Recuperation unit decreased hospitalizations of homeless individuals with COVID-19
2021-03-10
(Press-News.org) Boston - A new study shows that providing a non-acute care space after hospital discharge for patients with COVID-19 who are experiencing homelessness helped reduce hospitalizations and keep inpatient beds available for those requiring acute care. Published in JAMA Network Open and led by researchers at Boston Medical Center's (BMC) Grayken Center for Addiction, the study demonstrates the importance of developing innovative approaches to tackle issues facing people experiencing homelessness, including their inability to isolate, in order to mitigate additional COVID-19 exposure while simultaneously alleviating the strain on hospitals during surge situations.
Approximately nine percent of BMC patients experience homelessness, who also as a group have higher rates of mental health and substance use disorders than the general population. When diagnosed with COVID-19, people are told to isolate for a period of seven to 14 days in order to minimize exposure to others. However, for individuals experiencing homelessness and who live in a shelter or in a congregate setting, isolation is rarely an option.
"Early on in the pandemic, we recognized that we needed to be proactive in addressing the risk of COVID-19 exposure and spread among people experiencing homelessness. We also knew we had to act quickly as we saw rates of COVID-19 skyrocketing in Boston and globally," said Joshua Barocas, MD, an infectious disease physician at BMC and the study's corresponding author. In collaboration with the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, BMC established and opened the COVID Recuperation Unit (CRU) in a facility close to the hospital in early April 2020. The unit treated patients discharged from BMC who did not require acute care, providing a place to safely isolate and recover from COVID-19 in a medically supervised setting. In addition, staff on site at the CRU were also trained to help patients manage their substance use disorders, recognize medical emergencies, and address mental health concerns.
The researchers analyzed data from BMC's daily COVID-19 hospitalization census between March 1 and June 4, 2020. Between that time period, 8,864 patients were admitted to BMC (13.2 percent were people experiencing homelessness) and 226 patients were admitted to the CRU (84 percent were people experiencing homelessness). Among patients experiencing homelessness diagnosed with COVID-19, there was a 28 percent reduction in hospitalizations at BMC after the CRU opened.
"Our study indicates the need to think outside the box and develop cross-sector partnerships in order to improve public health responses in the future," added Barocas, who is also assistant professor of medicine at Boston University School of Medicine. "Our approach helped the hospital during a crucial time when space and resources were limited. Beyond that, however, we were able to engage with our patients and provide services that they needed for issues beyond COVID-19. Meeting patients where they are at is critical to improve outcomes--pandemic or no pandemic."
INFORMATION:
This study was supported in part through funding from the National Institutes of Health (R01 GM122876 04S1).
About Boston Medical Center
Boston Medical Center (BMC) is a private, not-for-profit, 514-bed, academic medical center that is the primary teaching affiliate of Boston University School of Medicine. It is the largest and busiest provider of trauma and emergency services in New England. BMC offers specialized care for complex health problems and is a leading research institution, receiving more than $166 million in sponsored research funding in fiscal year 2019. It is the 13th largest funding recipient in the U.S. from the National Institutes of Health among independent hospitals. In 1997, BMC founded Boston Medical Center Health Plan, Inc., now one of the top ranked Medicaid MCOs in the country, as a non-profit managed care organization. Boston Medical Center and Boston University School of Medicine are partners in Boston HealthNet - 12 community health centers focused on providing exceptional health care to residents of Boston. For more information, please visit http://www.bmc.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-10
Associations between strong predictors of suicidal behaviors over the life course, such as adverse childhood events (ACEs), remain understudied among youth of color. Although not previously considered high risk, suicide attempts among Black youth increased 73% between 1991 and 2017.
Published in the Children and Youth Services Review, University of Minnesota researchers pulled data from the 2016 Minnesota Student Survey (MSS) to examine associations between ACEs, school connectedness and suicide ideation and attempts among Somali, Latino, Hmong and Non-Hispanic ...
2021-03-10
Research published in Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry shows that the presence of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in bald eagle populations is slowly declining. Bald eagles are apex predators that nest and, more importantly, feed along water bodies, making them excellent bioindicators of environmental contaminants that bioaccumulate up the aquatic food web. The findings are both good news for eagles and instructive for regulators tasked with managing surface water quality by setting protective levels for wildlife, as well as fish consumption advisories for humans.
Lead author Bill Route from the National ...
