(Press-News.org) Researchers at UCL have solved a major piece of the puzzle that makes up the ancient Greek astronomical calculator known as the Antikythera Mechanism, a hand-powered mechanical device that was used to predict astronomical events.
Known to many as the world's first analogue computer, the Antikythera Mechanism is the most complex piece of engineering to have survived from the ancient world. The 2,000-year-old device was used to predict the positions of the Sun, Moon and the planets as well as lunar and solar eclipses.
Published in Scientific Reports, the paper from the multidisciplinary UCL Antikythera Research Team reveals a new display of the ancient Greek order of the Universe (Cosmos), within a complex gearing system at the front of the Mechanism.
Lead author Professor Tony Freeth (UCL Mechanical Engineering) explained: "Ours is the first model that conforms to all the physical evidence and matches the descriptions in the scientific inscriptions engraved on the Mechanism itself.
"The Sun, Moon and planets are displayed in an impressive tour de force of ancient Greek brilliance."
The Antikythera Mechanism has generated both fascination and intense controversy since its discovery in a Roman-era shipwreck in 1901 by Greek sponge divers near the small Mediterranean island of Antikythera.
The astronomical calculator is a bronze device that consists of a complex combination of 30 surviving bronze gears used to predict astronomical events, including eclipses, phases of the moon, positions of the planets and even dates of the Olympics.
Whilst great progress has been made over the last century to understand how it worked, studies in 2005 using 3D X-rays and surface imaging enabled researchers to show how the Mechanism predicted eclipses and calculated the variable motion of the Moon.
However, until now, a full understanding of the gearing system at the front of the device has eluded the best efforts of researchers. Only about a third of the Mechanism has survived, and is split into 82 fragments - creating a daunting challenge for the UCL team.
The biggest surviving fragment, known as Fragment A, displays features of bearings, pillars and a block. Another, known as Fragment D, features an unexplained disk, 63-tooth gear and plate.
Previous research had used X-ray data from 2005 to reveal thousands of text characters hidden inside the fragments, unread for nearly 2,000 years. Inscriptions on the back cover include a description of the cosmos display, with the planets moving on rings and indicated by marker beads. It was this display that the team worked to reconstruct.
Two critical numbers in the X-rays of the front cover, of 462 years and 442 years, accurately represent cycles of Venus and Saturn respectively. When observed from Earth, the planets' cycles sometimes reverse their motions against the stars. Experts must track these variable cycles over long time-periods in order to predict their positions.
"The classic astronomy of the first millennium BC originated in Babylon, but nothing in this astronomy suggested how the ancient Greeks found the highly accurate 462-year cycle for Venus and 442-year cycle for Saturn," explained PhD candidate and UCL Antikythera Research Team member Aris Dacanalis.
Using an ancient Greek mathematical method described by the philosopher Parmenides, the UCL team not only explained how the cycles for Venus and Saturn were derived but also managed to recover the cycles of all the other planets, where the evidence was missing.
PhD candidate and team member David Higgon explained: "After considerable struggle, we managed to match the evidence in Fragments A and D to a mechanism for Venus, which exactly models its 462-year planetary period relation, with the 63-tooth gear playing a crucial role."
Professor Freeth added: "The team then created innovative mechanisms for all of the planets that would calculate the new advanced astronomical cycles and minimize the number of gears in the whole system, so that they would fit into the tight spaces available."
"This is a key theoretical advance on how the Cosmos was constructed in the Mechanism," added co-author, Dr Adam Wojcik (UCL Mechanical Engineering). "Now we must prove its feasibility by making it with ancient techniques. A particular challenge will be the system of nested tubes that carried the astronomical outputs."
INFORMATION:
The discovery brings the research team a step closer to understanding the full capabilities of the Antikythera Mechanism and how accurately it was able to predict astronomical events. The device is kept at the National Archaeological Museum in Athens.
The UCL Antikythera Research Team is supported by the A.G. Leventis Foundation, Charles Frodsham & Co. and the Worshipful Company of Clockmakers.
The team is led by Dr Adam Wojcik and made up of Professor Tony Freeth, Professor Lindsay MacDonald (UCL CEGE), Dr Myrto Georgakopoulou (UCL Qatar) and PhD candidates David Higgon and Aris Dacanalis (both UCL Mechanical Engineering).
PHILADELPHIA -- (March 12, 2021) -- Scientists at The Wistar Institute identified a new function of ADAR1, a protein responsible for RNA editing, discovering that the ADAR1p110 isoform regulates genome stability at chromosome ends and is required for continued proliferation of cancer cells. These findings, reported in Nature Communications, reveal an additional oncogenic function of ADAR1 and reaffirm its potential as a therapeutic target in cancer.
