INFORMATION:
Modulation of photocarrier relaxation dynamics in two-dimensional semiconductors
2021-03-11
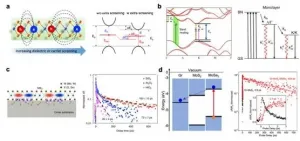
(Press-News.org) Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors can host a rich set of excitonic species because of the greatly enhanced Coulomb interactions. The excitonic states can exhibit large oscillator strengths and strong light-matter interactions, and dominate the optical properties of 2D semiconductors. In addition, because of the low dimensionality, excitonic dynamics of 2D semiconductors can be more susceptible to various external stimuli, enriching the possible tailoring methods that can be exploited. Understanding the factors that can influence the dynamics of the optically-generated excited states represents an important aspect of excitonic physics in 2D semiconductors, and is also crucial for practical application as excited state lifetimes are linked to the key figures of merit of multiple optoelectronic and photonic devices. While certain experiences have been accumulated for bulk semiconductors, the atomic nature of 2D semiconductors might makes these approaches less effective or difficult to be adapted. One the other hand, the unique properties of 2D semiconductors, such as the robust excitonic states, the sensitivity to external environmental factors and flexibility in constructing vdW heterostructures, promise modulation strategies different from conventional materials.
In a new review article published in Light: Science & Application, a team of researchers, led by Professor Fengqiu Wang from Nanjing University, China summarize the so far obtained knowledge and progresses on the modulation of photocarrier relaxation dynamics in 2D semiconductors. After a brief summary on the photocarrier relaxation dynamics in 2D semiconductors, the authors first discuss the modulation of Coulomb interactions and the resulting effects on the transient properties. The Coulomb interactions in 2D semiconductors can be modulated by introducing additional screening from the external dielectric environment or injected charge carriers, leading to the modification of quasi-particle bandgaps and the exciton binding energy. Then the influencing factors on photocarrier dynamics and the manipulating methods are discussed according to the relaxation pathways or mechanisms they are associated with. The first discussed factor is the initial distribution of photocarriers in electronic band structures, which can affect their decay processes by enabling different available relaxation pathways in the energy and momentum space. After that the defect-assisted and phonon-assisted relaxation are discussed. While the approaches utilizing defect-assisted relaxation such as ion bombardment and encapsulation are similar to those for bulk semiconductors, the modulation on phonon-assisted relaxation for 2D semiconductors can be different. "On one hand, the coupling between charge carriers and phonons can be enhanced due to the suppressed dielectric screening; on the other hand, the high surface-to-volume ratio make 2D materials more susceptible to the external phononic environment." Moreover, the flexibility in constructing vdW heterostructures and the ultrafast charge transfer across the interfaces enables tailoring the photocarrier dynamics though band alignment engineering. The transition between different particle species also offers the opportunity to modulate through changing the ratios between different quasiparticles, which can modify the relative portion of different relaxation pathways, and thus the transient optical responses of the whole sample. At last, the modulation of the dynamics of spin/valley polarization in 2D TMDs is discussed, and the discussion is mainly focusing on the methods to increase the lifetime of the spin/valley polarization.
Through this review, the authors aim to provide guidance for developing robust methods tuning the photocarrier relaxation behaviors and strength the physical understanding on this fundamental process in 2D semiconductors. As is commented by the authors at the end "Tremendous research efforts are still needed in both fundamental understanding and practical modulation of the photocarrier relaxation in 2D semiconductors."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
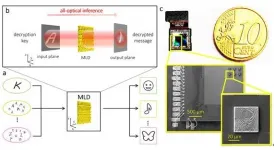
AI holographic nanostructures on CMOS chips for energy-efficient security schemes
2021-03-11
Today, machine learning based methods are of our everyday life, with millions of users every day unlocking their phones through facial recognition or passing through AI-enabled automated security checks at airports and train stations. Traditionally, the processing of information native to the optical domain is being executed in the electronic domain, requiring energy-hungry specialized electronic hardware and conversion between the two realms. Optical machine learning is emerging as an important field, where the processing of optical information is done directly within the optical domain, power-efficient and at the speed of light.
Machine learning tasks, such as pattern recognition or image classification, rely heavily on the multiplication of large matrices, a resource-hungry ...
Information transition mechanisms of spatiotemporal metasurfaces
2021-03-11
Spatiotemporal metasurfaces, driven by ultrafast dynamic modulations, opened up new possibilities for manipulating the harmonic modes of electromagnetic waves and generations of exotic physical phenomena, such as dispersion cancellation, Lorentz reciprocity broken, and Doppler illusions. In recent years, rapid development of information technologies have stimulated many information processing applications for metasurfaces, including computational imaging, wireless communications, and performing mathematical operations. With increasing amount of researches focused on the topic of information processing ...
