CT colonography most effective noninvasive colorectal cancer screening test
Compared with multi-target stool-DNA and fecal immunochemical test, CT colonography with 10 mm threshold most effectively targets advanced neoplasia--preserving detection while decreasing unnecessary colonoscopies
2021-03-12
(Press-News.org) Leesburg, VA, March 12, 2021--According to an open-access article in ARRS' American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), compared with multi-target stool-DNA (mt-sDNA) and fecal immunochemical test (FIT), CT colonography (CTC) with 10 mm threshold most effectively targets advanced neoplasia (AN)--preserving detection while decreasing unnecessary colonoscopies.
"CTC performed with a polyp size threshold for colonoscopy referral set at 10 mm represents the most effective and efficient non-invasive screening test for colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention and detection," clarified first author Perry J. Pickhardt from the department of radiology at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine & Public Health.
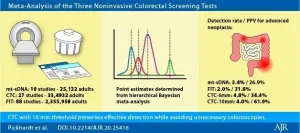
Because the relative performance characteristics of available noninvasive tests had not yet been adequately compared, Pickhardt's team systematically searched PubMed and Google Scholar, including 10 mt-sDNA, 27 CTC, and 88 FIT published screening studies involving 25,132, 33,4932, and 2,355,958 asymptomatic adults, respectively. To determine test-positivity rates (TPR) leading to optical colonoscopy (OC), as well as positive predictive value (PPV) and detection rate (DR) for both AN and CRC, meta-analysis with hierarchical Bayesian modeling was conducted, in accordance with Cochrane Collaboration and PRISMA guidelines.
Pickhardt and colleagues' results showed that CRC prevention via screen detection of AN was highest with CTC, followed by mt- sDNA, and lowest with FIT due to the differing TPR and PPV, although overlap existed in the 95% CIs when accounting for uncertainty. Compared with mt-sDNA and CTC6, FIT and CTC10 strategies yielded substantially lower colonoscopy resource utilization, while mt-sDNA performance appeared to be similar to FIT at low positivity thresholds.
Acknowledging that each CRC screening option has relative advantages and disadvantages that should be carefully considered and tailored to the individual, "in the end," the authors of this AJR article concluded, "the 'best' test may be the one that the patient is willing to undergo."
An electronic supplement to this article is available here: https://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.20.25416
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1900, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is the first and oldest radiological society in North America, dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of radiology and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in medical imaging since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with an annual scientific meeting, monthly publication of the peer-reviewed American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), quarterly issues of InPractice magazine, AJR Live Webinars and Podcasts, topical symposia, print and online educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Did you ever wonder how social networking applications like Facebook and LinkedIn make recommendations on the people you should friend or pages you should follow?
Behind the scenes are machine learning models that classify nodes based on the data they contain about users -- for example, their level of education, location or political affiliation. The models then use these classifications to recommend people and pages to each user. But there is significant bias in the recommendations made by these models -- known as graph neural networks (GNNs) ...
2021-03-12
A new study by UC Davis MIND Institute researchers suggests that executive control differences in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be the result of a unique approach, rather than an impairment.
Executive control difficulties are common in individuals with autism and are associated with challenges completing tasks and managing time. The study, published in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, sought to tease out whether these difficulties represent a disruption in proactive executive control (engaged and maintained before a ...
2021-03-12
Quantum dots are manmade nanoparticles of semiconducting material comprising only a few thousand atoms. Because of the small number of atoms, a quantum dot's properties lie between those of single atoms or molecules and bulk material with a huge number of atoms. By changing the nanoparticles' size and shape, it is possible to fine-tune their electronic and optical properties - how electrons bond and move through the material, and how light is absorbed and emitted by it.
Thanks to increasingly refined control of the nanoparticles' size and shape, the number ...
2021-03-12
A machine learning algorithm that predicts suicide attempt recently underwent a prospective trial at the institution where it was developed, Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
Over the 11 consecutive months concluding in April 2020, predictions ran silently in the background as adult patients were seen at VUMC. The algorithm, dubbed the Vanderbilt Suicide Attempt and Ideation Likelihood (VSAIL) model, uses routine information from electronic health records (EHRs) to calculate 30-day risk of return visits for suicide attempt, and, by extension, suicidal ideation.
Suicide has been on the rise in the U.S. for a generation ...
2021-03-12
What The Study Did: Researchers investigated whether acute COVID-19 symptoms are associated with the probability of subsequent depressive symptoms.
Authors: Roy H. Perlis, M.D., M.Sc., of the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.3223)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest and funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, ...
2021-03-12
What The Study Did: National claims data were used to look at changes in well-child care visits with out-of-pocket costs before and after passage of the Affordable Care Act.
Authors: Paul R. Shafer, Ph.D., of Boston University, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1248)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding ...
2021-03-12
What The Study Did: Researchers compared rates of psychotropic drug prescriptions during adolescence and young adulthood between individuals born preterm and at term.
Authors: Christine S. Bachmann, M.D., of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology in Trondheim, Norway, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1420)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
2021-03-12
(Philadelphia, PA) - About 6.2 million Americans suffer from heart failure, an incurable disease with a staggering mortality rate - some 40 percent of patients die within five years of diagnosis. Heart failure is one form of heart disease, for which new therapies are desperately needed.
Now, in new work, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM) at Temple University identify a path to a promising novel therapeutic strategy, taking aim at a molecule in the heart known as G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5). In a study published online in the journal Cardiovascular Research, the scientists show in mice that reducing GRK5 levels can significantly improve survival ...
2021-03-12
Scientists have long theorized that supermassive black holes can wander through space--but catching them in the act has proven difficult.
Now, researchers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian have identified the clearest case to date of a supermassive black hole in motion. Their results are published today in the Astrophysical Journal.
"We don't expect the majority of supermassive black holes to be moving; they're usually content to just sit around," says Dominic Pesce, an astronomer at the Center for Astrophysics who led the study. "They're just so heavy that it's tough to get them going. Consider how much more ...
2021-03-12
Since the pandemic hit, researchers have been uncovering ways COVID-19 impacts other parts of the body, besides the lungs.
Now, for the first time, a visual correlation has been found between the severity of the disease in the lungs using CT scans and the severity of effects on patient's brains, using MRI scans. This research is published in the American Journal of Neuroradiology. It will be presented at the 59th annual meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR) and has also been selected as a semifinalist for that organization's Cornelius Dyke Award.
The results show that by looking at lung CT scans of patients diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians may be able to predict just how badly they'll experience other ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] CT colonography most effective noninvasive colorectal cancer screening test
Compared with multi-target stool-DNA and fecal immunochemical test, CT colonography with 10 mm threshold most effectively targets advanced neoplasia--preserving detection while decreasing unnecessary colonoscopies




