Genetics, ...
2021-03-10
People with aphantasia - that is, the inability to visualise mental images - are harder to spook with scary stories, a new UNSW Sydney study shows.
The study, published today in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, tested how aphantasic people reacted to reading distressing scenarios, like being chased by a shark, falling off a cliff, or being in a plane that's about to crash.
The researchers were able to physically measure each participant's fear response by monitoring changing skin conductivity levels - in other words, how much the story made a person sweat. This type of test is commonly ...
2021-03-10
WESTMINSTER, Colorado - March 10, 2021 - The paperbark tree (Melaleuca quinquenervia) was introduced to the U.S. from Australia in the 1900s. Unfortunately, it went on to become a weedy invader that has dominated natural landscapes across southern Florida, including the fragile wetlands of the Everglades.
According to an article in the journal END ...
2021-03-10
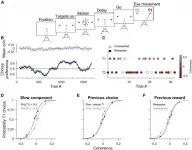
ften, humans display biases, i.e., unconscious tendencies towards a type of decision. Despite decades of study, we are yet to discover why biases are so persistent in all types of decisions. "Biases can help us make better decisions when we use them correctly in an action that has previously given us great reward. However, in other cases, biases can play against us, such as when we repeat actions in situations when it would be better not to", says Rubén Moreno Bote, coordinator of the UPF Theoretical and Cognitive Neuroscience Laboratory.
In these cases, decisions are guided by tendencies, or inclinations, that do not benefit our wellbeing. For example, playing the lottery more regularly after winning ...
2021-03-10
Recent studies estimate that we use an astounding 129 billion face masks globally every month - that is 3 million a minute. Most of them are disposable face masks made from plastic microfibers.
- With increasing reports on inappropriate disposal of masks, it is urgent to recognize this potential environmental threat and prevent it from becoming the next plastic problem, researchers warn in a comment in the scientific journal Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering.
The researchers are Environmental Toxicologist Elvis Genbo Xu from University of Southern Denmark and Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Reflecting on your own capabilities boosts resilience