(Press-News.org) WINSTON-SALEM, NC - March 12, 2021 - The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine is investigating how cats with chronic kidney disease could someday help inform treatment for humans.
In humans, treatment for chronic kidney disease -- a condition in which the kidneys are damaged and cannot filter blood as well as they should -- focuses on slowing the progression of the organ damage. The condition can progress to end-stage kidney failure, which is fatal without dialysis or a kidney transplant. An estimated 37 million people in the US suffer from chronic kidney disease, according to the Centers for Disease Control.
The American Veterinary Medical Association estimates there are about 58 million cats in the United States. Chronic kidney disease affects 30-50% of cats age 15 years or older. The fibrosis or scarring that occurs as a result of the disease is a common final pathway for kidney disease in both animals and people. For cats, end-stage kidney disease has no effective cure.
In a new study published online by Frontiers in Veterinary Science in the Veterinary Regenerative Medicine platform, the WFIRM research team set out to test the effects of a cell-derived molecular therapy to treat kidney fibrosis in cats. Regenerative therapies using stem cells and vascular fractions have been tested, but the collection of cells or cell fractions is expensive, time consuming, and requires advanced cell processing capabilities not available in most veterinary general practices.
Alternatively, "The use of cell-based molecules to treat kidney fibrosis may be a promising approach," said lead author Julie Bennington, DVM, a WFIRM research fellow and PhD candidate. "Current treatments include pharmaceutical therapies and dietary management to slow disease progression and increase longevity, and alternatives are needed."
In this study, authors used a cell-signaling chemokine -- CXCL12 -- that is produced by cells and stimulates tissue regeneration. Recombinant human CXCL12 is commercially available, inexpensive, and has been shown to reduce fibrosis in rodent models of chronic kidney disease.
The goal of this study was to test the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of ultrasound-guided intra-renal CXCL12 injection in cats with chronic kidney fibrosis, first in a preclinical cat model, and, then in a pilot study in cats that may have early kidney disease.
"Results of these studies together show that intra-renal injection of CXCL12 may be a potential new therapy to treat early kidney disease in cats with a capability for widespread use," said co-author Koudy Williams, DVM, also of WFIRM. "Further clinical evaluations are needed."
Piedmont Animal Health, the company that funded the research, is preparing to set up a clinical pilot study in the US, and Bennington will serve as a consultant.
WFIRM Director Anthony Atala, MD, said this research is a good example of "how a condition like chronic kidney disease, common to both dogs and cats, can be studied and potentially applied to the disease in humans."
INFORMATION:
Additional co-authors include: Shannon Lankford, Renata Magalhaes, Douglas Shankle, all of WFIRM; Jason Fanning of Wake Forest University; Gopal Badlani, MD, of Wake Forest Baptist Health Urology; and Cucu Kartini, Irma Suparto, Winda Kusumawardhani, M A. Putra, and Silmi Mariya, all of Indonesia.
About the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine: The Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine is recognized as an international leader in translating scientific discovery into clinical therapies, with many world firsts, including the development and implantation of the first engineered organ in a patient. Over 400 people at the institute, the largest in the world, work on more than 40 different tissues and organs. A number of the basic principles of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine were first developed at the institute. WFIRM researchers have successfully engineered replacement tissues and organs in all four categories - flat structures, tubular tissues, hollow organs and solid organs - and 15 different applications of cell/tissue therapy technologies, such as skin, urethras, cartilage, bladders, muscle, kidney, and vaginal organs, have been successfully used in human patients. The institute, which is part of Wake Forest School of Medicine, is located in the Innovation Quarter in downtown Winston-Salem, NC, and is driven by the urgent needs of patients. The institute is making a global difference in regenerative medicine through collaborations with over 400 entities and institutions worldwide, through its government, academic and industry partnerships, its start-up entities, and through major initiatives in breakthrough technologies, such as tissue engineering, cell therapies, diagnostics, drug discovery, biomanufacturing, nanotechnology, gene editing and 3D printing.
If you were given "ultrasound" in a word association game, "sound wave" might easily come to mind. But in recent years, a new term has surfaced: bubbles. Those ephemeral, globular shapes are proving useful in improving medical imaging, disease detection and targeted drug delivery. There's just one glitch: bubbles fizzle out soon after injection into the bloodstream.
Now, after 10 years' work, a multidisciplinary research team has built a better bubble. Their new formulations have resulted in nanoscale bubbles with customizable outer shells -- so small and durable that they can travel to and penetrate some of the ...
