(Press-News.org) Between 2015 and 2017, Seattle, Washington, became the first U.S. city to increase its hourly minimum wage to $15, more than double the federal minimum wage and 60 percent higher than Seattle's previous minimum wage. A new study examined the impact of this change on public safety. The study was motivated by the idea that since crime is sometimes the result of material deprivation, changes in the minimum wage might have implications for criminal activity: Boosting the minimum wage could raise workers' salaries (which could be associated with reduced crime). But if higher minimum wages spur employers to substitute capital for labor, this could increase unemployment (which could be associated with increased crime). The study found little evidence that Seattle's aggregate rate of violent or property crimes changed relative to other U.S. cities. It also found no meaningful adverse effects on low-wage workers' rates of employment.
The study, by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania, appears in Criminology & Public Policy, a publication of the American Society of Criminology.
"Our study suggests that Seattle increased its minimum wage without compromising public safety, at least in the short run," explains David Mitre-Becerril, a doctoral student in criminology at the University of Pennsylvania, who led the study.
Past research on the effects of minimum wage legislation on crime has been mixed.
In this study, researchers compared crime trends in Seattle to 118 U.S. cities in 18 states that did not increase their minimum wage but whose pre-2015 crime trends were comparable to Seattle. Seattle's minimum wage began to be implemented in 2015 and rose to $15/hour by 2017. For the period 2010 to 2017, researchers collected crime data from the FBI's Uniform Crime Reports and the Seattle Police Department. They also collected sociodemographic and employment/earnings data from the American Community Survey conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. Sociodemographic data included information on race, age, schooling, and poverty level.
The study found that Seattle's rate of violent crime (murder, robbery, aggravated assault) did not diverge significantly from the other cities' rates. With respect to property crimes (burglary, larceny, motor vehicle theft), the findings were more nuanced. Although researchers found evidence that Seattle's rate of burglaries may have increased 15 to 30 percent during the study period, driven by offenses on commercial premises, they did not detect an aggregate change in property crimes.
The increase in Seattle's minimum wage appears to have had little impact on arrest rates among any major demographic group, including young men, who tend to drive an outsized share of offending and whose employment has been considered the most sensitive to changes in the minimum wage. This, the authors note, may be because Seattle's law did not end up reducing employment for low-skilled workers.
This could be because Seattle has more college-educated workers and fewer low-wage earners than other cities, primarily because of its booming tech industry, which would mean that fewer workers were affected by a shift in the wage structure than in other cities.
The study's authors note that they focused on one city, thus limiting the generalizability of their findings to other cities. To address this matter, the researchers supplemented their work with analyses of four other U.S. cities that have increased their minimum wages substantially, though less than in Seattle, during the same period. In those cities--Chicago and three cities in California: San Francisco, San Jose, and Sunnyvale--the laws spurred few consistent increases in criminal offenses.
The authors also note that Washington State legalized recreational marijuana in December 2013 and allowed retail sales of recreational marijuana beginning in July 2014, which may have affected crime rates, though there is little evidence of a change in public safety immediately following the law.
"In the aftermath of Seattle's decision to raise the minimum wage, several other U.S. cities and states plan to follow suit," notes Aaron Chalfin, assistant professor of criminology at the University of Pennsylvania, who coauthored the study. "Therefore, the question of how high minimum wages can be pushed without compromising public safety is timely.
"However, the COVID-19 pandemic is likely to affect regional economic dynamics: Although a $15 minimum wage appears not to have disrupted Seattle's labor market during a period of broad economic growth, it could become a structural barrier to employment during the coming months, which may have implications for public safety."
INFORMATION:
Increases in the use of telehealth during the coronavirus pandemic among people with private insurance has occurred mostly among those who are more affluent and those who live in metropolitan areas, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Researchers say the findings raise concerns that the pandemic may be worsening existing disparities in overall health care utilization.
Overall, the study found there was a 20-fold increase in the rate of telemedicine utilization following the outset of the pandemic in March 2020. At the same time, the rate of office-based medical encounters declined by nearly 50% and was not fully offset by the increase in telemedicine.
The findings are published online by the American Journal of Preventive ...
Robotics researchers are developing exoskeletons and prosthetic legs capable of thinking and making control decisions on their own using sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
The system combines computer vision and deep-learning AI to mimic how able-bodied people walk by seeing their surroundings and adjusting their movements.
"We're giving robotic exoskeletons vision so they can control themselves," said Brokoslaw Laschowski, a PhD candidate in systems design engineering who leads a University of Waterloo research project called ExoNet.
Exoskeletons ...
