(Press-News.org) Around three times as many males are diagnosed with autism than females. This suggests that biological sex factors may play a role in the development and presentation of autism.
Studies on the neurobiology (brain biology) of males and females with autism have begun to examine brain networks but results have been mixed. This is largely due to the limited availability of data from autistic females.
In response, researchers from END
Are there differences in the brains of autistic men and women?
Large-scale brain imaging study suggest that atypical connectivity between brain hemispheres in autism reflects a combination of biological sex-dependent (i.e., specific to male or females) and independent (i.e., common across sexes) effects
2021-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Extinction cascading through ecosystems could spell trouble for humans
2021-03-12
Humans rely on nature extensively for everything from food production to coastal protection, but those contributions might be more threatened than previously thought, according to new findings from the University of Colorado Boulder.
This research, out today in Nature Communications, looked at three different coastal food webs that include those services provided to humans, or ecosystem services, and found that even if the services themselves aren't directly threatened, they can become threatened when other species around them go extinct--often called secondary ...
Using AI to assess surgical performance
2021-03-12
More than one million operations are performed in Switzerland every year. A surgeon's skill has a direct impact on the outcome of the operation. Training and experience, as well as momentary fatigue and other influencing factors all play a role. At present, skill is tested by experts, either directly during an operation or by evaluating video footage. This approach is very costly and only a limited number of experts are available. Moreover, the assessment may vary and is not always fully reproducible. For some time, attempts have been made to automate and objectify the assessment of surgeons' skills.
Proof of feasibility
The key result of the study is the proof of the fundamental feasibility of an ...
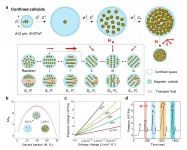
Confined magnetic colloidal system for controllable fluid transport
2021-03-12
Colloidal suspensions of microscopic particles show complex and interesting collective behaviors. In particular, the collective dynamics of colloids is fundamental and ubiquitous for materials assembly, robotic motion, microfluidic control, and in several biological scenarios. The collective dynamics of confined colloids can be completely different from that of free colloids: for instance, confined colloids can self-organize into vortex structures, coherent motion, or different phase behaviors. On one hand, due to the complexity of colloidal suspensions, how to finely tune the ...
New review explores effective sampling techniques for collecting airborne viruses and ultrafine part
2021-03-12
As the world continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, an international team of researchers have published a review of the best techniques to collect airborne aerosols containing viruses.
In the review, which was published by the Science of the Total Environment journal, a team led by the University of Surrey concluded that the most effective way to collect and detect airborne pathogens, particularly viruses, was to use cyclone sampling techniques.
For example, the sampler draws the air through the cyclone separator. It then uses centrifugal forces to collect the particles on a sterile cone containing the liquid collection vessel, such as DMEM (Dulbecco's minimal essential ...
Shedding light on perovskite films
2021-03-12
Photovoltaics decisively contributes to sustainable energy supply. The efficiency of solar cells in directly converting light energy into electrical energy depends on the material used. Metal-halide perovskites are considered very promising materials for solar cells of the next generation. With these semiconductors named after their special crystal structure, a considerable increase in efficiency was achieved in the past years. Meanwhile, perovskite solar cells have reached an efficiency of up to 25.5 percent, which is quite close to that of silicon ...
New proteins 'out of nothing'
2021-03-12
Proteins are the key component in all modern forms of life. Haemoglobin, for example, transports the oxygen in our blood; photosynthesis proteins in the leaves of plants convert sunlight into energy; and fungal enzymes help us to brew beer and bake bread. Researchers have long been examining the question of how proteins mutate or come into existence in the course of millennia. That completely new proteins - and, with them, new properties - can emerge practically out of nothing, was inconceivable for decades, in line with what the Greek philosopher Parmenides said: "Nothing can emerge from nothing" (ex nihilo nihil fit). Working with colleagues from the USA and ...
Evaluating the rehabilitation of an old mine waste rock pile
2021-03-12
The Cabeza de los Gatos waste rock pile, left from mining activities in the town of Tharsis (Huelva), underwent a rehabilitation process consisting of remodelling the slope of the pile, applying liming materials and then a layer of soil. Finally, trees and shrubs typical of the area were planted and a hydroseeding with a mixture of shrub and herbaceous seeds was applied. Twelve years later, a study led by researchers from IRNAS-CSIC, in collaboration with Sabina Rossini Oliva, a researcher from the University of Seville and the Environment and Water Agency of Andalusia (AMAYA), has proven the effectiveness of this sort of rehabilitation.
"The results obtained show that the steps taken were successful. Now, ...
High emotional intelligence 'can help to identify fake news'
2021-03-12
People with high levels of emotional intelligence are less likely to be susceptible to 'fake news', according to research at the University of Strathclyde.
The study invited participants to read a series of news items on social media and to ascertain whether they were real or fictitious, briefly describing the reasons for their answers. They were also asked to complete a test to determine their levels of emotional intelligence (EQ or emotional quotient) and were asked a number of questions when considering the veracity of each news item.
Researchers found that those who identified the types of news correctly were most likely to score highly in the EQ tests. There was a similar correlation between correct identification and educational attainment.
The ...
Release of serotonin from mast cells contribute to airway hyperresposivness in asthma
2021-03-12
In asthma, the airways become hyperresponsive. Researchers from Uppsala University have found a new mechanism that contributes to, and explains, airway hyperresponsiveness. The results are published in the scientific journal Allergy.
Some 10 per cent of Sweden's population suffer from asthma. In asthmatics, the airways are hyperresponsive (overreactive) to various types of stimuli, such as cold air, physical exertion and chemicals. The airways become constricted, making breathing difficult.
To diagnose asthma, a "methacholine test" is commonly used to determine whether a person is showing signs of airway hyperresponsiveness. Methacholine binds to what are known as muscarinic receptors in the smooth muscle cells lining the inside ...
'Magical' fire suppressant kills zombie fires 40% faster than water alone
2021-03-12
The researchers say this is a big step in tackling smouldering peat fires, which are the largest fires on Earth. They ignite very easily, are notoriously difficult to put out, and release up to 100 times more carbon into the atmosphere than flaming fires, contributing to climate change.
The fires, known as 'zombie fires' for their ability to hide and smoulder underground and then reanimate as new flames days or weeks after the wildfire had been extinguished, are prevalent in regions like Southeast Asia, North America, and Siberia.
They are driven by the burning of soils rich in organic content like peat, which is a large natural reservoir of carbon. Worldwide, peat fires account for millions of tonnes of carbon released into the atmosphere each year.
Firefighters currently use millions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
[Press-News.org] Are there differences in the brains of autistic men and women?Large-scale brain imaging study suggest that atypical connectivity between brain hemispheres in autism reflects a combination of biological sex-dependent (i.e., specific to male or females) and independent (i.e., common across sexes) effects