The important role of music in neurorehabilitation: Filling in critical gaps
Experts highlight current gaps in clinical applications of music therapy in this theme issue of NeuroRehabilitation
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) Amsterdam, NL, March 10, 2021 - Music-based interventions have become a core ingredient of effective neurorehabilitation in the past 20 years thanks to the growing body of knowledge. In this END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New technology could increase health inequities
2021-03-10
People are different. New technology is good for patients and the healthcare system. But it could also expand the already significant health disparities in Norway and other countries.
"Women and men with higher education in Norway live five to six years longer than people with that only have lower secondary school education," says Emil Øversveen, a postdoctoral fellow at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Sociology and Political Science.
He is affiliated with CHAIN, the Centre for Global Health Inequalities Research. The centre works to reduce social health ...
Manure improves soil and microbe community
2021-03-10
In the dry air and soil of Texas' Southern High Plains, improving soil health can be tough. We usually think of healthy soil as moist and loose with lots of organic matter. But this can be hard to achieve in this arid area of Texas.
Lindsey Slaughter, a member of the Soil Science Society of America, set out with her fellow researchers to test a solution that kills two birds with one stone. They put excess cow manure on these soils to see if they could make them healthier.
The team recently published their research in the Soil Science Society of America Journal.
"We know that planting perennial grasslands for cattle production can help protect and restore soil in semi-arid lands that are likely to erode and degrade from intense ...
As cases spread across US last year, pattern emerged suggesting link between governors' party affiliation and COVID-19 case and death numbers
2021-03-10
The per-capita rates of new COVID-19 cases and COVID-19 deaths were higher in states with Democrat governors in the first months of the pandemic last year, but became much higher in states with Republican governors by mid-summer and through 2020, possibly reflecting COVID-19 policy differences between GOP- and Democrat-led states, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Medical University of South Carolina.
For their study, the researchers analyzed data on SARS-CoV-2-positive nasal swab tests, COVID-19 diagnoses, and COVID-19 ...
How a receptor shapes the immune response
2021-03-10
Immune cells specialize to ensure the most efficient defense against viruses and other pathogens. Researchers at the University of Basel have shed light on this specialization of T cells and shown that it occurs differently in the context of an acute and a chronic infection. This could be relevant for new approaches against chronic viral infections.
Researchers led by Professor Carolyn King of the University of Basel have developed a method to study the specialization of T cells in the context of infections. In the journal eLife, they report the different directions ...
Material from Russia will triple the capacity of lithium-ion batteries
2021-03-10
The scientists of the National University of Science and Technology "MISIS" (NUST MISIS) being a part of an international team of researches managed to increase the capacity and extend the service life of lithium-ion batteries. According to the researchers, they have synthesized a new nanomaterial that can replace low-efficiency graphite used in lithium-ion batteries today. The results of the research are published in the Journal of Alloys and Compounds.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used for household appliances from smartphones to electric vehicles. The charge-discharge cycle in such battery is provided by ...
'Lost' ocean nanoplastic might be getting trapped on coasts
2021-03-10
As plastic debris weathers in aquatic environments, it can shed tiny nanoplastics. Although scientists have a good understanding of how these particles form, they still don't have a good grasp of where all the fragments end up. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have shown experimentally that most nanoplastics in estuarine waters can clump, forming larger clusters that either settle or stick to solid objects, instead of floating on into the ocean.
There is a huge discrepancy between the millions of tons of plastic waste entering rivers and streams and the amount researchers have found in the oceans. As large pieces of plastic break apart into ...
Study of mosquito protein could lead to treatments against life-threatening viruses
2021-03-10
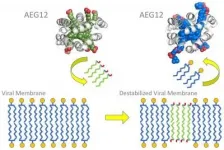
The mosquito protein AEG12 strongly inhibits the family of viruses that cause yellow fever, dengue, West Nile, and Zika and weakly inhibits coronaviruses, according to scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators. The researchers found that AEG12 works by destabilizing the viral envelope, breaking its protective covering. Although the protein does not affect viruses that do not have an envelope, such as those that cause pink eye and bladder infections, the findings could lead to therapeutics against viruses that affect millions of people around the world. The research ...
The quest for sustainable leather alternatives
2021-03-10
Throughout history, leather has been a popular material for clothes and many other goods. However, the tanning process and use of livestock mean that it has a large environmental footprint, leading consumers and manufacturers alike to seek out alternatives. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, details how sustainable materials are giving traditional leather a run for its money.
Traditional leather goods are known for their durability, flexibility and attractive finish, with a global market worth billions, writes ...
University of Minnesota scientists discover attacking fungi that show promise against emerald ash borer
2021-03-10
Since its introduction, the emerald ash borer (EAB) has become the most devastating invasive forest insect in the United States, killing hundreds of millions of ash trees at a cost of hundreds of millions of dollars.
Now, new research from the University of Minnesota's Minnesota Invasive Terrestrial Plants and Pests Center (MITPPC) shows a possible path forward in controlling the invasive pest that threatens Minnesota's nearly one billion ash trees.
In a recent study published in Fungal Biology, MITPPC researchers identified various fungi living in EAB-infested trees -- a critical ...
Producing highly efficient LEDs based on 2D perovskite films
2021-03-10
Energy-efficient light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have been used in our everyday life for many decades. But the quest for better LEDs, offering both lower costs and brighter colours, has recently drawn scientists to a material called perovskite. A recent joint-research project co-led by the scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has now developed a 2D perovskite material for the most efficient LEDs.
From household lighting to mobile phone displays, from pinpoint lighting needed for endoscopy procedures to light source to grow vegetables in Space, LEDs ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
[Press-News.org] The important role of music in neurorehabilitation: Filling in critical gapsExperts highlight current gaps in clinical applications of music therapy in this theme issue of NeuroRehabilitation