Loss induced nonreciprocity
2021-03-11
Optical nonreciprocity, which prohibits the light field returning along the original path after passing through the optical system in one direction, is not only of vast interest to fundamental science, which brings us a deeper understanding of Lorentz reciprocity, time-reversal symmetry, and topological effects, but is also of great importance for realizing nonreciprocal optical and electromagnetics devices such as isolators, circulator and directional amplifiers, which are indispensable for applications ranging from optical communication to optical information processing.
However, realizing nonreciprocity is rather difficult as it requires breaking of the Lorentz reciprocity ...
Uncovering exotic molecules of potential astrochemical interest
2021-03-11
Looking at the night sky, one's thoughts might be drawn to astrochemistry. What molecules inhabit the vast spaces between the stars? Would we see the same molecules that surround us here on Earth? Or would some of them be more exotic--something rarely observed or even unknown?
Recent research by a multinational team led by Prof. Robert Ko?os from the Institute of Physical Chemistry of the Polish Academy of Sciences has revealed an unusual molecule obtained and detected for the first time in laboratory conditions and also paved a smooth path to produce and further study another. Now that they can be seen and studied, they may prove worthy ...
Optimal design for acoustic unobservability in water
2021-03-11
Until now, it was only possible to optimize an acoustic cloaking structure for the air-environment. However, with this latest research, Acoustic cloak designed by topology optimization for acoustic-elastic coupled systems, published in the latest Applied Physics Letters, it is possible to design an acoustic cloak for underwater environments.
In the conventional topology optimization of acoustic cloaking, the design method was based on an analysis that approximated an elastic body in the air as a rigid body. However, since the approximation holds only for materials that are sufficiently ...
Seeing both sides of light collection
2021-03-11
Two types of materials are better than one when it comes to solar cells, as revealed by an international team that has tested a new combination of materials and architecture to improve solar-cell efficiency.
Silicon has long dominated as the premier material for solar cells, helped by its abundance as a raw material. However, perovskites, a class of hybrid organic-inorganic material, are a viable alternative due to their low-cost and large-scale manufacture and potentially higher performance. While still too unstable for full commercialization, they might become available to the market by 2022.
KAUST's Michele ...
Fossilized feeding frenzy
2021-03-11
It was not the fly itself that caught the scientists' attention, but its bulging abdomen suggesting it was still full with the fly's last food intake. Surprisingly, analysis of the stomach content revealed it was full with pollen from different plants. The fossil pollen from the fly's stomach was used to reconstruct the ancient environment inhabited by the fly, the biotic interactions between plant and fly, and the fly's behaviour during feeding.
Flies as pollinators
Today, bees, butterflies and bumblebees are the typical pollinators, which are also known to feed on pollen. That flies also play an important role in pollination ...
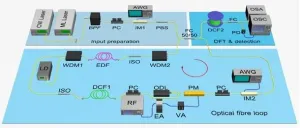
Real-time observation of frequency Bloch oscillations with fibre loop modulation
2021-03-11
BOs describe the periodic movement of electrons in solids to which an external static electric field is applied. However, it is challenging to measure the BOs directly in natural solids since the relaxation time of electrons is usually much shorter than the oscillation period. To date, analogies of electron BOs have been extended to the synthetic dimensions of time, frequency and angular momenta. In previous studies, the frequency BOs have been experimentally demonstrated in a nonlinear fibre with cross-phase modulation. However, the frequency spectrum has ...
New analysis of 2D perovskites could shape the future of solar cells and LEDs
2021-03-11
An innovative analysis of two-dimensional (2D) materials from engineers at the University of Surrey could boost the development of next-generation solar cells and LEDs.
Three-dimensional perovskites have proved themselves remarkably successful materials for LED devices and solar panels in the past decade. One key issue with these materials, however, is their stability, with device performance decreasing quicker than other state-of-the-art materials. The engineering community believes the 2D variant of perovskites could provide answers to these performance issues.
In a study published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, researchers from Surrey's Advanced Technology Institute (ATI) detail how to improve the physical properties of 2D perovskite called Ruddlesden-Popper.
The study ...
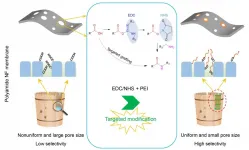
Novel targeted modification strategy improves selectivity of polyamide nanofiltration membranes
2021-03-11
Recently, a research group led by Prof. WAN Yinhua from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a novel targeted modification strategy to improve the separation selectivity of polyamide NF membranes.
The study was published in Journal of Membrane Science on March 10.
The low selectivity of commercial nanofiltration (NF) membranes to monosaccharides and monovalent salts is mainly due to the nonuniform pore size distribution and strong electronegativity.
Targeted modification can regulate the pore size distribution and electronegativity of polyamide NF membranes, and thus improve the separation selectivity.
In the strategy, carboxyl groups (-COOH) on the surface are activated by N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethyl ...