(Press-News.org) A new study published Tuesday 10 March, No Smoking Day, from King's College London highlights the 'clear benefit' of using e-cigarettes daily in order to quit smoking, and supports their effectiveness when compared to other methods of quitting, including nicotine replacement therapy or medication.
Although the number of people in England who smoke has continued to fall in recent years, tobacco smoking is still the leading preventable cause of premature death and disease - killing nearly 75,000 people in England in 2019.
While e-cigarettes have been around for more than a decade, evidence on their effectiveness for helping people to quit smoking is still limited. Recent studies have produced inconsistent findings or failed to measure important factors such as frequency of use or the effect of different types of e-cigarette on attempts to quit.
In their Cancer Research UK-funded study, the researchers analysed data from an online survey of more than 1,155 people, which included smokers, ex-smokers who had quit within one year prior to completing the survey, and e-cigarette users.
Five waves of data were collected between 2012 and 2017. The researchers analysed the effectiveness of e-cigarettes in aiding abstinence from smoking for at least one month at follow-up, and at least one month of abstinence between the first survey and subsequent follow-up waves.
Published today in the journal Addiction, the study found that people who used a refillable e-cigarette daily to quit smoking were over five times more likely to achieve abstinence from tobacco smoking for one month, compared to those using no quitting aids at all.
Similarly, people who used a disposable or cartridge e-cigarette daily were three times more likely to quit for one month, compared to those using no help.
Daily use of e-cigarettes was also more effective for quitting than other evidence-based methods of quitting - including nicotine replacement therapy, medication such as bupropion or varenicline, or any combination of these aids. None of these methods were associated with abstinence from smoking at follow-up, compared to using no help at all. However, in a secondary analysis, prescription medicine was associated with achieving at least one month of abstinence from smoking.
Dr Máirtín McDermott, Research Fellow at King's College London's National Addiction Centre and lead author of the study, said: "Our results show that when used daily, e-cigarettes help people to quit smoking, compared to no help at all. These findings are in line with previous research, showing that e-cigarettes are a more effective aid for quitting than nicotine replacement therapy and prescribed medication.
"It's important that we routinely measure how often people use e-cigarettes, as we've seen that more sporadic use at follow up - specifically of refillable types - was not associated with abstinence."
Dr Leonie Brose, Reader at King's College London's national Addiction Centre added: "Despite the World Health Organization's (WHO) cautious stance on e-cigarettes, studies like ours show they are still one of the most effective quitting aids available.
"The WHO is especially concerned about refillable e-cigarettes, as these could allow the user to add harmful substances or higher levels of nicotine. However, we've shown that refillable types in particular are a very effective quitting aid when used daily, and this evidence should be factored into any future guidance around their use."
INFORMATION:
Notes to editors
For further information please contact Louise Pratt, Head of Communications
Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience, King's College London
Tel: +44 7850 919020 @KingsIoPPN
Em: louise.a.pratt@kcl.ac.uk http://www.kcl.ac.uk/ioppn http://www.kingshealthpartners.org
King's College London is one of the top 10 UK universities in the world (QS World University Rankings, 2018/19) and among the oldest in England. King's has more than 31,000 students (including more than 12,800 postgraduates) from some 150 countries worldwide, and some 8,500 staff.
The Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) which is the premier centre for mental health and related neurosciences research in Europe. It produces more highly cited outputs (top 1% citations) on mental health than any other centre (SciVal 2019) and on this metric we have risen from 16th (2014) to 4th (2019) in the world for highly cited neuroscience outputs. World-leading research from the IoPPN has made, and continues to make, an impact on how we understand, prevent and treat mental illness and other conditions that affect the brain. https://www.kcl.ac.uk/ioppn @KingsIoPPN
There's a surprising amount of information stored in the hardened plaque, or calculus, between teeth. And if that calculus belongs to the remains of a person who lived in ancient times, the information could reveal new insights about the past. But the tiny samples can be difficult to work with. Now, in ACS' Journal of Proteome Research, scientists apply a new method to this analysis, finding more proteins than traditional approaches.
