INFORMATION:
Novel targeted modification strategy improves selectivity of polyamide nanofiltration membranes
2021-03-11
(Press-News.org) Recently, a research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a novel targeted modification strategy to improve the separation selectivity of polyamide NF membranes.
The study was published in Journal of Membrane Science on March 10.
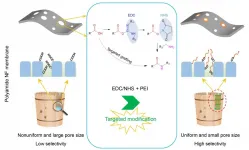
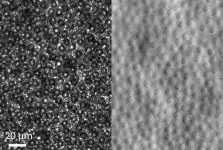
The low selectivity of commercial nanofiltration (NF) membranes to monosaccharides and monovalent salts is mainly due to the nonuniform pore size distribution and strong electronegativity.
Targeted modification can regulate the pore size distribution and electronegativity of polyamide NF membranes, and thus improve the separation selectivity.
In the strategy, carboxyl groups (-COOH) on the surface are activated by N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethyl carbodiimide (EDC) and N-Hydroxy succinimide (NHS), and subsequently grafted onto monomer or polymer containing amino groups (-NH2) for more precise separation.
The novel targeted modification strategy reduced the effective mean pore size while maintaining the porosity of the NF membrane, due to pore segmentation. This resulted in a remarkable improvement in glucose/fructose rejection (from 67.96% to 84.14%) and separation factor (from 2.20 to 6.78), with only a 4.70% permeability loss.
"The outcome of this work not only improves the separation efficiency of small organic and inorganic salts by NF, but also provides a new perspective in regulating pore size distribution and surface charge of NF membranes for precisely separating small molecules," said Prof. LUO Jianquan from IPE, the corresponding author of the study.
The modified membrane also maintained separation performance in crossflow filtration and after alkaline cleaning, which outperformed the pristine NF membrane and those modified by uniform coating and simple physical adsorption.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ADHD: Aggressive behavior is genetically coded
2021-03-11
An international collaboration headed by researchers from iPSYCH has found genetic variants that increase the risk of aggression in children with ADHD. In the same study, the researchers also discovered that the genetics which increase aggression in some children with ADHD, are the same genetics that affect aggression in children without a diagnosis.
For the first time, researchers have found positions in the genome that increase the risk of getting ADHD with disruptive behaviour disorders (DBDs). DBDs are child psychiatric disorders characterised by antisocial and ...
New approach found for energy-efficient AI applications
2021-03-11
Most new achievements in artificial intelligence (AI) require very large neural networks. They consist of hundreds of millions of neurons arranged in several hundred layers, i.e. they have very "deep" network structures. These large, deep neural networks consume a lot of energy in the computer. Those neural networks that are used in image classification (e.g. face and object recognition) are particularly energy-intensive, since they have to send very many numerical values from one neuron layer to the next with great accuracy in each time cycle.
Computer scientist Wolfgang Maass, together with his PhD student Christoph Stöckl, has ...
50 new genes for eye colour
2021-03-11
The genetics of human eye colour is much more complex than previously thought, according to a new study published today.
An international team of researchers led by King's College London and Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam have identified 50 new genes for eye colour in the largest genetic study of its kind to date. The study, published today in Science Advances, involved the genetic analysis of almost 195,000 people across Europe and Asia.
These findings will help to improve the understanding of eye diseases such as pigmentary glaucoma and ocular albinism, where eye pigment levels play a role.
In addition, the team found ...
Probiotics increase gut bacteria diversity in extremely preterm infants
2021-03-11
Extremely preterm infants can suffer from a life-threatening inflammation of the gut. A new clinical study has shown that supplements of a lactic acid bacterium may have positive effects by increasing the diversity of intestinal bacteria in these infants. The study has been led by researchers at Linköping University, Sweden, and published in the scientific journal Cell Reports Medicine.
A litre of milk weighs a kilogram. Most infants who are born extremely prematurely weigh less than that. An infant who should have developed and grown for three more months in the protective environment of the mother's womb is, of course, extremely vulnerable. As a consequence of advances in neonatal care, many premature infants survive, although one out of four of the extremely ...
Robots learn faster with quantum technology
2021-03-11
Robots solving computer games, recognizing human voices, or helping in finding optimal medical treatments: those are only a few astonishing examples of what the field of artificial intelligence has produced in the past years. The ongoing race for better machines has led to the question of how and with what means improvements can be achieved. In parallel, huge recent progress in quantum technologies have confirmed the power of quantum physics, not only for its often peculiar and puzzling theories, but also for real-life applications. Hence, the idea of merging the two fields: on one hand, artificial intelligence ...
Tracing and controlling High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza
2021-03-11
Scientists have discovered a route of introduction for High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus (HPAIV) H5N8 into Japan and, in parallel, have investigated the potential of two human anti-influenza drugs for the control of HPAI in birds.
Since October 30, 2020, there have been over 30 recorded outbreaks of High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza (HPAI) in domestic poultry and wild fowl in Japan. This outbreak was caused by the influenza A virus H5N8, a known High Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Virus (HPAIV). In such a scenario, identification of the source of the virus and its transmission route is important to control its spread.
A team of scientists led by Professor Yoshihiro Sakoda of Hokkaido University have recently found the probable route of introduction of ...
Researchers set new resolution record for imaging the human eye
2021-03-11
WASHINGTON -- Researchers have developed a noninvasive technique that can capture images of rod and cone photoreceptors with unprecedented detail. The advance could lead to new treatments and earlier detection for retinal diseases such as macular degeneration, a leading cause of vision loss.
"We are hopeful that this technique will better reveal subtle changes in the size, shape and distribution of rod and cone photoreceptors in diseases that affect the retina," said research team leader Johnny Tam from the National Eye Institute. "Figuring out what happens to these cells before they are lost is an important step toward developing earlier interventions to treat and prevent blindness."
In Optica, The Optical Society's (OSA) journal for high impact research, the researchers show that ...
NIH-led team sets new bar in retinal imaging
2021-03-11
A team led by scientists at the National Eye Institute (NEI) has noninvasively visualized the light-sensing cells in the back of the eye, known as photoreceptors, in greater detail than ever before. Published in Optica, the researchers report how they improved imaging resolution by a third by selectively blocking the light used to image the eye. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
The achievement is the latest in an evolving strategy to monitor cell changes in retinal tissue that, in turn, will help identify new ways to treat and prevent vision loss from diseases such as age-related macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in people age ...
Non-O blood type may increase stroke risk among women who smoke, take oral contraceptives
2021-03-11
DALLAS, March 11, 2021 -- Non-O blood type may increase the risk of stroke among women who smoke and take oral contraceptives, according to preliminary research to be presented at the American Stroke Association's International Stroke Conference 2021. The virtual meeting is March 17-19, 2021 and is a world premier meeting for researchers and clinicians dedicated to the science of stroke and brain health.
According to the most recent comprehensive data (January 2020) from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), stroke is the fifth leading cause of death in the United States and a major contributor to long-term disability. Some risk factors ...
The secrets of the best rainbows on Earth
2021-03-11
Rainbows are some of the most spectacular optical phenomena in the natural world and Hawai'i has an amazing abundance of them. In a new publication, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa makes an impassioned case for Hawaii being the best place on Earth to experience the wonder of rainbows. He begins by highlighting the Hawaiian cultural significance of rainbows, he reviews the science of rainbows and the special combination of circumstances that makes Hawai'i a haven for rainbows.
"The cultural importance of rainbows is reflected in the Hawaiian language, which has many words and phrases to describe the variety of manifestations in Hawai'i," said author Steven Businger, professor in the UH ...