In the first all-sky survey by the eROSITA X-ray telescope onboard SRG, astronomers at the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics have identified a previously unknown supernova remnant, dubbed "Hoinga". The finding was confirmed in archival radio data and marks the first discovery of a joint Australian-eROSITA partnership established to explore our Galaxy using multiple wavelengths, from low-frequency radio waves to energetic X-rays. The Hoinga supernova remnant is very large and located far from the galactic plane - a surprising first finding - implying that the next years might bring many more ...
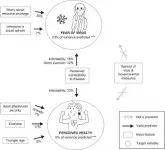
During pandemics, protective behaviors need to be motivated by effective communication. A critical factor in understanding a population's response to such a threat is the fear it elicits, since fear both contributes to motivating protective responses, but can also lead to panic-driven behaviors. Furthermore, lockdown measures affect well-being, making it important to identify protective factors that help to maintain high perceived levels of health during restrictions. An international team of researchers led by scientists from the University of Vienna has now identified psychological predictors of fear and health during the lockdowns. The result of the study, published in PLOS ONE: Individual psychological variables have a much better predictive power than environmental variables.
The ...
We all have a clear picture in mind when we think of metals: We think of solid, unbreakable objects that conduct electricity and exhibit a typical metallic sheen. The behaviour of classical metals, for example their electrical conductivity, can be explained with well-known, well-tested physical theories.
But there are also more exotic metallic compounds that pose riddles: Some alloys are hard and brittle, special metal oxides can be transparent. There are even materials right at the border between metal and insulator: tiny changes in chemical composition turn the metal into an insulator - or vice versa. ...
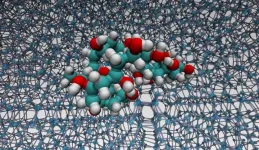
Cryoprotectants are used to protect biological material during frozen storage
They have to be removed when defrosting, and how much to use and how exactly they inhibit ice recrystallisation is poorly understood
The polymer poly(vinyl)alcohol (PVA) is arguably the most potent ice recrystallisation inhibitor and researchers from the University of Warwick have unravelled how exactly it works.
This newly acquired knowledge base provides novel guidelines to design the next generation of cryoprotectants
When biological material (cells, blood, tissues) is frozen, cryoprotectants are used to prevent the damage associated with the formation of ...
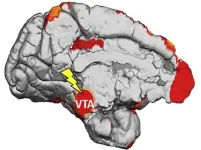
Researchers uncovered for the first time what happens in animals' brains when they learn from subconscious, visual stimuli. In time, this knowledge can lead to new treatments for a number of conditions. The study, a collaboration between KU Leuven, Massachusetts General Hospital, and Harvard was published in Neuron.
An experienced birdwatcher recognises many more details in a bird's plumage than the ordinary person. Thanks to extensive training, he or she can identify specific features in the plumage. This learning process is not only dependent on conscious processes. Previous research has shown that when people are rewarded during the presentation of visual stimuli that are not consciously perceivable, ...
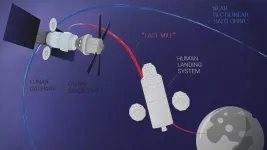
Researchers from Skoltech and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have analyzed several dozen options to pick the best one in terms of performance and costs for the 'last mile' of a future mission to the Moon - actually delivering astronauts to the lunar surface and back up to the safety of the orbiting lunar station. The paper was published in the journal Acta Astronautica.
Ever since December 1972, when the crew of Apollo 17 left the lunar surface, humans have been eager to return to the Moon. In 2017, the US government launched the Artemis program, which intends ...
An RCSI study conducted in Beaumont Hospital in Dublin has found that surgery, rather than antibiotics-only, should remain as the mainstay of treatment for acute uncomplicated appendicitis.
Published in the Annals of Surgery and led by researchers from the RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, the study entitled the COMMA trial (Conservative versus Open Management of Acute uncomplicated Appendicitis) examined the efficacy and quality of life associated with antibiotic-only treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis versus surgical intervention. The results revealed that antibiotic-only treatment resulted in high recurrence rates and an inferior quality ...
Drugs such as beta-adrenergic antagonists (beta blockers) have been linked to a range of adverse effects, including depression. But how reliable are these data, and which psychiatric side effects might indeed be caused by these drugs? These questions have been addressed by a team of researchers from Charité - Universitätsmedizin Berlin, whose comprehensive meta-analysis has been published in Hypertension*. While treatment with beta blockers was not found to be associated with an increased incidence of depression, some studies recorded higher levels of sleep disturbance.
Beta-adrenergic ...