Debris of stellar explosion found at unusual location
eROSITA space telescope finds largest supernova remnant ever discovered with X-rays
2021-03-15
(Press-News.org) In the first all-sky survey by the eROSITA X-ray telescope onboard SRG, astronomers at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics have identified a previously unknown supernova remnant, dubbed "Hoinga". The finding was confirmed in archival radio data and marks the first discovery of a joint Australian-eROSITA partnership established to explore our Galaxy using multiple wavelengths, from low-frequency radio waves to energetic X-rays. The Hoinga supernova remnant is very large and located far from the galactic plane - a surprising first finding - implying that the next years might bring many more discoveries.
Massive stars end their lives in gigantic supernova explosions when the fusion processes in their interiors no longer produce enough energy to counter their gravitational collapse. But even with hundreds of billions of stars in a galaxy, these events are pretty rare. In our Milky Way, astronomers estimate that a supernova should happen on average every 30 to 50 years. While the supernova itself is only observable on a timescale of months, their remnants can be detected for about 100 000 years. These remnants are composed of the material ejected by the exploding star at high velocities and forming shocks when hitting the surrounding interstellar medium.
About 300 such supernova remnants are known today - much less than the estimated 1200 that should be observable throughout our home Galaxy. So, either astrophysicists have misunderstood the supernova rate or a large majority has been overlooked so far. An international team of astronomers are now using the all-sky scans of the eROSITA X-ray telescope to look for previously unknown supernova remnants. With temperatures of millions of the degrees, the debris of such supernovae emits high-energy radiation, i.e. they should show up in the high-quality X-ray survey data.
"We were very surprised that the first supernova remnant popped up straight away," says Werner Becker at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics. Named after the first author's hometown's Roman name, "Hoinga" is the largest supernova remnant ever discovered in X-rays. With a diameter of about 4.4 degrees, it covers an area about 90 times bigger than the size of the full Moon. "Moreover, it lies very far off the galactic plane, which is very unusual," he adds. Most previous searches for supernova remnants have concentrated on the disk of our galaxy, where star formation activity is highest and stellar remnants therefore should be more numerous, but it seems that many supernova remnants have been overlooked by this search strategy.
After the astronomers found the object in the eROSITA all-sky data, they turned to other resources to confirm its nature. Hoinga is - although barely - visible also in data taken by the ROSAT X-ray telescope 30 years ago, but nobody noticed it before due to its faintness and its location at high galactic latitude. However, the real confirmation came from radio data, the spectral band where 90% of all known supernova remnants were found so far.
"We went through archival radio data and it had been sitting there, just waiting to be discovered," marvels Natasha Walker-Hurley, from the Curtin University node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy Research in Australia. "The radio emission in 10-year-old surveys clearly confirmed that Hoinga is a supernova remnant, so there may be even more of these out there waiting for keen eyes."
The eROSITA X-ray telescope will perform a total of eight all-sky surveys and is about 25 times more sensitive than its predecessor ROSAT. Both observatories were designed, build and are operated by the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics. The astronomers expected to discover new supernova remnants in its X-ray data over the next few years, but they were surprised to identify one so early in the programme. Combined with the fact that the signal is already present in decades-old data, this implies that many supernova remnants might have been overlooked in the past due to low-surface brightness, being in unusual locations or because of other nearby emission from brighter sources. Together with upcoming radio surveys, the eROSITA X-ray survey shows great promise for finding many of the missing supernova remnants, helping to solve this long-standing astrophysical mystery.
INFORMATION:
Original publication
W. Becker, N. Hurley-Walker, Ch. Weinberger, L. Nicastro, M. G. F. Mayer, A. Merloni, J. Sanders
Hoinga - A Supernova Remnant Discovered in the SRG/eROSITA All-Sky Survey eRASS1
Astronomy & Astrophysics, accepted 12 February 2021
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-15
During pandemics, protective behaviors need to be motivated by effective communication. A critical factor in understanding a population's response to such a threat is the fear it elicits, since fear both contributes to motivating protective responses, but can also lead to panic-driven behaviors. Furthermore, lockdown measures affect well-being, making it important to identify protective factors that help to maintain high perceived levels of health during restrictions. An international team of researchers led by scientists from the University of Vienna has now identified psychological predictors of fear and health during the lockdowns. The result of the study, published in PLOS ONE: Individual psychological variables have a much better predictive power than environmental variables.
The ...
2021-03-15
We all have a clear picture in mind when we think of metals: We think of solid, unbreakable objects that conduct electricity and exhibit a typical metallic sheen. The behaviour of classical metals, for example their electrical conductivity, can be explained with well-known, well-tested physical theories.
