INFORMATION:
This work was funded by the Royal Society, Wellcome Trust, the Swiss National Science Foundation, the European Union, and the Swiss National Centre of Competence in Research.
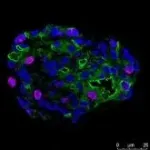
"Biodegradable Harmonophores for Targeted High-Resolution In Vivo Tumor Imaging" by Ali Yasin Sonay, Konstantinos Kalyviotis, Sine Yaganoglu, Aysen Unsal, Martina Konantz, Claire Teulon, Ingo Lieberwirth, Sandro Sieber, Shuai Jiang, Shahed Behzadi, Daniel Crespy, Katharina Landfester, Sylvie Roke, Claudia Lengerke, and Periklis Pantazis, published 25 Febr
Tumours illuminated brightly and precisely with new biodegradable nanoprobe
2021-03-11
(Press-News.org) To highlight tumours in the body for cancer diagnosis, doctors can use tiny optical probes (nanoprobes) that light up when they attach to tumours. These nanoprobes allow doctors to detect the location, shape and size of cancers in the body.
Most nanoprobes are fluorescent; they absorb light of a specific colour, like blue and then emit back light of a different colour, like green. However, as tissues of the human body can emit light as well, distinguishing the nanoprobe light from the background light can be tough and could lead to the wrong interpretation.
Now, researchers at Imperial College London have developed new nanoprobes, named bioharmonophores and patented at Imperial, which emit light with a new type of glowing technology known as second harmonic generation (SHG).
After testing the nanoprobes in zebrafish embryos, the researchers found that bioharmonophores, which were modified to target cancer cells, highlighted tumours more brightly and for longer periods than fluorescent nanoprobes. Their light can be easily spotted and distinguished by the tissue generally emitted light, and they also attach precisely to tumour cells and no healthy cells, making them more precise in detecting tumour edges.
Lead researcher Dr Periklis Pantazis of Imperial's Department of Bioengineering said: "Bioharmonophores could be a more effective way to detect tumours than is currently available. They uniquely combine features that could be great for cancer diagnosis and therapy in clinical practice and could eventually improve patient outcomes following further research."
The findings are published in ACS Nano.
Bioharmonophores are both biocompatible and biodegradable as they are made of peptides - the same ingredients of proteins found in the body. They are metabolised naturally in the body within 48 hours and are therefore unlikely to pose long-term health risks.
To investigate precise tumour detection, the researchers first injected zebrafish embryos with malignant cancer cells, which allowed tumour cells to proliferate unchecked. Twenty-four hours later they injected bioharmonophores which were modified to target p32 peptide molecules that are specifically found in tumour cells. They then used imaging techniques at Imperial's Facility for Imaging by Light Microscopy to study how well the modified bioharmonophores detected the tumours.
They found that bioharmonophores had outstanding detection sensitivity, meaning they attached to specific tumour cells but not to healthy ones. Fluorescence-enabled nanoprobes tend to attach less specifically, meaning they can misrepresent healthy cells as tumour cells, or vice versa.
They also found that unlike fluorescence, bioharmonophores did not 'bleach', meaning they did not lose their ability to emit light over time. In addition, the light emitted by bioharmonophores did not saturate as happens with fluorescent nanoprobes, meaning they got brighter when illuminated with more light. This way tumours became even clearer.
Dr Pantazis said: "It is very important that tumour nanoprobes highlight cells specifically and clearly for cancer diagnosis. Our proof-of-concept study suggests that the very bright bioharmonophores could be powerful tools in diagnosing cancer and targeting treatments in the coming years."
The manufacture of bioharmonophores is cheap, reproducible, scalable and takes around two days at room temperature. They now need to be tested in mammals to identify how well the findings translate beyond zebrafish.
The researchers are also looking into how bioharmonophores could be used to guide surgical interventions during cancer surgery, as well as how they could generate light at different frequencies to potentially help kill tumour cells with high precision.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new model predicts snakebites to save human lives
2021-03-11
About 1.8 million envenoming snakebites occur around the world annually, killing about 94,000 people. In tropical areas, especially in Southeast Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa, snakebites are considered a major cause of death, especially among farmers who encounter snakes in their fields. In response, the World Health Organization has launched a strategic plan to reduce snakebites by 50% by 2030. An important basis for attaining this goal is expanding relevant scientific research.
An international research group, including researchers from Tel Aviv University, has recently created an innovative simulation model for predicting snakebites, based on an improved ...
Rare VEXAS disease affecting only men is found to be more common than first thought
2021-03-11
A rare disease first identified in 2020 is much more common than first thought, say researchers at the University of Leeds investigating its origins.
VEXAS syndrome is a serious inflammatory condition which develops in men over 50, causing them to become very sick and fatigued, and can be fatal. It was originally thought to be rare, but a new study has identified genetic mutations which indicate that the disease is actually much more common.
The researchers developed a genetic test to identify patients who may have the disease, and now want to screen more people showing symptoms to understand exactly how common it is.
