First lab-grown mini-thyroids use patients' own tissue
New research unlocks new clues for treating hypothyroidism
2021-03-11
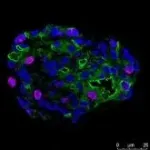
(Press-News.org) Hormones produced by the thyroid gland are essential regulators of organ function. The absence of these hormones either through thyroid dysfunction due to, for example, irradiation, thyroid cancer or autoimmune disease or thyroidectomy leads to symptoms like fatigue, feeling cold, constipation, and weight gain. The condition called hypothyroidism is estimated to affect up to 11% of the global population. Although hypothyroidism can be treated by hormone replacement therapy, some patients have persistent symptoms and/or experience side effects. To investigate potential alternative treatment strategies for these patients, researchers have now for the first time succeeded in generating thyroid mini-organs in the lab. In a END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Changing defaults can have a significant and lasting effect
2021-03-11
People often choose the standard option. Choosing to be an organ donor, printing on both sides of the page - such decisions are influenced by which is the standard setting, or default. In fact, economists and sociologists call this the default effect. Researchers at ETH Zurich and the University of Warwick in the UK have now managed to clearly demonstrate this effect. Private households, but also self-employed people and SMEs, are more likely to procure sustainably produced electricity if that is their provider's default offer.
The scientists conclude this from an analysis of data from two Swiss electricity suppliers - one large and one medium-sized. ...
Making green energy the default choice can help tackle climate change, study finds
2021-03-11
Researchers studying the Swiss energy market have found that making green energy the default option for consumers leads to an enduring shift to renewables and thus has the potential to cut CO2 emissions by millions of tonnes.
The study, published today in Nature Human Behaviour, investigated the effect of changes in the Swiss energy market that presented energy from renewable sources as the standard option for consumers - the 'green default.'
Both business and private customers largely accepted the default option, even though it was slightly more expensive, and the switch to green sources proved a lasting one.
Professor Ulf Liebe (University of Warwick), Doctor Jennifer Gewinner and Professor em. Andreas Diekmann (both ETH Zurich) analysed data from two Swiss ...
Combining public health and environmental science to develop pollen forecasting
2021-03-11
New research, which brings healthcare data together with ground-breaking ecological techniques, could set a roadmap for refining pollen forecasts in the future.
Current pollen forecasts, crucial for people with allergic asthma or hay fever to manage their symptoms, rely on measuring the total load of grass pollen in the atmosphere. However, these do not distinguish between pollen from different types of grass.
Now, a potential link between pollen from certain grass species and respiratory health issues has been revealed.
The results, published in Current Biology, (11.3.21DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.02.019 ) have been produced by the first project to use an ecological biomonitoring ...
New study finds shared origins for individual chronic diseases in multimorbidity
2021-03-11
A new study published today in Nature Medicine has identified key risk factors that increase the likelihood of individuals developing not only one but multiple non-communicable diseases, which include cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic respiratory disease and diabetes.
The analysis of over 11,000 people found that rather than being due to chance, there are often underlying biological links in individuals with multimorbidity, which is defined as the co-occurrence of two or more long-term health conditions and is a growing public health challenge.
Multimorbidity, which affects about two thirds of people aged 65 years or over in the UK, impairs an individual's quality of life over and above the cumulative burden from each individual disease. Understanding which diseases ...
Targeted screening for prostate cancer could prevent one in six deaths
2021-03-11
A national screening programme targeted at those men who are genetically pre-disposed to prostate cancer, and involving a blood test and MRI scan before an invasive biopsy, could prevent one in six prostate cancer deaths and significantly reduce over-diagnosis, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
Prostate cancer is the most common form of cancer in men with around 130 new cases diagnosed in the UK every day and more than 10,000 men a year dying as a result of the disease. However, unlike breast and cervical cancer there is currently no national screening programme for this disease in the UK.
Currently, men suspected of having prostate cancer have a blood test that detects raised levels of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA)*. Following the UCL-led ...
Experiences of Latinx individuals hospitalized for COVID-19
2021-03-11
What The Study Did: Experiences of Latinx patients who were hospitalized with and survived COVID-19 are described in this study.
Authors: Lilia Cervantes, M.D., of Denver Health in Colorado, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0684)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study and commentary are linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide ...
Clear vs covered masks during surgical clinic visits
2021-03-11
What The Study Did: This randomized clinical trial evaluated the effect on patient perceptions of communication, trust and empathy of surgeons who wore clear masks that showed their faces versus standard masks that obscured them during outpatient clinic visits.
Authors: Muneera R. Kapadia, M.D., M.M.E., of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.0836)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full ...
Cancer surgery in Canadian Universal Health Care System during COVID-19
2021-03-11
What The Study Did: Researchers sought to quantify cancer surgical backlog and determine whether there were differences in sociodemographic and hospital characteristics among patients undergoing cancer surgery before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Authors: Antoine Eskander, M.D., Sc.M., of Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1104)
Editor's Note: The article includes ...
Assessment of use, fit of face masks among people in public during COVID-19 pandemic in China
2021-03-11
What The Study Did: In this study of face mask fit among people in China, although most people used face masks in public places, compromised protection due to suboptimal airtightness was common. The simple approach of sealing the upper edge of the face mask with an adhesive tape strip was associated with substantially improved its airtightness.
Authors: Lin Duo, Ph.D., of Fuwai Yunnan Cardiovascular Hospital in Kunming, China, and Chengye Sun, Ph.D., of the National Institute of Occupational Health and Poison Control, Chinese Center for Disease ...
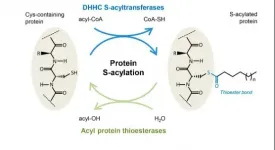
Revealing the way a critical enzyme works in the cell
2021-03-11
S-acylation is the process of chemically linking a lipid to protein via a thioester bond. It is an important process of the cell that regulates the localization and function of numerous proteins. It promotes lipid membrane association of the protein, for instance to the plasma membrane, Golgi apparatus, or inner nuclear membrane.
Like most biochemical processes in the cell, protein S-acylation is reversible to regulate the functions of acylated proteins. S-acylation is reversed by the enzymes acyl protein thioesterases (APTs).
To do their work, APTs have to interact with the lipid membranes that their target proteins are bound to. But even though APTs are central to the important acylation deacylation process little is known about how APTs carry ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] First lab-grown mini-thyroids use patients' own tissueNew research unlocks new clues for treating hypothyroidism