(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR, Mich. - For teens, pandemic restrictions may have meant months of virtual school, less time with friends and canceling activities like sports, band concerts and prom.
And for young people who rely heavily on social connections for emotional support, these adjustments may have taken a heavy toll on mental health, a new national poll suggests.
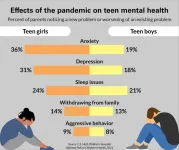
Forty-six percent of parents say their teen has shown signs of a new or worsening mental health condition since the start of the pandemic in March 2020, according to the C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health at Michigan Medicine. Parents of teen girls were more likely to say their child had a new onset or worsening of depressive symptoms and anxiety than parents of teen boys.
"Just as young people are at the age of being biologically primed to seek independence from their families, COVID-19 precautions have kept them at home," says poll co-director and Mott pediatrician Gary L. Freed, M.D., M.P.H.
"Pandemic-related lifestyle changes have wreaked havoc on teens' lives, with many experiencing disruptions to their normal routines. Our poll suggests that pandemic-era changes may have had a significant mental health impact for some teenagers."
The nationally representative report is based on responses from 977 parents of teens ages 13-18.
One in three teen girls and one in five teen boys have experienced new or worsening anxiety, the poll suggests. More parents of teen girls than parents of teen boys note an increase in anxiety/worry (36% vs. 19%) or depression/sadness (31% vs. 18%).
But similar proportions of parents report negative changes in their teen's sleep (24% for girls vs. 21% for boys), withdrawing from family (14% vs. 13%) and aggressive behavior (8% vs. 9%).
Recent research has shown teen depression during the pandemic to be associated with teens' own fears and uncertainties, as well as high levels of parental stress, Freed notes.
"Isolation during the pandemic may be triggering new problems for some teens but for others, the situation has exacerbated existing emotional health issues," Freed says.
Parents in the poll say their kids seem hardest hit by changes in social interactions over the last year, with three in four reporting a negative impact on their teen's connections to friends.
Many parents say their teens have been texting (64%), using social media (56%), online gaming (43%), and talking on the phone (35%) every day or almost every day. Few parents say their teens have been getting together in person with friends daily or almost every day, indoors (9%) or outdoors (6%).
"Peer groups and social interactions are a critical part of development during adolescence. But these opportunities have been limited during the pandemic," Freed says. "Many teens may feel frustrated, anxious and disconnected due to social distancing and missing usual social outlets, like sports, extracurricular activities and hanging out with friends."
Parents who note negative changes in their teens' mental health have tried different strategies to help their teen, the Mott Poll suggests, including relaxing COVID-19 rules and family rules on social media, seeking professional help and even using mental health apps.
"Parents play a critical role in helping their teens cope with the stress of the pandemic," Freed says. "There are strategies parents can engage to help, whether or not their teen is showing signs of problems. One of the most important things for parents to do is keep lines of communication open; ask their teen how they are doing and create the space for them to speak honestly so they can provide help when needed."
More Mott Poll findings on methods parents have used to improve children's mental health and what Mott experts recommend:
1. Relaxing family rules
Half of parents have tried relaxing family COVID-19 rules to allow their teen to have more contact with friends, with most (81%) saying it has helped. Freed says families should encourage social interactions that follow COVID-19 safety guidelines, such as spending time outside or participating in activities wearing masks and socially distanced.
Half of parents have also loosened social media restrictions - and most (70%) say it helped. Experts recommend that families allow teens to engage with peers on age-appropriate platforms but to continue providing boundaries to ensure screen time doesn't interfere with other health-related behaviors, such as physical activity and sleep. This could mean banning electronics close to bedtime, encouraging or only allowing social media use during designated times of the day.
2. Talking to an expert
One in four parents sought help for their teen from a mental health provider, with three-fourths feeling it helped.
A third of parents also talked to teachers or school counselors, with over half (57%) saying that strategy was helpful.
"Teens may experience a wide range of severity of mental health problems, but if parents hear their teen express any thoughts of suicide or self-harm, they should seek mental health assistance immediately," Freed says.
3. Trying a Web-based program
A quarter of parents encouraged their teen to try a web-based program or app to improve their mental health, and 60% say it has helped. A third of parents in the poll also looked for information online (58% say it helped.)
Apps may make therapy more accessible, efficient, and portable, Freed notes, but parents should consult their primary care provider or other trusted sources for app recommendations as well as for online resources about teen mental health.
4. Keeping communication open but also giving space
One in seven parents in the poll reported their teen has withdrawn from family since the start of the pandemic.
Parents may try to show teens they're not alone by sharing some of their own worries and successful strategies that help them cope while asking questions that create a safe space for candid conversations.
At the same time, Freed notes, it's also normal for teens to crave privacy from their family. Giving them space for some quiet time, creative time or music time can be helpful to their mental health.
5. Encouraging sleep hygiene
Child health experts emphasize the importance of sleep for teens, especially when they are under stress. Almost one in four parents in the Mott Poll say their teens were experiencing negative changes in their sleep since the pandemic started.
Experts recommend helping teens craft a healthy and productive routine to their days and nights - whether they're in virtual or in-person school. This includes a regular sleep and wake cycle that fits with their online learning schedule, other responsibilities around the house and their interactions with peers and family. Making time to get outside is also helpful in regulating sleep.