VEXAS syndrome causes unexplained fevers, painful skin rashes and affects the bone ...
How the habitability of exoplanets is influenced by their rocks
2021-03-11
The conditions on Earth are ideal for life. Most places on our planet are neither too hot nor too cold and offer liquid water. These and other requirements for life, however, delicately depend on the right composition of the atmosphere. Too little or too much of certain gases - like carbon dioxide - and Earth could become a ball of ice or turn into a pressure cooker. When scientists look for potentially habitable planets, a key component is therefore their atmosphere.
Sometimes, that atmosphere is primitive and largely consists of the gases that were around when the planet formed - as is the case for Jupiter and Saturn. On terrestrial planets like Mars, Venus or Earth, however, such primitive atmospheres are lost. Instead, their remaining atmospheres are strongly influenced ...
Electricity could help speed wound healing, new study shows
2021-03-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Electric stimulation may be able to help blood vessels carry white blood cells and oxygen to wounds, speeding healing, a new study suggests.
The study, published in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Lab on a Chip, found that steady electrical stimulation generates increased permeability across blood vessels, providing new insight into the ways new blood vessels might grow.
The electrical stimulation provided a constant voltage with an accompanying electric current in the presence of fluid flow. The findings indicate that stimulation increases ...
Researchers test using environmental DNA to monitor grass pollen levels
2021-03-11
Grass pollen is a major outdoor allergen, responsible for widespread and costly respiratory conditions including allergic asthma and hay fever (rhinitis). Now, researchers re-porting in the journal Current Biology on March 11 suggest that environmental DNA could help to better understand which grasses are the worst offenders.
"These findings represent a first step towards changing and improving our understanding of the complex relationships between pollen and population health," said Benedict Wheeler of the University of Exeter, UK. "If confirmed and refined, this research could help to improve pollen forecasts and warnings in the future, supporting individual and community-level prevention strategies and management ...
First lab-grown mini-thyroids use patients' own tissue
2021-03-11
Hormones produced by the thyroid gland are essential regulators of organ function. The absence of these hormones either through thyroid dysfunction due to, for example, irradiation, thyroid cancer or autoimmune disease or thyroidectomy leads to symptoms like fatigue, feeling cold, constipation, and weight gain. The condition called hypothyroidism is estimated to affect up to 11% of the global population. Although hypothyroidism can be treated by hormone replacement therapy, some patients have persistent symptoms and/or experience side effects. To investigate potential alternative treatment strategies for these patients, researchers have now for the first time succeeded in generating thyroid mini-organs in the lab. In a END ...
Changing defaults can have a significant and lasting effect
2021-03-11
People often choose the standard option. Choosing to be an organ donor, printing on both sides of the page - such decisions are influenced by which is the standard setting, or default. In fact, economists and sociologists call this the default effect. Researchers at ETH Zurich and the University of Warwick in the UK have now managed to clearly demonstrate this effect. Private households, but also self-employed people and SMEs, are more likely to procure sustainably produced electricity if that is their provider's default offer.
The scientists conclude this from an analysis of data from two Swiss electricity suppliers - one large and one medium-sized. ...
Making green energy the default choice can help tackle climate change, study finds
2021-03-11
Researchers studying the Swiss energy market have found that making green energy the default option for consumers leads to an enduring shift to renewables and thus has the potential to cut CO2 emissions by millions of tonnes.
The study, published today in Nature Human Behaviour, investigated the effect of changes in the Swiss energy market that presented energy from renewable sources as the standard option for consumers - the 'green default.'
Both business and private customers largely accepted the default option, even though it was slightly more expensive, and the switch to green sources proved a lasting one.
Professor Ulf Liebe (University of Warwick), Doctor Jennifer Gewinner and Professor em. Andreas Diekmann (both ETH Zurich) analysed data from two Swiss ...
Combining public health and environmental science to develop pollen forecasting
2021-03-11
New research, which brings healthcare data together with ground-breaking ecological techniques, could set a roadmap for refining pollen forecasts in the future.
Current pollen forecasts, crucial for people with allergic asthma or hay fever to manage their symptoms, rely on measuring the total load of grass pollen in the atmosphere. However, these do not distinguish between pollen from different types of grass.
Now, a potential link between pollen from certain grass species and respiratory health issues has been revealed.
The results, published in Current Biology, (11.3.21DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.02.019 ) have been produced by the first project to use an ecological biomonitoring ...
New study finds shared origins for individual chronic diseases in multimorbidity
2021-03-11
A new study published today in Nature Medicine has identified key risk factors that increase the likelihood of individuals developing not only one but multiple non-communicable diseases, which include cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic respiratory disease and diabetes.
The analysis of over 11,000 people found that rather than being due to chance, there are often underlying biological links in individuals with multimorbidity, which is defined as the co-occurrence of two or more long-term health conditions and is a growing public health challenge.
Multimorbidity, which affects about two thirds of people aged 65 years or over in the UK, impairs an individual's quality of life over and above the cumulative burden from each individual disease. Understanding which diseases ...