Long-term stroke death rates are higher among Black Medicare patients
American Stroke Association International Stroke Conference -- presentation P655
2021-03-11
(Press-News.org) DALLAS, March 11, 2021 — A long-term look at Medicare patients shows that Black patients who have an ischemic stroke (blocked blood flow to the brain) die at a higher rate than white patients, even after accounting for preexisting health conditions, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
“So much of what we know is limited to the early or acute phase — the first two weeks after a stroke,” said lead study author Judith H. Lichtman, Ph.D., M.P.H., professor and chair of the department of epidemiology at the Yale School of Public Health in New Haven, Connecticut. “When you have a stroke, it’s not just about the acute event, it’s about the early recovery period to secondary prevention visits that affect your long-term chances of survival.”
Researchers analyzed data on 744,044 Medicare beneficiaries (ages 65 and older) who had been treated at U.S. hospitals for ischemic stroke between 2005 and 2007. Overall, 85.6% were white, 9.9% were Black and 4.5% were of other races or ethnic groups. Black patients had higher rates of kidney failure, dementia and diabetes. Atherosclerosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were more common in white patients.
Patients were followed over a 10-year period, and analysis of the data found:
Overall, the death rate was about 75%. Black patients had the highest death rate at 76.4%, followed by whites at 75.4%; and the death rate for those of other races or other ethnic groups was 70.3%.
Even after adjusting for differences in preexisting health problems, the risk of death within 10 years after stroke was about 4% higher for Black patients than white patients. However, the stroke death risk was about 8% lower for those of other races.
Importantly, within the first year after hospital discharge for ischemic stroke, the death rate for Black patients started to climb slightly in comparison to whites and other races, and these differences continued over the decade.
“These are racial differences in long-term stroke survivorship, and these differences start within the first year after a stroke,” Lichtman said. “We need to take a closer look at the recovery period and think about how we can optimize secondary prevention and post-stroke care for everybody. Stroke care during the first year after a stroke plays an important role in the long run.”
Future research will need to investigate the reasons behind these differences in death rates among Black patients and white patients. “Currently, much of the focus is on the acute stroke event, itself, yet we need to find out more – are there racial differences using rehab services, are some people not seeing neurologists and getting follow up care?” Lichtman said. “Stroke is an acute event, but it’s just as important to focus on early follow-up care that will support patients for better long-term outcomes and survival.”
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are Erica C. Leifheit, Ph.D.; Yun Wang, Ph.D.; Andrew Arakaki, M.P.H.; and Larry B. Goldstein, M.D. The authors’ disclosures are available in the abstract.
The study was funded by the American Heart Association and the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available on the right column of release link https://newsroom.heart.org/news/long-term-stroke-death-rates-are-higher-among-black-medicare-patients?preview=61bb19ecbb6986bc5d17491112fb0285
What is Brain Health?
Stroke risk factors
More stroke awareness, better eating habits may help reduce stroke risk for young adult African Americans
Risk of stroke may more than double for African Americans who smoke
African Americans live shorter lives due to heart disease and stroke
For more news at ASA International Stroke Conference 2021, follow us on Twitter @HeartNews #ISC21.
Statements and conclusions of studies that are presented at the American Heart Association’s scientific meetings are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association’s policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives funding primarily from individuals; foundations and corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations and fund specific Association programs and events. The Association has strict policies to prevent these relationships from influencing the science content. Revenues from pharmaceutical and biotech companies, device manufacturers and health insurance providers are available here, and the Association’s overall financial information is available here.
The American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference (ISC) is the world’s premier meeting dedicated to the science and treatment of cerebrovascular disease. ISC 2021 will be held virtually, March 17-19, 2021. The 3-day conference will feature more than 1,200 compelling presentations in 21 categories that emphasize basic, clinical and translational sciences as they evolve toward a better understanding of stroke pathophysiology with the goal of developing more effective therapies. Engage in the International Stroke Conference on social media via #ISC21.
About the American Stroke Association
The American Stroke Association is devoted to saving people from stroke — the No. 2 cause of death in the world and a leading cause of serious disability. We team with millions of volunteers to fund innovative research, fight for stronger public health policies and provide lifesaving tools and information to prevent and treat stroke. The Dallas-based association officially launched in 1998 as a division of the American Heart Association. To learn more or to get involved, call 1-888-4STROKE or visit stroke.org. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-11
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- Ambulances with specialized staff and equipment to provide rapid stroke treatment report financial difficulties due to limited reimbursement from health care insurers, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
According to the most recent comprehensive data from the Centers for Disease Control ...
2021-03-11
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 — The ongoing U.S. opioid epidemic may have led to an increase in the number of strokes due to more bacterial infections of the heart, or infective endocarditis, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
According to the most recent comprehensive data (January 2020) from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States and a major contributor to ...