But there are also more exotic metallic compounds that pose riddles: Some alloys are hard and brittle, special metal oxides can be transparent. There are even materials right at the border between metal and insulator: tiny changes in chemical composition turn the metal into an insulator - or vice versa. ...
2021-03-15
Cryoprotectants are used to protect biological material during frozen storage
They have to be removed when defrosting, and how much to use and how exactly they inhibit ice recrystallisation is poorly understood
The polymer poly(vinyl)alcohol (PVA) is arguably the most potent ice recrystallisation inhibitor and researchers from the University of Warwick have unravelled how exactly it works.
This newly acquired knowledge base provides novel guidelines to design the next generation of cryoprotectants
When biological material (cells, blood, tissues) is frozen, cryoprotectants are used to prevent the damage associated with the formation of ...
2021-03-15
Researchers uncovered for the first time what happens in animals' brains when they learn from subconscious, visual stimuli. In time, this knowledge can lead to new treatments for a number of conditions. The study, a collaboration between KU Leuven, Massachusetts General Hospital, and Harvard was published in Neuron.
An experienced birdwatcher recognises many more details in a bird's plumage than the ordinary person. Thanks to extensive training, he or she can identify specific features in the plumage. This learning process is not only dependent on conscious processes. Previous research has shown that when people are rewarded during the presentation of visual stimuli that are not consciously perceivable, ...
2021-03-15
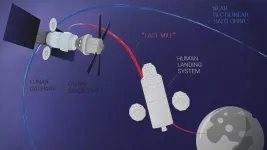
Researchers from Skoltech and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have analyzed several dozen options to pick the best one in terms of performance and costs for the 'last mile' of a future mission to the Moon - actually delivering astronauts to the lunar surface and back up to the safety of the orbiting lunar station. The paper was published in the journal Acta Astronautica.
Ever since December 1972, when the crew of Apollo 17 left the lunar surface, humans have been eager to return to the Moon. In 2017, the US government launched the Artemis program, which intends ...
2021-03-15
An RCSI study conducted in Beaumont Hospital in Dublin has found that surgery, rather than antibiotics-only, should remain as the mainstay of treatment for acute uncomplicated appendicitis.
Published in the Annals of Surgery and led by researchers from the RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, the study entitled the COMMA trial (Conservative versus Open Management of Acute uncomplicated Appendicitis) examined the efficacy and quality of life associated with antibiotic-only treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis versus surgical intervention. The results revealed that antibiotic-only treatment resulted in high recurrence rates and an inferior quality ...
2021-03-15
Drugs such as beta-adrenergic antagonists (beta blockers) have been linked to a range of adverse effects, including depression. But how reliable are these data, and which psychiatric side effects might indeed be caused by these drugs? These questions have been addressed by a team of researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, whose comprehensive meta-analysis has been published in Hypertension*. While treatment with beta blockers was not found to be associated with an increased incidence of depression, some studies recorded higher levels of sleep disturbance.
Beta-adrenergic ...
2021-03-15
During the past decade the European People's Party in the European Parliament was criticized for its unwillingness to vote for measures that would sanction the Hungarian Fidesz government, which is accused of breaching key democratic principles.
Researchers have said the EPP protected Fidesz in order to safeguard Hungarian votes in its ranks and protect their own interests, but this support had weakened by 2019, when Fidesz was suspended from the EPP.
Researchers analysed the votes of EPP MEPs for 24 resolutions covering the protection of EU fundamental values ...
2021-03-15
(Boston)-- Warning signs for Alzheimer's disease (AD) can begin in the brain years before the first symptoms appear. Spotting these clues may allow for lifestyle changes that could possibly delay the disease's destruction of the brain.
"Improving the diagnostic accuracy of Alzheimer's disease is an important clinical goal. If we are able to increase the diagnostic accuracy of the models in ways that can leverage existing data such as MRI scans, then that can be hugely beneficial," explained corresponding author Vijaya B. Kolachalama, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at Boston University School ...
2021-03-15
COLUMBUS, Ohio - An analysis of historic and projected simulations from 19 global climate models shows that, because of climate change, the temperature in the Antarctic peninsula will increase by 0.5 to 1.5 degrees Celsius by 2044.
The projections also showed that precipitation - a threat to ice if it manifests as rain - will likely increase on the peninsula by about 5% to 10% over that same time period.
The estimates were published recently in the journal Climate Dynamics.
"We are concerned about these findings. We've been seeing overall quite big changes on the peninsula, generally getting warmer and ice shelves and glaciers discharging into the ocean," said David Bromwich, a leading author of the study and a research professor at The Ohio State University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Debris of stellar explosion found at unusual location
eROSITA space telescope finds largest supernova remnant ever discovered with X-rays