The human mouth is full of interesting molecules: DNA and enzymes in saliva, proteins and lipids from bits of food stuck between teeth, the bacterial ...
Amsterdam, NL, March 10, 2021 - Music-based interventions have become a core ingredient of effective neurorehabilitation in the past 20 years thanks to the growing body of knowledge. In this END ...
People are different. New technology is good for patients and the healthcare system. But it could also expand the already significant health disparities in Norway and other countries.
"Women and men with higher education in Norway live five to six years longer than people with that only have lower secondary school education," says Emil Øversveen, a postdoctoral fellow at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Department of Sociology and Political Science.
He is affiliated with CHAIN, the Centre for Global Health Inequalities Research. The centre works to reduce social health ...
In the dry air and soil of Texas' Southern High Plains, improving soil health can be tough. We usually think of healthy soil as moist and loose with lots of organic matter. But this can be hard to achieve in this arid area of Texas.
Lindsey Slaughter, a member of the Soil Science Society of America, set out with her fellow researchers to test a solution that kills two birds with one stone. They put excess cow manure on these soils to see if they could make them healthier.
The team recently published their research in the Soil Science Society of America Journal.
"We know that planting perennial grasslands for cattle production can help protect and restore soil in semi-arid lands that are likely to erode and degrade from intense ...
The per-capita rates of new COVID-19 cases and COVID-19 deaths were higher in states with Democrat governors in the first months of the pandemic last year, but became much higher in states with Republican governors by mid-summer and through 2020, possibly reflecting COVID-19 policy differences between GOP- and Democrat-led states, according to a study led by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Medical University of South Carolina.
For their study, the researchers analyzed data on SARS-CoV-2-positive nasal swab tests, COVID-19 diagnoses, and COVID-19 ...
Immune cells specialize to ensure the most efficient defense against viruses and other pathogens. Researchers at the University of Basel have shed light on this specialization of T cells and shown that it occurs differently in the context of an acute and a chronic infection. This could be relevant for new approaches against chronic viral infections.
Researchers led by Professor Carolyn King of the University of Basel have developed a method to study the specialization of T cells in the context of infections. In the journal eLife, they report the different directions ...
The scientists of the National University of Science and Technology "MISIS" (NUST MISIS) being a part of an international team of researches managed to increase the capacity and extend the service life of lithium-ion batteries. According to the researchers, they have synthesized a new nanomaterial that can replace low-efficiency graphite used in lithium-ion batteries today. The results of the research are published in the Journal of Alloys and Compounds.
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used for household appliances from smartphones to electric vehicles. The charge-discharge cycle in such battery is provided by ...
As plastic debris weathers in aquatic environments, it can shed tiny nanoplastics. Although scientists have a good understanding of how these particles form, they still don't have a good grasp of where all the fragments end up. Now, researchers reporting in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology have shown experimentally that most nanoplastics in estuarine waters can clump, forming larger clusters that either settle or stick to solid objects, instead of floating on into the ocean.
There is a huge discrepancy between the millions of tons of plastic waste entering rivers and streams and the amount researchers have found in the oceans. As large pieces of plastic break apart into ...
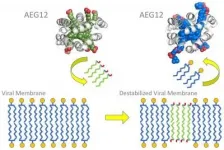
The mosquito protein AEG12 strongly inhibits the family of viruses that cause yellow fever, dengue, West Nile, and Zika and weakly inhibits coronaviruses, according to scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and their collaborators. The researchers found that AEG12 works by destabilizing the viral envelope, breaking its protective covering. Although the protein does not affect viruses that do not have an envelope, such as those that cause pink eye and bladder infections, the findings could lead to therapeutics against viruses that affect millions of people around the world. The research ...
Throughout history, leather has been a popular material for clothes and many other goods. However, the tanning process and use of livestock mean that it has a large environmental footprint, leading consumers and manufacturers alike to seek out alternatives. An article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society, details how sustainable materials are giving traditional leather a run for its money.
Traditional leather goods are known for their durability, flexibility and attractive finish, with a global market worth billions, writes ...