2021-03-11
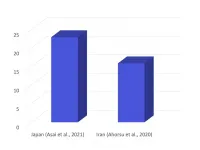
Pregnant women in Japan who responded to an online survey early in the COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated higher levels of anxiety compared to women undergoing fertility treatments and to pregnant women in Iran.
The findings were published in the Journal of Affective Disorders Reports.
"The pandemic has changed the social environments of pregnant women and fertility patients," says Tohoku University clinical psychologist Koubon Wakashima.
For example, restrictions in Japan meant that pregnant women have been unable to participate in group parenting classes or travel to their parents' homes to receive traditional childbirth assistance. Medical institutions in the country reported fewer women accessing infertility ...
2021-03-11
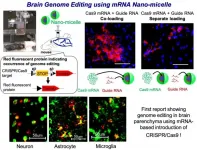
March 10, 2021 - Kawasaki, Japan: The research group of Deputy Principal Research Scientist Dr. Satoshi Uchida (Associate Professor, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine) at the Innovation Center of NanoMedicine (Director General: Prof. Kazunori Kataoka, Location: Kawasaki-Japan, Abbreviation: iCONM) reported that optimized nano-micelles can induce efficient genome editing in the mouse brain.
The 2020 Chemistry Nobel Prize-winning technology CRISPR/Cas9 holds great promise for treating various diseases such as congenital disorders and viral infections, by correcting the disease-specific genomic ...
2021-03-11
WASHINGTON--Biological differences between females and males affect virtually every aspect of medicine and biomedical research. In a new Scientific Statement released today, the Endocrine Society called for sex differences to be studied thoroughly to improve public health.
"When we understand the ways sex differences operate at baseline in health, which can either worsen the course of a disease to amplify differences in health outcomes, or protect against it, we can more effectively prevent and treat medical conditions," said Aditi Bhargava, Ph.D., of the University of California, San Francisco in San Francisco, Calif., and the chair of the writing group that authored the Society's Scientific Statement.
For instance, SARS CoV-2 infection, cause of the COVID-19 pandemic, disproportionately ...
2021-03-11
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 11, 2021- For people who are overweight or obese and have type 2 diabetes, the first line of treatment is usually lifestyle intervention, including weight loss and increased physical activity. While this approach has cardiovascular benefit for many, it can be detrimental for people who have poor blood sugar control, according to a study conducted by researchers at Wake Forest School of Medicine.
In the study, published in the current issue of the journal Diabetes Care, the researchers re-evaluated the National Institutes of Health Action ...
2021-03-11
Several years after scientists discovered what was considered the oldest crater a meteorite made on the planet, another team found it's actually the result of normal geological processes.
During fieldwork at the Archean Maniitsoq structure in Greenland, an international team of scientists led by the University of Waterloo's Chris Yakymchuk found the features of this region are inconsistent with an impact crater. In 2012, a different team identified it as the remnant of a three-billion-year-old meteorite crater.
"Zircon crystals in the rock are like little ...
2021-03-11
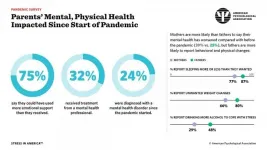
WASHINGTON -- As growing vaccine demand signals a potential turning point in the global COVID-19 pandemic, the nation's health crisis is far from over. One year after the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic, many adults report undesired changes to their weight, increased drinking and other negative behavior changes that may be related to an inability to cope with prolonged stress, according to the American Psychological Association's latest Stress in America™ poll.
APA's survey of U.S. adults, conducted in late February 2021 by The Harris Poll, shows that a majority of adults (61%) experienced undesired weight changes - weight gain ...
2021-03-11
The U.S. Congress and Biden-Harris administration have a clear opportunity to supercharge global health research and development (R&D) in the wake of a pandemic that has revealed both the sector's chronic neglect and amazing potential, according to a detailed agency-by-agency action plan released today by the nonprofit Global Health Technologies Coalition (GHTC).
"The same core capabilities instrumental to defeating COVID-19 can also defeat diseases that have plagued humanity for generations--such as AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and Ebola--while targeting emerging pathogens of pandemic potential," said GHTC Director Jamie Bay Nishi. "Developing vaccines in ...
2021-03-11
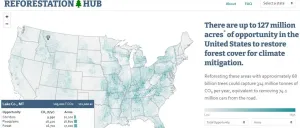
Reforestation could help to combat climate change, but whether and where to plant trees is a complex choice with many conflicting factors. To combat this problem, researchers reporting in the journal One Earth on December 18 have created the Reforestation Hub, an interactive map of reforestation opportunity in the United States. The tool will help foresters, legislators, and natural resource agency staff weigh the options while developing strategies to restore lost forests.
"Often the information we need to make informed decisions about where to deploy reforestation already exists, it's just scattered across a lot of different locations," says author Susan Cook-Patton, a Senior Forest Restoration Scientist at the Nature Conservancy. "Not everybody has the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Long-term stroke death rates are higher among Black Medicare patients
American Stroke Association International Stroke Conference -- presentation P655