INFORMATION:
PULLMAN, Wash. - People who talk with their doctors are more likely to get vaccinated during a pandemic, according to a study of evidence collected during the "swine flu," the last pandemic to hit the U.S. before COVID-19.
Researchers from Washington State University and University of Wisconsin-Madison surveyed patients about the vaccine for the H1N1 virus, also known as the swine flu, which was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization in 2009. They found that doctor-patient communication helped build trust in physicians, which led to more positive attitudes toward the H1N1 vaccine--and it was more than just talk; it correlated to people actually getting vaccinated. ...
(COLUMBUS, Ohio) - High-powered magnets are small, shiny magnets made from powerful rare earth metals. Since they started showing up in children's toys in the early 2000s and then later in desk sets in 2009, high-powered magnets have caused thousands of injuries and are considered to be among the most dangerous ingestion hazards in children.
When more than one is swallowed, these high-powered magnets attract to each other across tissue, cutting off blood supply to the bowel and causing obstructions, tissue necrosis, sepsis and even death. The U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) found them dangerous enough that in 2012 they halted the sale of high-powered magnet sets and instituted a recall followed by a federal rule that ...
A fear of poor SATs results is driving headteachers to separate pupils by ability despite the impact on children's self-esteem and confidence, according to a study by researchers from UCL published in the peer-reviewed British Journal of Sociology of Education.
The findings, based on a survey of nearly 300 principals of primary schools in England, provide new evidence of a high-stakes culture around testing where some pupils are prioritised above others and physically segregated from them.
More than a third (35%) of headteachers said SATs were the reason for grouping children into different ability sets for English, and just under half (47%) for maths, according to the results which also ...
In the world of neurodevelopment, one thing is clear: the earlier the intervention the better. Infancy is a critical time in brain development, and neuroscientists are increasingly identifying factors that can negatively impact cognition and ones that can improve cognition early in life. At the annual meeting of the Cognitive Neuroscience Society (CNS), researchers from the University of Minnesota are presenting new work on two early interventions: one on the potential use of engineered gut microbes for antibiotic-exposed infants and another on a choline supplement to treat infants exposed prenatally to alcohol.
"These talks underscore how patient-based neuroscience can advance ...
Men experiencing vital exhaustion are more likely to have a heart attack, according to research presented today at ESC Acute CardioVascular Care 2021, an online scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 The risk of a myocardial infarction linked with exhaustion was particularly pronounced in never married, divorced and widowed men.
"Vital exhaustion refers to excessive fatigue, feelings of demoralisation and increased irritability," said study author Dr. Dmitriy Panov of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics, Novosibirsk, Russian Federation. "It is thought to be a response to intractable problems in people's lives, particularly when they are unable to adapt to prolonged ...
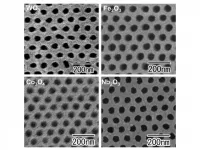
Tokyo, Japan - Scientists from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new method for making ordered arrays of nanoholes in metallic oxide thin films using a range of transition metals. The team used a template to pre-pattern metallic surfaces with an ordered array of dimples before applying electrochemistry to selectively grow an oxide layer with holes. The process makes a wider selection of ordered transition metal nanohole arrays available for new catalysis, filtration, and sensing applications.
A key challenge of nanotechnology is getting control over the structure of materials at the nanoscale. In the search for materials that are porous at this length scale, the field of electrochemistry offers a particularly elegant ...
MRI scanning can more precisely define and detect head, neck, thoracic, abdominal and spinal malformations in unborn babies, finds a large multidisciplinary study led by King's College London with Evelina London Children's Hospital, Great Ormond Street Hospital and UCL.
In the study, published today in Lancet Child and Adolescent Health, the team of researchers and clinicians demonstrate the ways that MRI scanning can show malformations in great detail, including their effect on surrounding structures. Importantly, they note that MRI is a very safe procedure for pregnant women and their babies.
They say the work is invaluable both to clinicians caring for babies before they are born and for teams planning care of the baby after delivery.
Recent research has concentrated ...
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) dramatically increased children's preventive healthcare while reducing out-of-pocket costs, according to a new Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) study.
Published in JAMA Network Open, the study found that checkups with out-of-pocket costs dropped from 54.2% of visits in 2010 (the year the ACA passed) to 14.5% in 2018.
"This is a great feather in the cap of the ACA, even though there is still some work to do," says study lead author Dr. Paul Shafer, assistant professor of health law, policy & management at BUSPH.
"We found ...
MIAMI--A new study lead by scientists at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science demonstrates that under realistic environmental conditions oil drifting in the ocean after the DWH oil spill photooxidized into persistent compounds within hours to days, instead over long periods of time as was thought during the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill. This is the first model results to support the new paradigm of photooxidation that emerged from laboratory research.
After an oil spill, oil droplets on the ocean surface ...
Cancer cells can dodge chemotherapy by entering a state that bears similarity to certain kinds of senescence, a type of "active hibernation" that enables them to weather the stress induced by aggressive treatments aimed at destroying them, according to a new study by scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine. These findings have implications for developing new drug combinations that could block senescence and make chemotherapy more effective.
In a study published Jan. 26 in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, the investigators reported that this biologic process could help explain why cancers so often recur after treatment. The research was done in both organoids and mouse models ...