More heart infections and strokes in the US linked to national opioid epidemic
American Stroke Association International Stroke Conference -- presentation P658
2021-03-11
(Press-News.org) DALLAS, March 11, 2021 — The ongoing U.S. opioid epidemic may have led to an increase in the number of strokes due to more bacterial infections of the heart, or infective endocarditis, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
According to the most recent comprehensive data (January 2020) from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States and a major contributor to long-term disability. Typically each year in the United States, up to 47,000 people are treated in the hospital for endocarditis, which increases stroke risk. This serious, sometimes deadly infection occurs when bacteria in the bloodstream reach the heart lining, valves or blood vessels. While endocarditis is uncommon, people with certain heart conditions are at greater risk.
Another risk factor for endocarditis is intravenous (IV) drug use. During IV drug use, bacteria from the injection needle enter the blood stream. In light of the ongoing, two decades-long national opioid epidemic, researchers wanted to understand the risk of stroke among patients with endocarditis from IV drug use compared to patients with endocarditis due to other causes. They also measured the frequency of endocarditis related to IV drug use.
This study included 351 patients treated for endocarditis at Ohio State University’s Wexner Medical Center between January 1, 2014 and July 1, 2018. Nearly half of the patients had a history of IV drug use.
The researchers found:
Over the four-year study, the occurrence of endocarditis from IV drug use increased by 630%.
Patients with endocarditis due to IV drug use were much more likely (26%) than those with endocarditis from other causes (14%) to have a stroke.
Patients with endocarditis from IV drug use were more likely than other patients to be homeless, unemployed and uninsured.
“Patients who are known IV drug users who have endocarditis should be more carefully screened for symptoms of cardiovascular disease,” said the study’s corresponding author Shahid M. Nimjee, M.D., Ph.D., associate professor of neurosurgery and surgical director of the Comprehensive Stroke Center at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center in Columbus, Ohio.
“The wider societal impact of the opioid epidemic is not well understood,” Nimjee said. “Our research suggests that the impact of the opioid epidemic is far-reaching and contributes to increased costs in the criminal justice, health care systems and the workplace. The increased costs can be particularly substantial for stroke care.”
Medical costs were more than two times higher among patients with endocarditis from IV drug use than among those with endocarditis from other causes. This translated into a difference of more than $100,000 in health care costs during admission per patient, Nimjee noted.
The study did not control for other factors that could have affected stroke risk, and it included patients from only one hospital, therefore, the findings may not apply to other groups of patients.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are Nguyen Hoang, M.D.; Varun Shah, B.S.; Bipul Gnywali, B.S.; Jessica Granger, B.A.; Victoria Schuneman, M.D.; David Dornbos III, M.D.; H. Francis Farhadi, M.D., Ph.D.; Patrick P. Youssef, M.D.; and Ciaran J. Powers, M.D., Ph.D. The study authors report no funding or disclosures.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available on the right column of release link https://newsroom.heart.org/news/more-heart-infections-and-strokes-in-the-u-s-linked-to-national-opioid-epidemic?preview=037cb78b2fe2ff2bdc9daf23f83a50b1
AHA resources on infective endocarditis
Alarming number of heart infections tied to opioid epidemic
Opioid epidemic fueling a rise in infection-related stroke
Opioid use may increase risk of dangerous heart rhythm disorder
AHA Opioid Education for Healthcare Providers
For more news at ASA International Stroke Conference 2021, follow us on Twitter @HeartNews #ISC21.
Statements and conclusions of studies that are presented at the American Heart Association’s scientific meetings are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association’s policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers are available here, and the Association’s overall financial information is available here.
The American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference (ISC) is the world’s premier meeting dedicated to the science and treatment of cerebrovascular disease. ISC 2021 will be held virtually, March 17-19, 2021. This 3-day conference will feature more than 1,200 compelling presentations in 21 categories that emphasize basic, clinical and translational sciences as they evolve toward a better understanding of stroke pathophysiology with the goal of developing more effective therapies. Engage in the International Stroke Conference on social media via #ISC21.
About the American Stroke Association
The American Stroke Association is devoted to saving people from stroke — the No. 2 cause of death in the world and a leading cause of serious disability. We team with millions of volunteers to fund innovative research, fight for stronger public health policies and provide lifesaving tools and information to prevent and treat stroke. The Dallas-based association officially launched in 1998 as a division of the American Heart Association. To learn more or to get involved, call 1-888-4STROKE or visit stroke.org. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-11
Pregnant women in Japan who responded to an online survey early in the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated higher levels of anxiety compared to women undergoing fertility treatments and to pregnant women in Iran.
The findings were published in the Journal of Affective Disorders Reports.
"The pandemic has changed the social environments of pregnant women and fertility patients," says Tohoku University clinical psychologist Koubon Wakashima.
For example, restrictions in Japan meant that pregnant women have been unable to participate in group parenting classes or travel to their parents' homes to receive traditional childbirth assistance. Medical institutions in the country reported fewer women accessing infertility ...
