(Press-News.org) Boston, MA - Vaccinating adults age 26 and older against the human papillomavirus (HPV)--the virus that causes more than 90% of cervical cancers as well as several other cancers--may not be cost-effective, according to a new study led by researchers at the Harvard T.H. School of Public Health.
"Our study found that the added health benefit of increasing the vaccination age limit beyond 26 years is minimal, and that the cost-effectiveness is much lower than in pre-adolescents, the target age group for the HPV vaccine," said Jane Kim, K.T. Li Professor of Health Economics and lead author of the study.
The study will be published March 11, 2021, in PLOS Medicine.
HPV vaccines have been shown to be highly effective in preventing HPV infections that are associated with cervical, anal, oropharyngeal, vulvar, vaginal, and penile cancers, as well as genital warts. Current U.S. guidelines recommend HPV vaccination for girls and boys at age 11 or 12, and catch-up vaccination for people through age 26 if they were not vaccinated when younger. For adults beyond age 26, the guidelines don't specifically recommend catch-up vaccination but suggest that, for people aged 27-45, clinicians and patients make decisions about HPV vaccination on an individual basis.
The new study, undertaken to inform these national guidelines, used two mathematical models--from Harvard and Cancer Council New South Wales, Australia--that simulated scenarios of extending HPV vaccination to women and men up to age 45 years. Using U.S. data, the models projected cost and health outcomes of the six HPV-associated cancers and genital warts, taking into account historical and future vaccination uptake in younger people, cervical cancer screening practices among women, vaccine efficacy, and vaccination costs. The researchers sought to determine whether the benefits of HPV vaccination at older ages would have an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) that was in line with a commonly-cited upper threshold of $200,000 per quality-adjusted life year (QALY). QALYs are a measure of life expectancy adjusted to account for quality of life associated with health conditions and events.
The researchers found that HPV vaccination beyond age 26 in the U.S. would provide limited health benefit at the population level, at a substantial cost, given current HPV vaccine prices. Their analysis showed that the ICER for vaccinating people up to age 45 years ranged from $315,700 to $440,600 per QALY gained.
Kim noted that current HPV vaccines are prophylactic and therefore most effective when given prior to HPV exposure, which can happen soon after sexual initiation; once someone is exposed to HPV, the vaccine won't clear those infections. "By the time you vaccinate individuals in their 30s and 40s, many have already been exposed to HPV, so the health benefit really decreases at these older ages," she said. "It's also important to emphasize that cervical cancer screening remains an effective and cost-effective way to protect women from cervical cancer."
The study results, which were previously reported to the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, helped inform the committee's June 2019 recommendations to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention on HPV vaccination. "Other countries that are considering extending the upper age limit of HPV vaccination to include older adults should consider the opportunity costs of doing so," said Kim.
INFORMATION:
Other Harvard Chan School co-authors of the study included Emily Burger, Stephen Sy, and Catherine Regan.
Funding for the study came from the National Cancer Institute at the National Institutes of Health (grant number U01CA199334).
"Human papillomavirus vaccination for adults aged 30 to 45 years in the United States: A cost-effectiveness analysis," Jane J. Kim, Kate T. Simms, James Killen, Megan A. Smith, Emily A. Burger, Stephen Sy, Catherine Regan, Karen Canfell, PLOS Medicine, online March 11, 2021, doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003534
Visit the Harvard Chan School website for the latest news, press releases, and multimedia offerings.
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health brings together dedicated experts from many disciplines to educate new generations of global health leaders and produce powerful ideas that improve the lives and health of people everywhere. As a community of leading scientists, educators, and students, we work together to take innovative ideas from the laboratory to people's lives--not only making scientific breakthroughs, but also working to change individual behaviors, public policies, and health care practices. Each year, more than 400 faculty members at Harvard Chan School teach 1,000-plus full-time students from around the world and train thousands more through online and executive education courses. Founded in 1913 as the Harvard-MIT School of Health Officers, the School is recognized as America's oldest professional training program in public health.
Eating is a dangerous business. Naturally occurring toxins in food and potentially harmful foodborne microbes can do a number on our intestines, leading to repeated minor injuries. In healthy people, such damage typically heals in a day or two. But in people with Crohn's disease, the wounds fester, causing abdominal pain, bleeding, diarrhea and other unpleasant symptoms.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and the Cleveland Clinic have discovered that a fungus found in foods such as cheese and processed meats can infect sites of intestinal damage in mice and people with Crohn's and prevent healing. Moreover, treating infected mice with antifungal medication eliminates the fungus and allows the wounds ...