(BOSTON) -- There is a great need to generate various types of cells for use in new therapies to replace tissues that are lost due to disease or injuries, or for studies outside the human body to improve our understanding of how organs and tissues function in health and disease. Many of these efforts start with human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) that, in theory, have the capacity to differentiate into virtually any cell type in the right culture conditions. The 2012 Nobel Prize awarded to Shinya Yamanaka recognized his discovery of a strategy that can reprogram adult cells to become iPSCs ...
Arlington, Va. (March 12, 2021)--A new supplement offering guidance on severe COVID-19 management in resource-limited settings is now available on the American Journal of Tropical Medicine (AJTMH) website. Pragmatic Recommendations for the Management of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in Low- and Middle-Income Countries was coordinated by a COVID-LMIC Task Force headed by Alfred Papali, MD, of Atrium Health, Charlotte, NC, and Marcus Schultz, MD, PhD, of Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand; University of Oxford, United Kingdom; and Amsterdam University Medical Centers, The Netherlands. ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. - University at Buffalo computer scientists have developed a tool that automatically identifies deepfake photos by analyzing light reflections in the eyes.
The tool proved 94% effective in experiments described in a paper accepted at the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing to be held in June in Toronto, Canada.
"The cornea is almost like a perfect semisphere and is very reflective," says the paper's lead author, Siwei Lyu, PhD, SUNY Empire Innovation Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering. "So, anything that is coming to the eye with a light emitting from those sources will have an image on ...
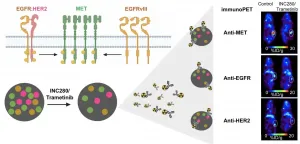
Reston, VA--Immuno-positron emission tomography (PET) imaging can provide early insight into a tumor's response to targeted therapy, allowing physicians to select the most effective treatment for patients who have cancer. The new research was published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
The research showed that immuno-PET successfully visualizes changes in different cancer receptors (receptor tyrosine kinases, or RTKs) within tumors during targeted therapies. This gives physicians a tool that can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment soon after its administration.
"When healthy cells turn into cancer cells, there is a disruption in the RTK signaling. This makes RTKs a valuable therapeutic and ...
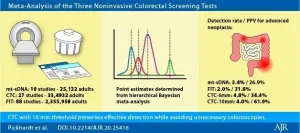
Leesburg, VA, March 12, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), compared with multi-target stool-DNA (mt-sDNA) and fecal immunochemical test (FIT), CT colonography (CTC) with 10 mm threshold most effectively targets advanced neoplasia (AN)--preserving detection while decreasing unnecessary colonoscopies.
"CTC performed with a polyp size threshold for colonoscopy referral set at 10 mm represents the most effective and efficient non-invasive screening test for colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention and detection," clarified first author Perry J. Pickhardt from the department of radiology ...
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Did you ever wonder how social networking applications like Facebook and LinkedIn make recommendations on the people you should friend or pages you should follow?
Behind the scenes are machine learning models that classify nodes based on the data they contain about users -- for example, their level of education, location or political affiliation. The models then use these classifications to recommend people and pages to each user. But there is significant bias in the recommendations made by these models -- known as graph neural networks (GNNs) ...
A new study by UC Davis MIND Institute researchers suggests that executive control differences in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be the result of a unique approach, rather than an impairment.
Executive control difficulties are common in individuals with autism and are associated with challenges completing tasks and managing time. The study, published in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, sought to tease out whether these difficulties represent a disruption in proactive executive control (engaged and maintained before a ...
Quantum dots are manmade nanoparticles of semiconducting material comprising only a few thousand atoms. Because of the small number of atoms, a quantum dot's properties lie between those of single atoms or molecules and bulk material with a huge number of atoms. By changing the nanoparticles' size and shape, it is possible to fine-tune their electronic and optical properties - how electrons bond and move through the material, and how light is absorbed and emitted by it.
Thanks to increasingly refined control of the nanoparticles' size and shape, the number ...
A machine learning algorithm that predicts suicide attempt recently underwent a prospective trial at the institution where it was developed, Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Over the 11 consecutive months concluding in April 2020, predictions ran silently in the background as adult patients were seen at VUMC. The algorithm, dubbed the Vanderbilt Suicide Attempt and Ideation Likelihood (VSAIL) model, uses routine information from electronic health records (EHRs) to calculate 30-day risk of return visits for suicide attempt, and, by extension, suicidal ideation.
Suicide has been on the rise in the U.S. for a generation ...