2021-03-11
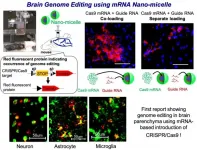
March 10, 2021 - Kawasaki, Japan: The research group of Deputy Principal Research Scientist Dr. Satoshi Uchida (Associate Professor, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine) at the Innovation Center of NanoMedicine (Director General: Prof. Kazunori Kataoka, Location: Kawasaki-Japan, Abbreviation: iCONM) reported that optimized nano-micelles can induce efficient genome editing in the mouse brain.
The 2020 Chemistry Nobel Prize-winning technology CRISPR/Cas9 holds great promise for treating various diseases such as congenital disorders and viral infections, by correcting the disease-specific genomic ...
2021-03-11
WASHINGTON--Biological differences between females and males affect virtually every aspect of medicine and biomedical research. In a new Scientific Statement released today, the Endocrine Society called for sex differences to be studied thoroughly to improve public health.
"When we understand the ways sex differences operate at baseline in health, which can either worsen the course of a disease to amplify differences in health outcomes, or protect against it, we can more effectively prevent and treat medical conditions," said Aditi Bhargava, Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco in San Francisco, Calif., and the chair of the writing group that authored the Society's Scientific Statement.
For instance, SARS CoV-2 infection, cause of the COVID-19 pandemic, disproportionately ...
2021-03-11
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 11, 2021- For people who are overweight or obese and have type 2 diabetes, the first line of treatment is usually lifestyle intervention, including weight loss and increased physical activity. While this approach has cardiovascular benefit for many, it can be detrimental for people who have poor blood sugar control, according to a study conducted by researchers at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
In the study, published in the current issue of the journal Diabetes Care, the researchers re-evaluated the National Institutes of Health Action ...
2021-03-11
Several years after scientists discovered what was considered the oldest crater a meteorite made on the planet, another team found it's actually the result of normal geological processes.
During fieldwork at the Archean Maniitsoq structure in Greenland, an international team of scientists led by the University of Waterloo's Chris Yakymchuk found the features of this region are inconsistent with an impact crater. In 2012, a different team identified it as the remnant of a three-billion-year-old meteorite crater.
"Zircon crystals in the rock are like little ...
2021-03-11
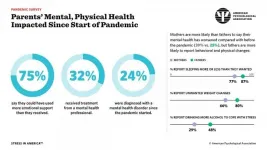
WASHINGTON -- As growing vaccine demand signals a potential turning point in the global COVID-19 pandemic, the nation's health crisis is far from over. One year after the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic, many adults report undesired changes to their weight, increased drinking and other negative behavior changes that may be related to an inability to cope with prolonged stress, according to the American Psychological Association's latest Stress in America™ poll.
APA's survey of U.S. adults, conducted in late February 2021 by The Harris Poll, shows that a majority of adults (61%) experienced undesired weight changes - weight gain ...
2021-03-11
The U.S. Congress and Biden-Harris administration have a clear opportunity to supercharge global health research and development (R&D) in the wake of a pandemic that has revealed both the sector's chronic neglect and amazing potential, according to a detailed agency-by-agency action plan released today by the nonprofit Global Health Technologies Coalition (GHTC).
"The same core capabilities instrumental to defeating COVID-19 can also defeat diseases that have plagued humanity for generations--such as AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and Ebola--while targeting emerging pathogens of pandemic potential," said GHTC Director Jamie Bay Nishi. "Developing vaccines in ...
2021-03-11
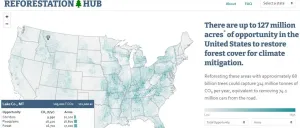
Reforestation could help to combat climate change, but whether and where to plant trees is a complex choice with many conflicting factors. To combat this problem, researchers reporting in the journal One Earth on December 18 have created the Reforestation Hub, an interactive map of reforestation opportunity in the United States. The tool will help foresters, legislators, and natural resource agency staff weigh the options while developing strategies to restore lost forests.
"Often the information we need to make informed decisions about where to deploy reforestation already exists, it's just scattered across a lot of different locations," says author Susan Cook-Patton, a Senior Forest Restoration Scientist at the Nature Conservancy. "Not everybody has the ...
2021-03-11
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on public health is staggering; more than one hundred million cases and two million deaths worldwide. In response, most countries and local governments have taken substantial measures -- such as travel restrictions and physical distancing -- to keep their citizens safe. Both the pandemic and related protective measures pose challenges for ongoing clinical research studies seeking to treat and prevent the world's greatest public health emergencies including COVID-19, but also Alzheimer's disease and other dementia.
In a new paper from the World-Wide FINGERS network in Alzheimer's ...
2021-03-11
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- As integral members of stroke treatment teams, nurses coordinate patient assessment and collaborate care among multiple health care professionals to facilitate the best possible outcomes for patients with acute ischemic stroke. Nurses also advocate for patients and their caregivers to ensure they receive appropriate information and education to successfully navigate phases of treatment in the hospital and after discharge. A series of three new Scientific Statements, "Care of the Patient With Acute Ischemic Stroke," from the American Heart Association, published today in Stroke, a journal of the American Stroke Association, a division of the American Heart Association, provide the latest evidence-based guidance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] More heart infections and strokes in the US linked to national opioid epidemic
American Stroke Association International Stroke Conference -- presentation P658