Insights into how bacterial proteins work as a network to take control of our cells could help predict infection outcomes and develop new treatments.
Much like a hacker seizes control of a company's software to cause chaos, disease-causing bacteria, such as E. coli and Salmonella, use miniature molecular syringes to inject their own chaos-inducing agents (called effectors) into the cells that keep our guts healthy.
These effectors take control of our cells, overwhelming their defences and blocking key immune responses, allowing the infection to take hold.
Previously, studies have investigated single effectors. Now a team led by scientists at Imperial College London and The Institute of Cancer ...
A team led by Christoph Utschick and Prof. Rudolf Gross, physicists at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), has developed a coil with superconducting wires capable of transmitting power in the range of more than five kilowatts contactless and with only small losses. The wide field of conceivable applications include autonomous industrial robots, medical equipment, vehicles and even aircraft.
Contactless power transmission has already established itself as a key technology when it comes to charging small devices such as mobile telephones and electric toothbrushes. Users would also like to see contactless charging made available for larger electric machines such as industrial robots, medical equipment and electric vehicles.
Such devices could ...
How do you turn "dumb" headphones into smart ones? Rutgers engineers have invented a cheap and easy way by transforming headphones into sensors that can be plugged into smartphones, identify their users, monitor their heart rates and perform other services.
Their invention, called END ...
Irvine, Calif., March 11, 2021 - Catastrophic collapse of materials and structures is the inevitable consequence of a chain reaction of locally confined damage - from solid ceramics that snap after the development of a small crack to metal space trusses that give way after the warping of a single strut.
In a study published this week in Advanced Materials, engineers at the University of California, Irvine and the Georgia Institute of Technology describe the creation of a new class of mechanical metamaterials that delocalize deformations to prevent failure. They did so by turning to tensegrity, a century-old design principle in which isolated ...
LAWRENCE -- Much like coronavirus, circulating HIV-1 viruses mutate into diverse variants that pose challenges for scientists developing vaccines to protect people from HIV/AIDS.
"AIDS vaccine development has been a decades-long challenge partly because our immune systems have difficulty recognizing all the diverse variants of the rapidly mutating HIV virus, which is the cause of AIDS," said Brandon DeKosky, assistant professor of pharmaceutical chemistry and chemical & petroleum engineering at the University of Kansas.
In the past five years, tremendous progress has been ...
Philadelphia, March 12, 2021 - Researchers from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have determined what happens at a cellular level as the lung alveolus forms and allows newborns to breathe air. Understanding this process gives researchers a better sense of how to develop therapies and potentially regenerate this critical tissue in the event of injury. The findings were published online today by the journal Science.
The lung develops during both embryonic and postnatal stages, during which lung tissue forms and a variety of cell types perform specific roles. During the transition from embryo to newborn is when the alveolar region of the lung ...
Skoltech researchers were able to show that patterns that can cause neural networks to make mistakes in recognizing images are, in effect, akin to Turing patterns found all over the natural world. In the future, this result can be used to design defenses for pattern recognition systems currently vulnerable to attacks. The paper, available as an arXiv preprint, was presented at the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-21).
Deep neural networks, smart and adept at image recognition and classification as they already are, can still be vulnerable ...
An enzyme called MARK2 has been identified as a key stress-response switch in cells in a study by researchers at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Overactivation of this type of stress response is a possible cause of injury to brain cells in neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. The discovery will make MARK2 a focus of investigation for its possible role in these diseases, and may ultimately be a target for neurodegenerative disease treatments.
In addition to its potential relevance to neurodegenerative diseases, the finding is an advance in understanding basic cell biology.
The paper describing ...
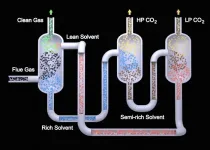
RICHLAND, Wash.--As part of a marathon research effort to lower the cost of carbon capture, chemists have now demonstrated a method to seize carbon dioxide (CO2) that reduces costs by 19 percent compared to current commercial technology. The new technology requires 17 percent less energy to accomplish the same task as its commercial counterparts, surpassing barriers that have kept other forms of carbon capture from widespread industrial use. And it can be easily applied in existing capture systems.
In a study published in the March 2021 edition of International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory--along with collaborators from ...