Well-child visits with out-of-pocket costs before, after ACA
2021-03-12
(Press-News.org) What The Study Did: National claims data were used to look at changes in well-child care visits with out-of-pocket costs before and after passage of the Affordable Care Act.
Authors: Paul R. Shafer, Ph.D., of Boston University, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1248)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes conflicts of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media advisory: The full study is linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1248?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=031221
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is the new online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-12
What The Study Did: Researchers compared rates of psychotropic drug prescriptions during adolescence and young adulthood between individuals born preterm and at term.
Authors: Christine S. Bachmann, M.D., of the Norwegian University of Science and Technology in Trondheim, Norway, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.1420)
Editor's Note: Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
2021-03-12
(Philadelphia, PA) - About 6.2 million Americans suffer from heart failure, an incurable disease with a staggering mortality rate - some 40 percent of patients die within five years of diagnosis. Heart failure is one form of heart disease, for which new therapies are desperately needed.
Now, in new work, scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine (LKSOM) at Temple University identify a path to a promising novel therapeutic strategy, taking aim at a molecule in the heart known as G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 (GRK5). In a study published online in the journal Cardiovascular Research, the scientists show in mice that reducing GRK5 levels can significantly improve survival ...
2021-03-12
Scientists have long theorized that supermassive black holes can wander through space--but catching them in the act has proven difficult.
Now, researchers at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian have identified the clearest case to date of a supermassive black hole in motion. Their results are published today in the Astrophysical Journal.
"We don't expect the majority of supermassive black holes to be moving; they're usually content to just sit around," says Dominic Pesce, an astronomer at the Center for Astrophysics who led the study. "They're just so heavy that it's tough to get them going. Consider how much more ...
2021-03-12
Since the pandemic hit, researchers have been uncovering ways COVID-19 impacts other parts of the body, besides the lungs.
Now, for the first time, a visual correlation has been found between the severity of the disease in the lungs using CT scans and the severity of effects on patient's brains, using MRI scans. This research is published in the American Journal of Neuroradiology. It will be presented at the 59th annual meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR) and has also been selected as a semifinalist for that organization's Cornelius Dyke Award.
The results show that by looking at lung CT scans of patients diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians may be able to predict just how badly they'll experience other ...
2021-03-12
ITHACA, N.Y. - A new Penn State and Cornell study describes an effort to produce the most comprehensive and high-resolution map yet of chromosome architecture and gene regulation in yeast, a major step toward improving understanding of development, evolution and environmental responses in higher organisms.
Specifically, the study mapped precise binding sites of more than 400 different chromosomal proteins in the yeast genome, most of which regulate the expression of genes.
Yeast cells provide a simple model system with 6,000 genes, most of which are found in other organisms, including humans, making them excellent candidates for studying fundamental genetics and complex biological pathways.
The paper, "A High-Resolution Protein Architecture of the Budding Yeast ...
2021-03-12
Around three times as many males are diagnosed with autism than females. This suggests that biological sex factors may play a role in the development and presentation of autism.
Studies on the neurobiology (brain biology) of males and females with autism have begun to examine brain networks but results have been mixed. This is largely due to the limited availability of data from autistic females.
In response, researchers from END ...
2021-03-12
Humans rely on nature extensively for everything from food production to coastal protection, but those contributions might be more threatened than previously thought, according to new findings from the University of Colorado Boulder.
This research, out today in Nature Communications, looked at three different coastal food webs that include those services provided to humans, or ecosystem services, and found that even if the services themselves aren't directly threatened, they can become threatened when other species around them go extinct--often called secondary ...
2021-03-12
More than one million operations are performed in Switzerland every year. A surgeon's skill has a direct impact on the outcome of the operation. Training and experience, as well as momentary fatigue and other influencing factors all play a role. At present, skill is tested by experts, either directly during an operation or by evaluating video footage. This approach is very costly and only a limited number of experts are available. Moreover, the assessment may vary and is not always fully reproducible. For some time, attempts have been made to automate and objectify the assessment of surgeons' skills.
Proof of feasibility
The key result of the study is the proof of the fundamental feasibility of an ...
2021-03-12
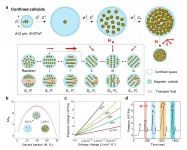
Colloidal suspensions of microscopic particles show complex and interesting collective behaviors. In particular, the collective dynamics of colloids is fundamental and ubiquitous for materials assembly, robotic motion, microfluidic control, and in several biological scenarios. The collective dynamics of confined colloids can be completely different from that of free colloids: for instance, confined colloids can self-organize into vortex structures, coherent motion, or different phase behaviors. On one hand, due to the complexity of colloidal suspensions, how to finely tune the ...
2021-03-12
As the world continues to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic, an international team of researchers have published a review of the best techniques to collect airborne aerosols containing viruses.
In the review, which was published by the Science of the Total Environment journal, a team led by the University of Surrey concluded that the most effective way to collect and detect airborne pathogens, particularly viruses, was to use cyclone sampling techniques.
For example, the sampler draws the air through the cyclone separator. It then uses centrifugal forces to collect the particles on a sterile cone containing the liquid collection vessel, such as DMEM (Dulbecco's minimal essential ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Well-child visits with out-of-pocket costs before, after ACA