(Press-News.org) Healthcare personnel who were infected with COVID-19 had stronger risk factors outside the workplace than in their hospital or healthcare setting. That is the finding of a new study published today in JAMA Network Open conducted by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers, colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and three other universities.
The study examined survey data from nearly 25,000 healthcare providers in Baltimore, Atlanta, and Chicago including at University of Maryland Medical System (UMMS) hospitals. They found that having a known exposure to someone who tested positive for COVID-19 in the community was the strongest risk factor for testing positive for COVID-19. Living in a zip code with a high COVID-19 cumulative incidence was also a strong risk factor.
"The news is reassuring in that it shows the measures taken are working to prevent infections from spreading in healthcare facilities," said study co-author Anthony Harris, MD, MPH, Professor of Epidemiology & Public Health at UMSOM. "Vaccination for healthcare workers, however, should remain a priority because of continual exposures in the workplace. There is also an urgent need to keep healthcare providers healthy so they can care for sick patients and reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to vulnerable patients."
Researchers from Emory University School of Medicine and Rollins School of Public Health in Atlanta, Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, and Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine also participated in this study. UMSOM faculty Robert Christenson, PhD, Brent King, MD, Surbhi Leekha, MBBS, Lyndsay O'Hara, PhD, Peter Rock, MD, MBA, and Gregory Schrank, MD, were co-authors on this study. The study was funded by CDC's Prevention Epicenters Program.
"Factors presumed to contribute most to infection risk among healthcare providers, including caring for COVID-19 patients, were not associated with increased risk in this study," said study co-author Sujan Reddy MD, an infectious disease specialist at the CDC. "The highest risks to healthcare workers may be from exposures in the community."
The study did, however, have some important caveats. Since infection control practices were not standardized across the various healthcare sites, the study could not determine the level of effectiveness of personal protective equipment (N95 respirator, surgical mask, gowns, face shields). Nor could the study determine whether certain infection control practices, such as frequent disinfection of surfaces in exam rooms, were better than others in preventing infection spread.
Confirming evidence from other studies, this study found that Black Americans who were healthcare personnel were more likely to test positive for COVID-19 infections than their white counterparts. This may be due to existing disparities in community exposure rather than from healthcare-associated exposures.
"We're proud of this very important collaborative clinical work with our research colleagues," said Mohan Suntha, MD, MBA, President and CEO of UMMS. "We have made the safety of our team members a top priority throughout this pandemic, and it is incredibly gratifying to see that our efforts to prevent the spread of COVID-19 in hospitals have worked. This is also another example of the importance of the partnership between our academic-focused health care System and the groundbreaking discovery-based medicine work happening every day at the UM School of Medicine."
"As front-line and support staff at hospitals and health systems continue to tirelessly battle COVID-19, they can draw reassurance in this important research finding that the infection control measures in place protected themselves and their families," said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, UM Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, University of Maryland School of Medicine. "We need to know that we are doing all we can to protect our healthcare heroes, from providing them with adequate protective gear to giving them early access to vaccines."
INFORMATION:
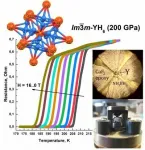
An international team led by Artem R. Oganov, a Professor at Skoltech and MISIS, and Dr. Ivan Troyan from the Institute of Crystallography of RAS performed theoretical and experimental research on a new high-temperature superconductor, yttrium hydride (YH6). Their findings were published in the journal Advanced Materials.
Yttrium hydrides rank among the three highest-temperature superconductors known to date. The leader among the three is a material with an unknown S-C-H composition and superconductivity at 288 K, which is followed by lanthanum hydride, LaH10, superconducting at temperatures up to 259 K), and, finally, yttrium hydrides, YH6 and YH9, with maximum superconductivity temperatures of 224 K and 243 K, respectively. The superconductivity of YH6 ...
Boston - A new study shows that providing a non-acute care space after hospital discharge for patients with COVID-19 who are experiencing homelessness helped reduce hospitalizations and keep inpatient beds available for those requiring acute care. Published in JAMA Network Open and led by researchers at Boston Medical Center's (BMC) Grayken Center for Addiction, the study demonstrates the importance of developing innovative approaches to tackle issues facing people experiencing homelessness, including their inability to isolate, in order to mitigate additional ...