2021-03-10
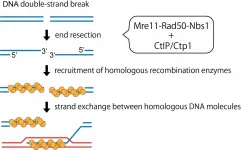
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have uncovered mechanisms underlying the activation of the MRN complex-- the cell's DNA scissors. Using purified yeast proteins, they demonstrated that phosphorylation of Ctp1, a homolog of a tumor-suppressor protein, plays a key role in activating MRN complex's DNA clipping activity. Intriguingly, a short segment of yeast Ctp1 or its human counterpart could stimulate endonuclease activity of their respective MRN complexes, suggesting its conserved function across species.
DNA functions as a roadmap that guides the identity and functions of cells. A glitch in the DNA ...
2021-03-10
BINGHAMTON, NY -- Star employees often get most of the credit when things go right, but also shoulder most of the blame when things go wrong, according to new research from Binghamton University, State University of New York.
The study explored the potential risks and rewards of collaborating with stars - individuals who have a reputation for exhibiting exceptional performance - and how individual performance factors into how much credit and blame is shared with collaborators.
"Stars are human, and they fail from time to time. We wanted to shift the focus away from stars, and find out what happens to the people who collaborate ...
2021-03-10
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Geoscientists at Sandia National Laboratories used 3D-printed rocks and an advanced, large-scale computer model of past earthquakes to understand and prevent earthquakes triggered by energy exploration.
Injecting water underground after unconventional oil and gas extraction, commonly known as fracking, geothermal energy stimulation and carbon dioxide sequestration all can trigger earthquakes. Of course, energy companies do their due diligence to check for faults -- breaks in the earth's upper crust that are prone to earthquakes -- but sometimes ...
2021-03-10
Eye contact is a key to establishing a connection, and teachers use it often to encourage participation. But can a robot do this too? Can it draw a response simply by making "eye" contact, even with people who are less inclined to speak up. A recent study suggests that it can.
Researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology published results of experiments in which robots led a Swedish word game with individuals whose proficiency in the Nordic language was varied. They found that by redirecting its gaze to less proficient players, a robot can elicit involvement from even the most reluctant participants.
Researchers Sarah Gillet and Ronald Cumbal say the results offer evidence that robots could play a productive role in educational settings.
Calling on someone by name isn't ...
2021-03-10
The protein α-synuclein is one of the most abundant proteins in the human brain. It is often referred to as the "Parkinson protein", as deposition of this protein in brain cells is a hallmark of Parkinson's disease. Despite the high interest of biomedical research in the protein, many questions concerning the function and physiology of α-synuclein in living cells still remain to be answered. For example, it was previously unclear whether and to what extent the protein binds to and interacts with internal cell components such as membranes. As such processes could play a role in the development of the disease, the team led by Konstanz-based physical chemist Professor Malte Drescher used the further development of an established measurement method called ...
2021-03-10
An article published by the researchers of the Biodiversity Unit at the University of Turku, Finland, highlights how amateur venom-extraction business is threatening scorpion species. Sustainably produced scorpion venoms are important, for example, in the pharmacological industry. However, in the recent years, there has been a dramatic increase in the number of people involved in the trade and vast numbers of scorpions are harvested from nature. This development is endangering the future of several scorpion species in a number of areas.
Scorpions have existed on Earth for over 430 million years. Currently comprising over 2,500 extant species, scorpions occur on almost all the major landmasses in a range of habitats from ...
2021-03-10
Gravity is the weakest of all known forces in nature - and yet it is most strongly present in our everyday lives. Every ball we throw, every coin we drop - all objects are attracted by the Earth's gravity. In a vacuum, all objects near the Earth's surface fall with the same acceleration: their velocity increases by about 9.8 m/s every second. The strength of gravity is determined by the mass of the Earth and the distance from the center. On the Moon, which is about 80 times lighter and almost 4 times smaller than the Earth, all objects fall 6 times slower. And on a planet of the size of a ladybug? ...
2021-03-10
A new study published Tuesday 10 March, No Smoking Day, from King's College London highlights the 'clear benefit' of using e-cigarettes daily in order to quit smoking, and supports their effectiveness when compared to other methods of quitting, including nicotine replacement therapy or medication.
Although the number of people in England who smoke has continued to fall in recent years, tobacco smoking is still the leading preventable cause of premature death and disease - killing nearly 75,000 people in England in 2019.
While e-cigarettes have been around for more than a decade, evidence on their effectiveness for helping people to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Recuperation unit decreased hospitalizations of homeless individuals with COVID-19