The lab of Kazuko Nishikura, Ph.D., professor in the Gene Expression & Regulation Program of The Wistar Institute Cancer Center, was one of the first to discover ADAR1 in mammalian cells and to characterize the process of RNA editing ...
A factor that turns malignant tumors into benign ones? - That is exactly what scientists at St. Anna Children's Cancer Research Institute have discovered. Together with colleagues from the Medical University of Vienna and the University of Vienna (Faculty of Chemistry), they studied tumors of the peripheral nervous system in children, namely neuroblastomas. The scientists discovered that the uncontrolled growth of benign neuroblastomas is stopped by a signal molecule produced by Schwann cells present within these tumors. This natural "brake" also works on malignant neuroblastoma ...
Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) are found in furniture, electronics, and kitchenware to slow the spread of flames in the event of a fire. However, it has been shown that these molecules may lead to early mammary gland development, which is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer. The study on the subject by Professor Isabelle Plante from the Institut national de la recherche scientifique (INRS) made the cover of the February issue of the journal Toxicological Sciences.
Part of the flame retardants are considered to be endocrine disruptors, i.e. they interfere with the hormonal system. Since they are not directly bound to the material in which they are added, the molecules escape easily. They are then found in house ...
Chest pain is misdiagnosed in women more frequently than in men, according to research presented today at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The study also found that women with chest pain were more likely than men to wait over 12 hours before seeking medical help.
"Our findings suggest a gender gap in the first evaluation of chest pain, with the likelihood of heart attack being underestimated in women," said study author Dr. Gemma Martinez-Nadal of the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona, Spain. "The low suspicion of heart attack occurs in both women themselves and in physicians, leading to higher risks of late diagnosis and misdiagnosis."
This study examined gender differences in the presentation, ...
As gatherings to observe whooping cranes join the ranks of online-only events this year, a new study offers insight into how the endangered bird is faring on a landscape increasingly dotted with wind turbines. The paper, published this week in Ecological Applications, reports that whooping cranes migrating through the U.S. Great Plains avoid "rest stop" sites that are within 5 km of wind-energy infrastructure.
Avoidance of wind turbines can decrease collision mortality for birds, but can also make it more difficult and time-consuming for migrating flocks to find safe and suitable rest and refueling locations. The study's insights into migratory behavior ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Overweight low-income mothers of young kids ate fewer fast-food meals and high-fat snacks after participating in a study - not because researchers told them what not to eat, but because the lifestyle intervention being evaluated helped lower the moms' stress, research suggests.
The 16-week program was aimed at preventing weight gain by promoting stress management, healthy eating and physical activity. The methods to get there were simple steps tucked into lessons on time management and prioritizing, many demonstrated in a series ...
In the field of robotics, metals offer advantages like strength, durability, and electrical conductivity. But, they are heavy and rigid--properties that are undesirable in soft and flexible systems for wearable computing and human-machine interfaces.
Hydrogels, on the other hand, are lightweight, stretchable, and biocompatible, making them excellent materials for contact lenses and tissue engineering scaffolding. They are, however, poor at conducting electricity, which is needed for digital circuits and bioelectronics applications.
Researchers in Carnegie Mellon University's Soft Machines Lab have developed a unique silver-hydrogel composite that has high electrical ...
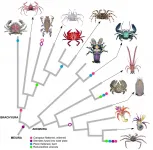
Crabs are living the meme life on social media lately. The memes joke that everything will eventually look like a crab. But it's actually based in some truth.
The crab shape has evolved so many times the evolutionary biologist L.A. Borradaile coined the term carcinization in 1916 to describe the convergent evolution process in which a crustacean evolves into a crab-like form from a non-crab-like form. Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura and are considered "true crabs", most of which are carcinized. "False crabs" are of the ...
As experts nationwide point to a mental health crisis among teens and young adults, a pilot program teaching mindfulness and coping techniques to students at the University of Washington has helped lower stress and improve emotional well-being.
New studies by the psychology researchers who created the program find that the strategies, offered first in residence halls and later through classes and other organized campus groups, have provided participants with successful methods for coping with stress, managing their emotions and learning self-compassion.
Researchers say the results show the potential for preventive mental health services offered in an accessible, peer-group environment.
"This program is not a substitute ...
In Brazil, a study conducted by researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo (USP) and collaborators showed that deforestation in the Amazon causes an increase in the diversity of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. An article on the study, published in Soil Biology and Biochemistry, compares the microorganisms that live in the soil of native forest with those found in pasture and croplands. The researchers found a far larger number of genes considered markers of antibiotic resistance in deforested than forested areas.
“Bacteria produce substances with which to attack each other in a competition for resources that’s ...