Associations between strong predictors of suicidal behaviors over the life course, such as adverse childhood events (ACEs), remain understudied among youth of color. Although not previously considered high risk, suicide attempts among Black youth increased 73% between 1991 and 2017.
Published in the Children and Youth Services Review, University of Minnesota researchers pulled data from the 2016 Minnesota Student Survey (MSS) to examine associations between ACEs, school connectedness and suicide ideation and attempts among Somali, Latino, Hmong and Non-Hispanic ...
Research published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry shows that the presence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in bald eagle populations is slowly declining. Bald eagles are apex predators that nest and, more importantly, feed along water bodies, making them excellent bioindicators of environmental contaminants that bioaccumulate up the aquatic food web. The findings are both good news for eagles and instructive for regulators tasked with managing surface water quality by setting protective levels for wildlife, as well as fish consumption advisories for humans.
Lead author Bill Route from the National ...
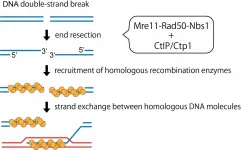
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have uncovered mechanisms underlying the activation of the MRN complex-- the cell's DNA scissors. Using purified yeast proteins, they demonstrated that phosphorylation of Ctp1, a homolog of a tumor-suppressor protein, plays a key role in activating MRN complex's DNA clipping activity. Intriguingly, a short segment of yeast Ctp1 or its human counterpart could stimulate endonuclease activity of their respective MRN complexes, suggesting its conserved function across species.
DNA functions as a roadmap that guides the identity and functions of cells. A glitch in the DNA ...
BINGHAMTON, NY -- Star employees often get most of the credit when things go right, but also shoulder most of the blame when things go wrong, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The study explored the potential risks and rewards of collaborating with stars - individuals who have a reputation for exhibiting exceptional performance - and how individual performance factors into how much credit and blame is shared with collaborators.
"Stars are human, and they fail from time to time. We wanted to shift the focus away from stars, and find out what happens to the people who collaborate ...
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Geoscientists at Sandia National Laboratories used 3D-printed rocks and an advanced, large-scale computer model of past earthquakes to understand and prevent earthquakes triggered by energy exploration.
Injecting water underground after unconventional oil and gas extraction, commonly known as fracking, geothermal energy stimulation and carbon dioxide sequestration all can trigger earthquakes. Of course, energy companies do their due diligence to check for faults -- breaks in the earth's upper crust that are prone to earthquakes -- but sometimes ...
Eye contact is a key to establishing a connection, and teachers use it often to encourage participation. But can a robot do this too? Can it draw a response simply by making "eye" contact, even with people who are less inclined to speak up. A recent study suggests that it can.
Researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology published results of experiments in which robots led a Swedish word game with individuals whose proficiency in the Nordic language was varied. They found that by redirecting its gaze to less proficient players, a robot can elicit involvement from even the most reluctant participants.
Researchers Sarah Gillet and Ronald Cumbal say the results offer evidence that robots could play a productive role in educational settings.
Calling on someone by name isn't ...
The protein α-synuclein is one of the most abundant proteins in the human brain. It is often referred to as the "Parkinson protein", as deposition of this protein in brain cells is a hallmark of Parkinson's disease. Despite the high interest of biomedical research in the protein, many questions concerning the function and physiology of α-synuclein in living cells still remain to be answered. For example, it was previously unclear whether and to what extent the protein binds to and interacts with internal cell components such as membranes. As such processes could play a role in the development of the disease, the team led by Konstanz-based physical chemist Professor Malte Drescher used the further development of an established measurement method called ...
An article published by the researchers of the Biodiversity Unit at the University of Turku, Finland, highlights how amateur venom-extraction business is threatening scorpion species. Sustainably produced scorpion venoms are important, for example, in the pharmacological industry. However, in the recent years, there has been a dramatic increase in the number of people involved in the trade and vast numbers of scorpions are harvested from nature. This development is endangering the future of several scorpion species in a number of areas.
Scorpions have existed on Earth for over 430 million years. Currently comprising over 2,500 extant species, scorpions occur on almost all the major landmasses in a range of habitats from ...